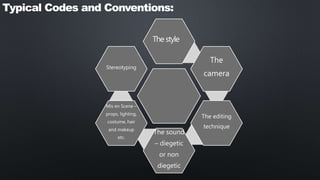
Technical codes and conventions in music videos include camera angles, shots, editing style, diegetic and non-diegetic sound, and genre to convey meaning. Symbolic techniques portray meaning through facial expressions, gestures, and mise-en-scene. Common codes are performance videos where the artist solely performs, narrative videos that tell a story linearly or fragmented, and various camera shots like close-ups that reveal emotion. Sound is also essential, using diegetic sounds from the environment and non-diegetic music to set mood.