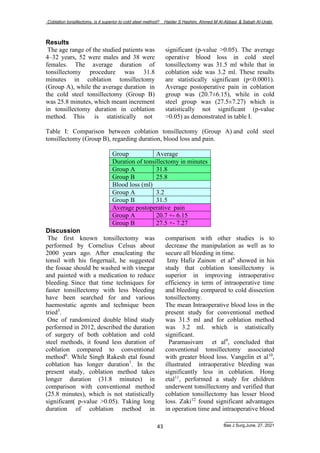
This study compared coblation tonsillectomy to cold steel (conventional) tonsillectomy. 90 patients underwent either coblation (Group A) or cold steel (Group B) tonsillectomy. The average surgery duration was longer for coblation at 31.8 minutes compared to 25.8 minutes for cold steel, but this difference was not statistically significant. However, the average intraoperative blood loss was significantly less for coblation at 3.2 ml compared to 31.5 ml for cold steel. Postoperative pain scores were not significantly different between the groups. While coblation took longer, it significantly reduced blood loss during surgery compared to cold steel tonsillectomy.