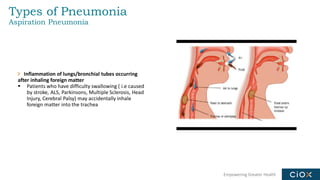
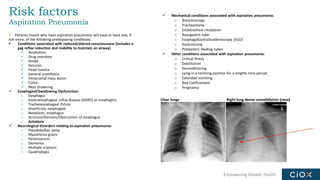
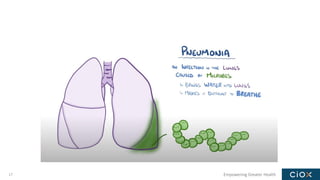
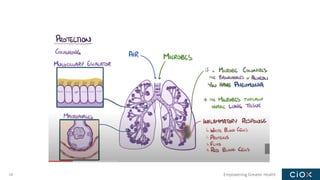
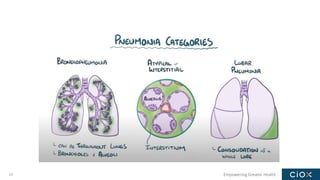
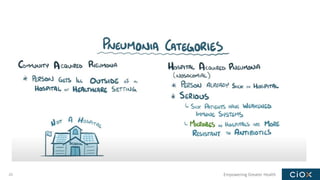
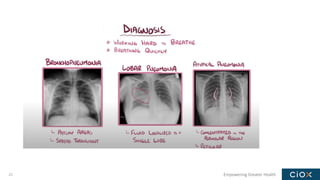
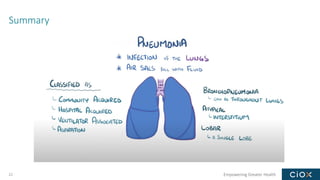
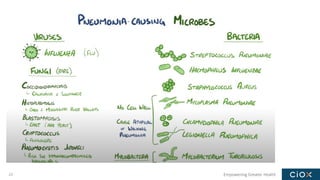
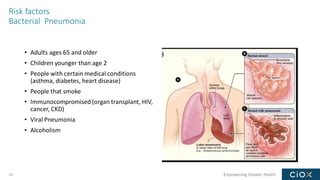
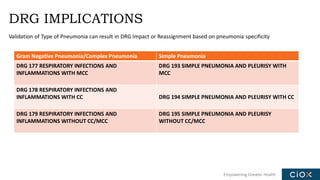
This document discusses a webinar on pneumonia coding. It provides information on different types of pneumonia including aspiration pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, and viral pneumonia. It describes clinical evaluation and treatment for these types of pneumonia. It also discusses new guidelines published in 2019 for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia from the Infectious Diseases Society of America and American Thoracic Society.