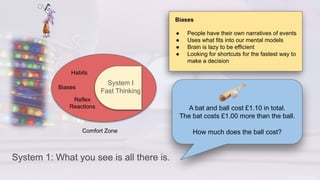
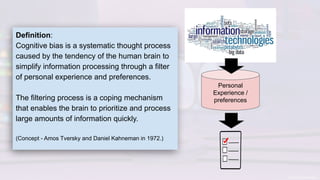
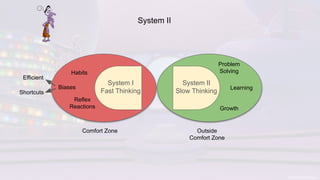
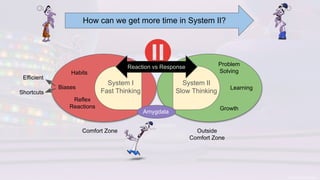
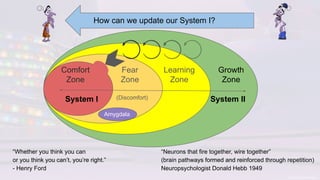
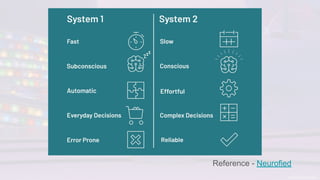
The document discusses the challenges of change, emphasizing cognitive biases that hinder decision-making, such as anchoring, framing, and confirmation biases. It highlights the importance of understanding and overcoming these biases to facilitate growth and learning, advocating for an environment that encourages psychological safety. Additionally, strategies to ease the change process include open discussions about motivations, pausing for thoughtful responses, and fostering a growth mindset.