This document discusses code optimization techniques. It defines code optimization as modifying a program to utilize the least memory and minimize CPU time for faster execution. The main techniques discussed are:
1) Compile time evaluation such as constant folding and propagation to replace expressions with pre-computed values.
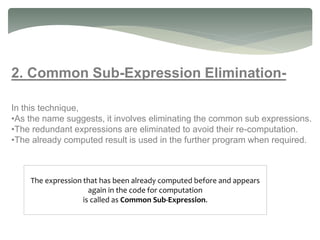
2) Common sub-expression elimination to avoid recomputing redundant expressions.
3) Code movement techniques like hoisting code outside loops if computation does not depend on iteration.
4) Dead code elimination to remove unused or unreachable code.
5) Strength reduction to replace expensive operators like multiplication with simpler ones like addition. The optimized code has advantages of faster speed, efficient memory usage, and better performance.






![3. Code Movement-
• In this technique,
• As the name suggests, it involves movement of the code.
• The code present inside the loop is moved out if it does not matter whether it is
present inside or outside.
• Such a code unnecessarily gets execute again and again with each iteration of the
loop.
• This leads to the wastage of time at run time.
Code Before Optimization Code After Optimization
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++)
{
x = y + z ;
a[j] = 6 x j;
}
x = y + z ;
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++)
{
a[j] = 6 x j;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cd-221102125011-11d8e876/85/Code-optimization-8-320.jpg)


