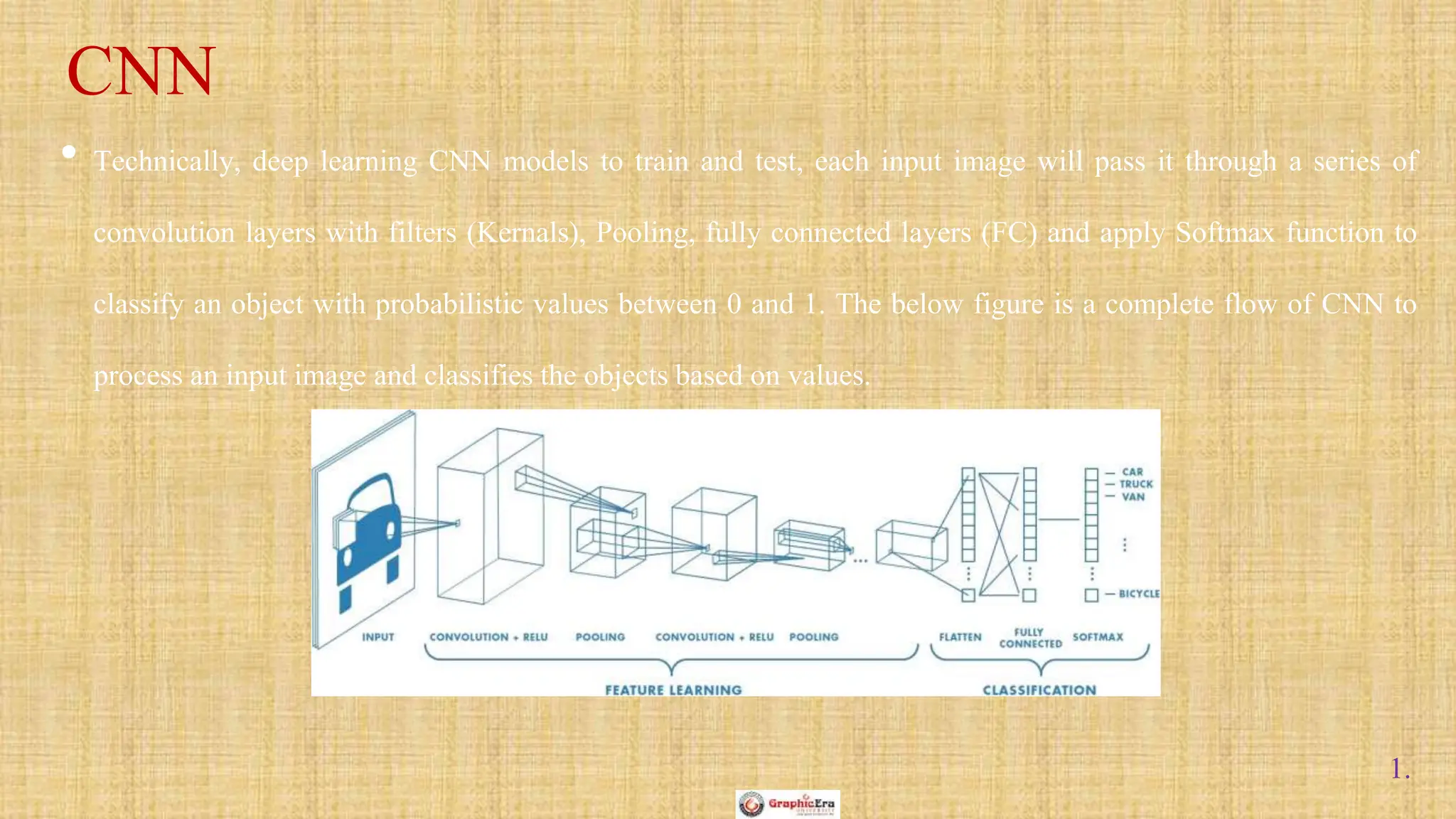
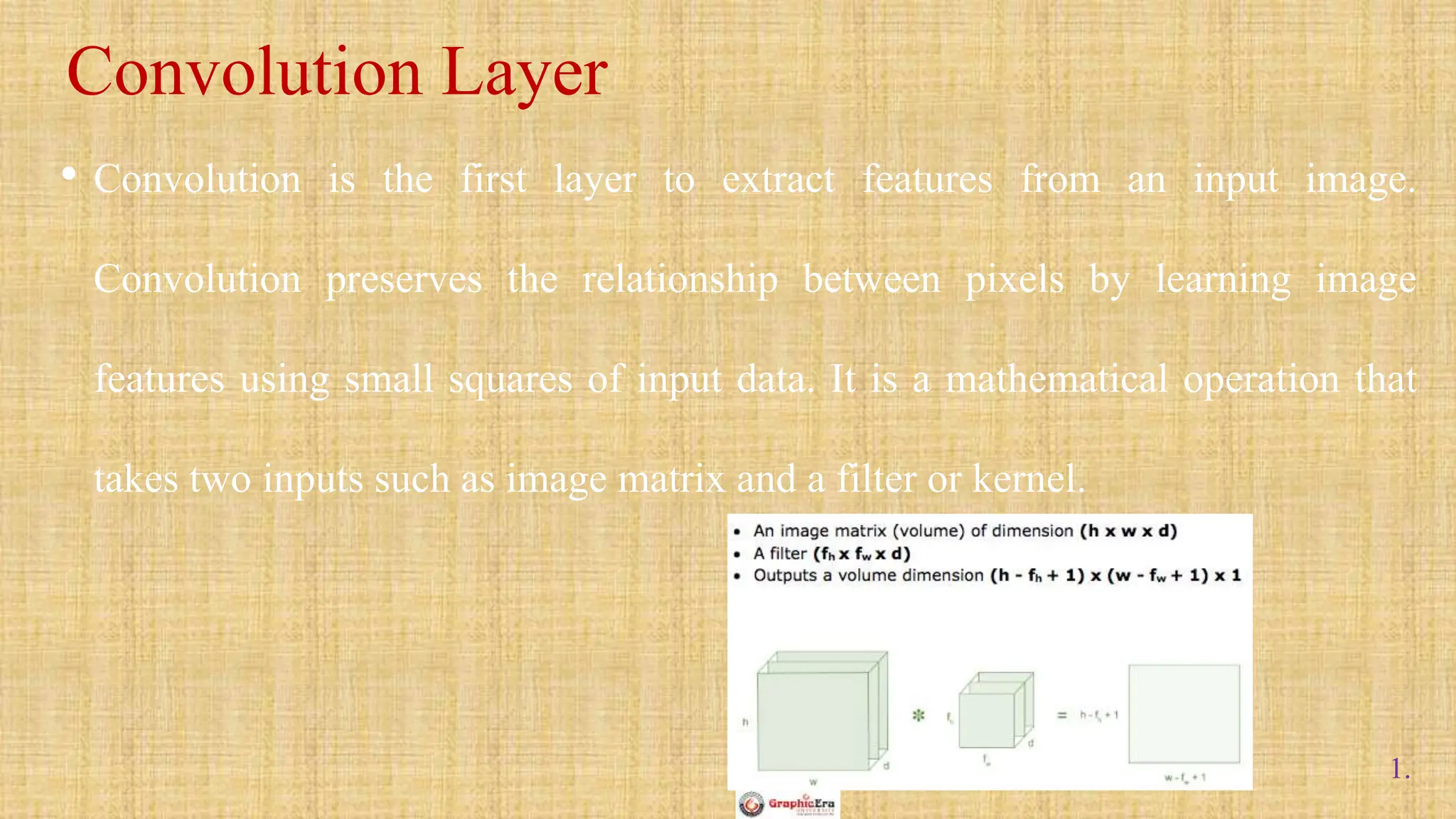
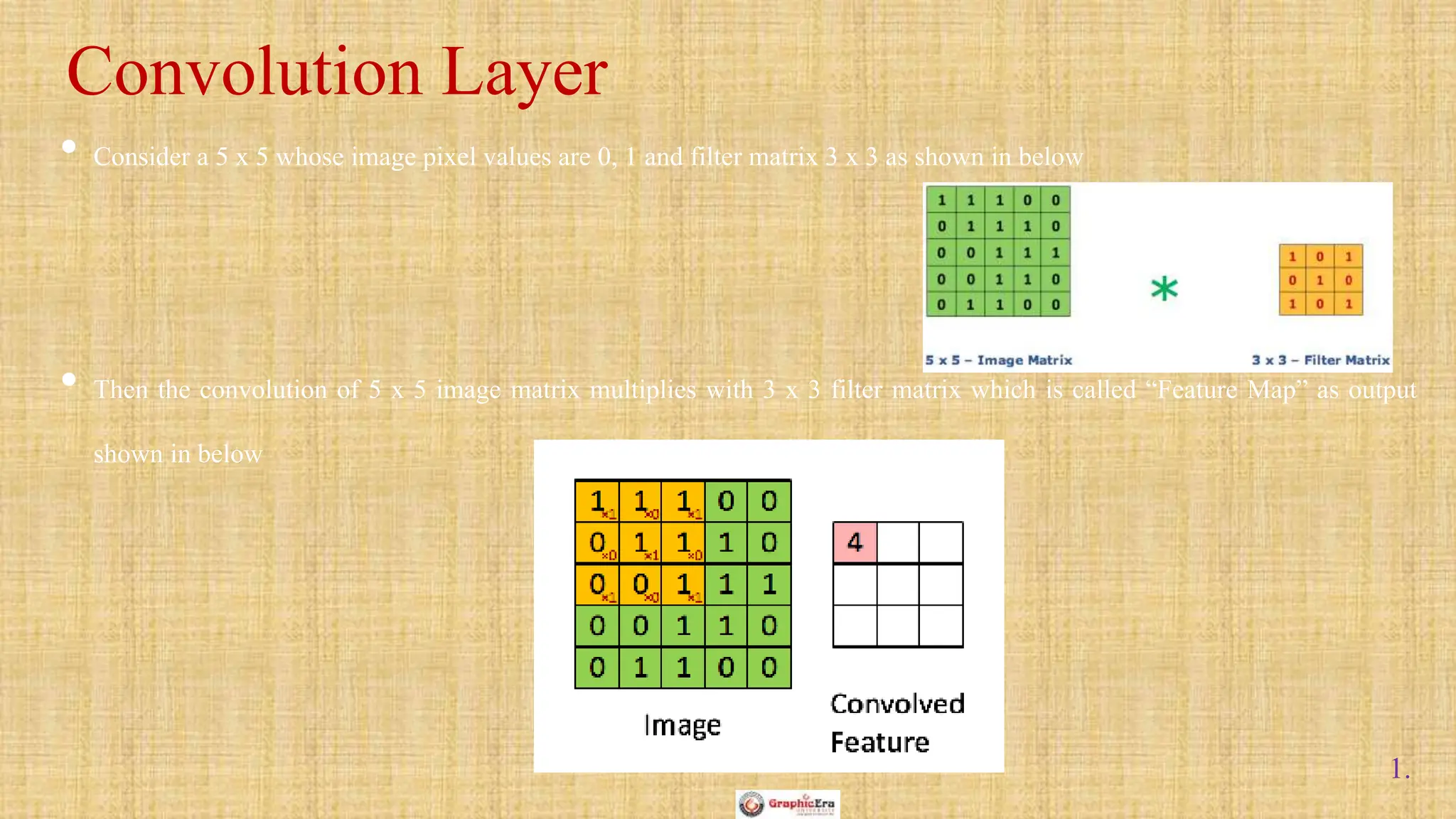
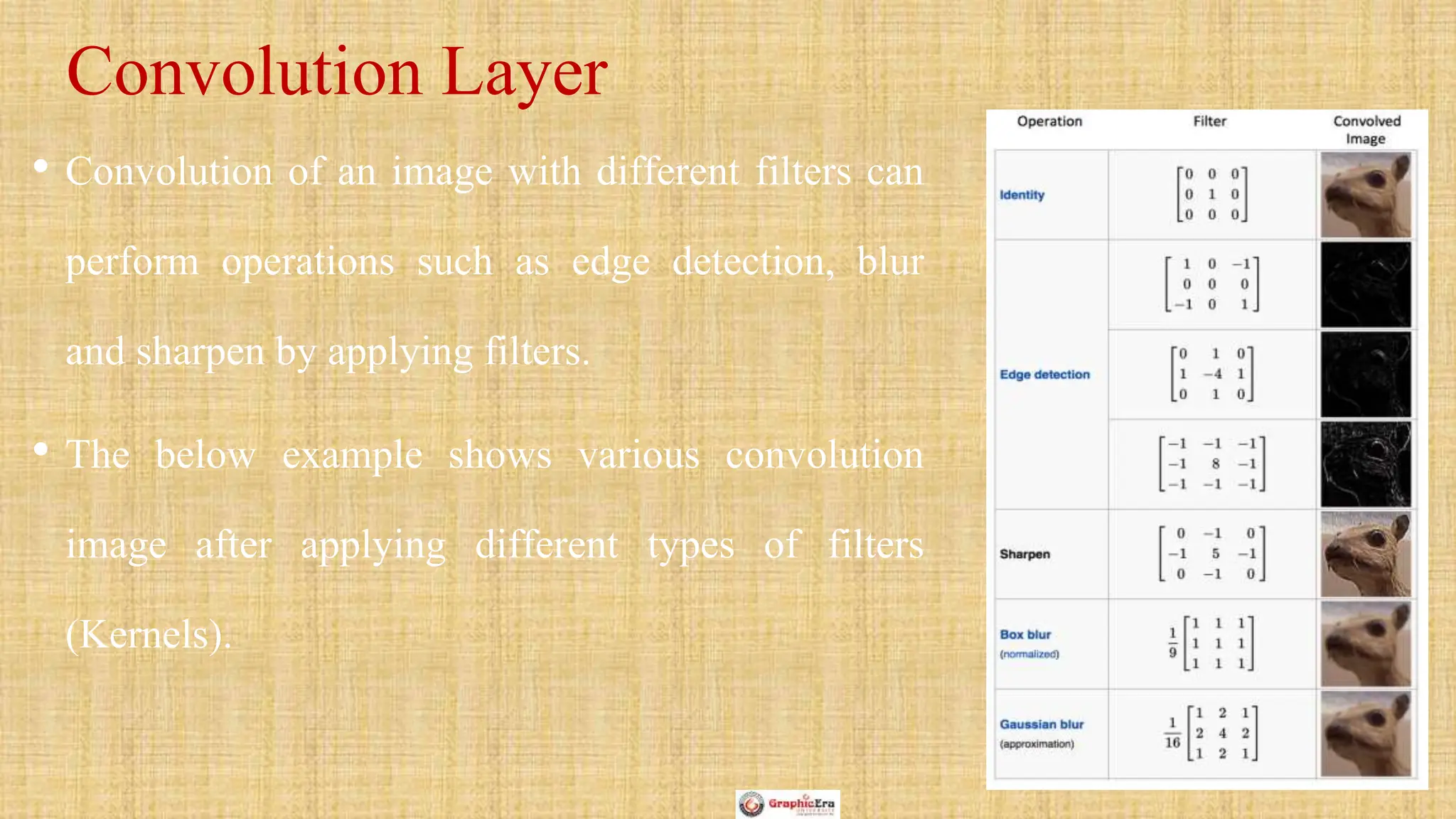
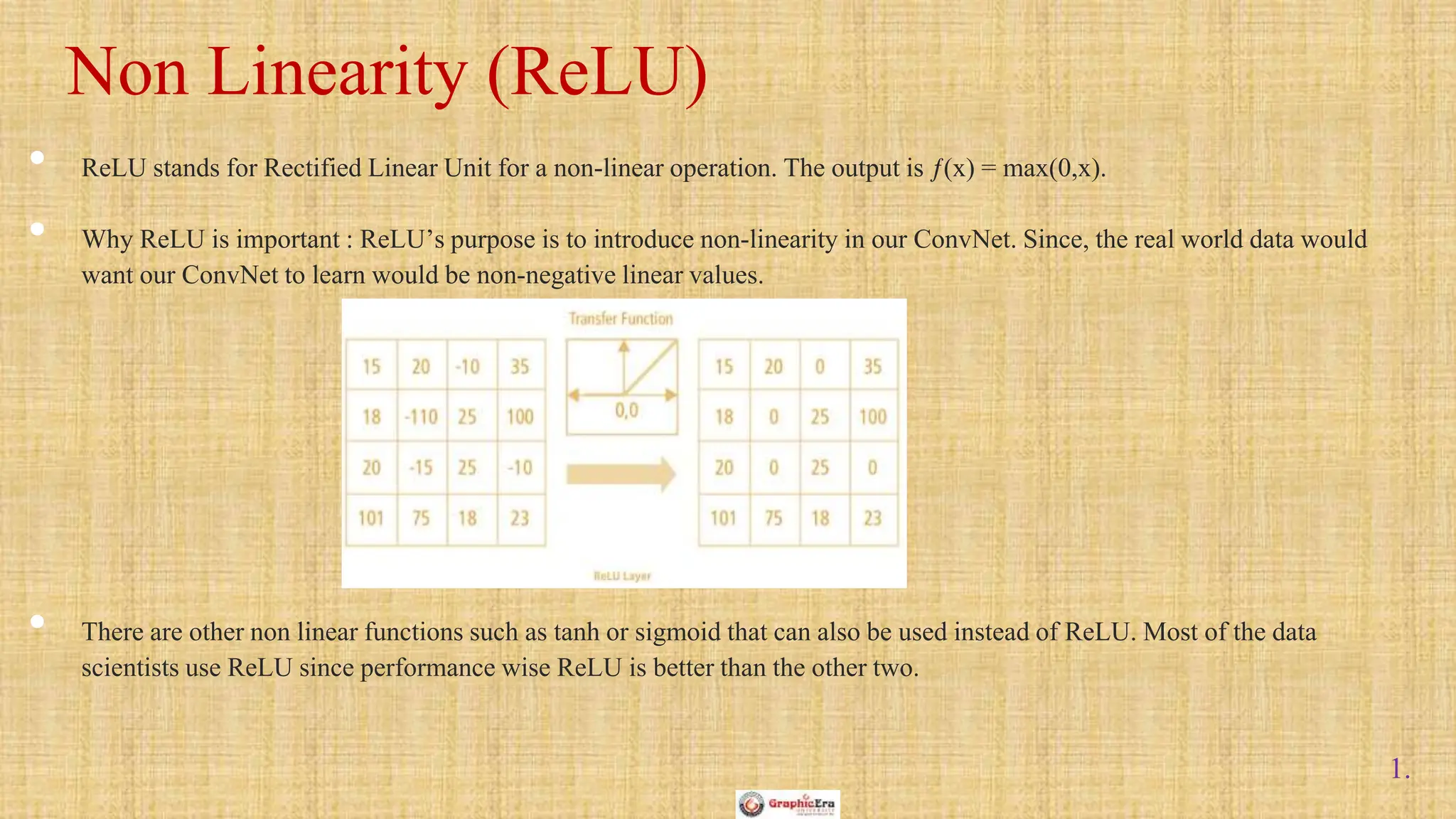
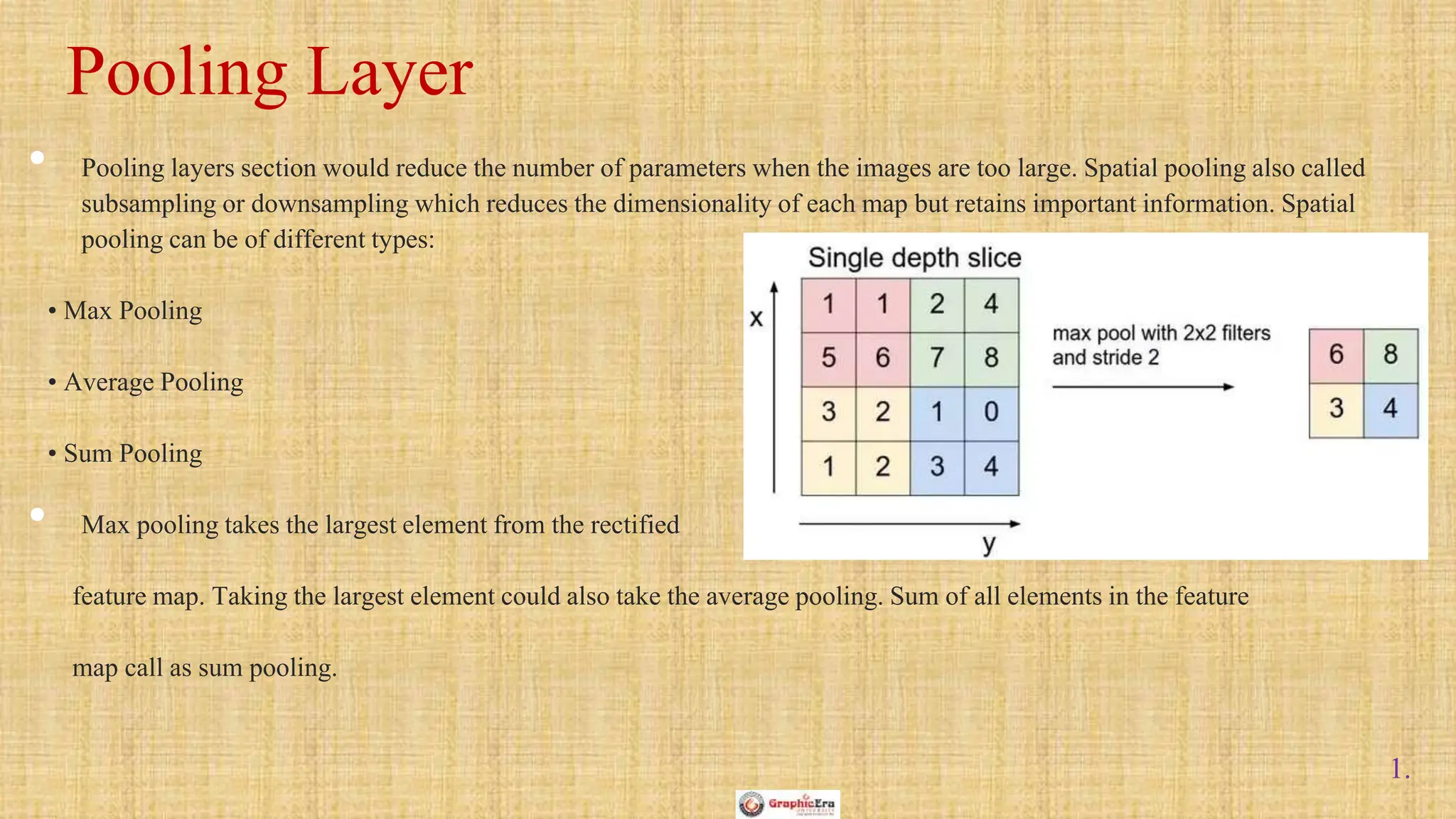
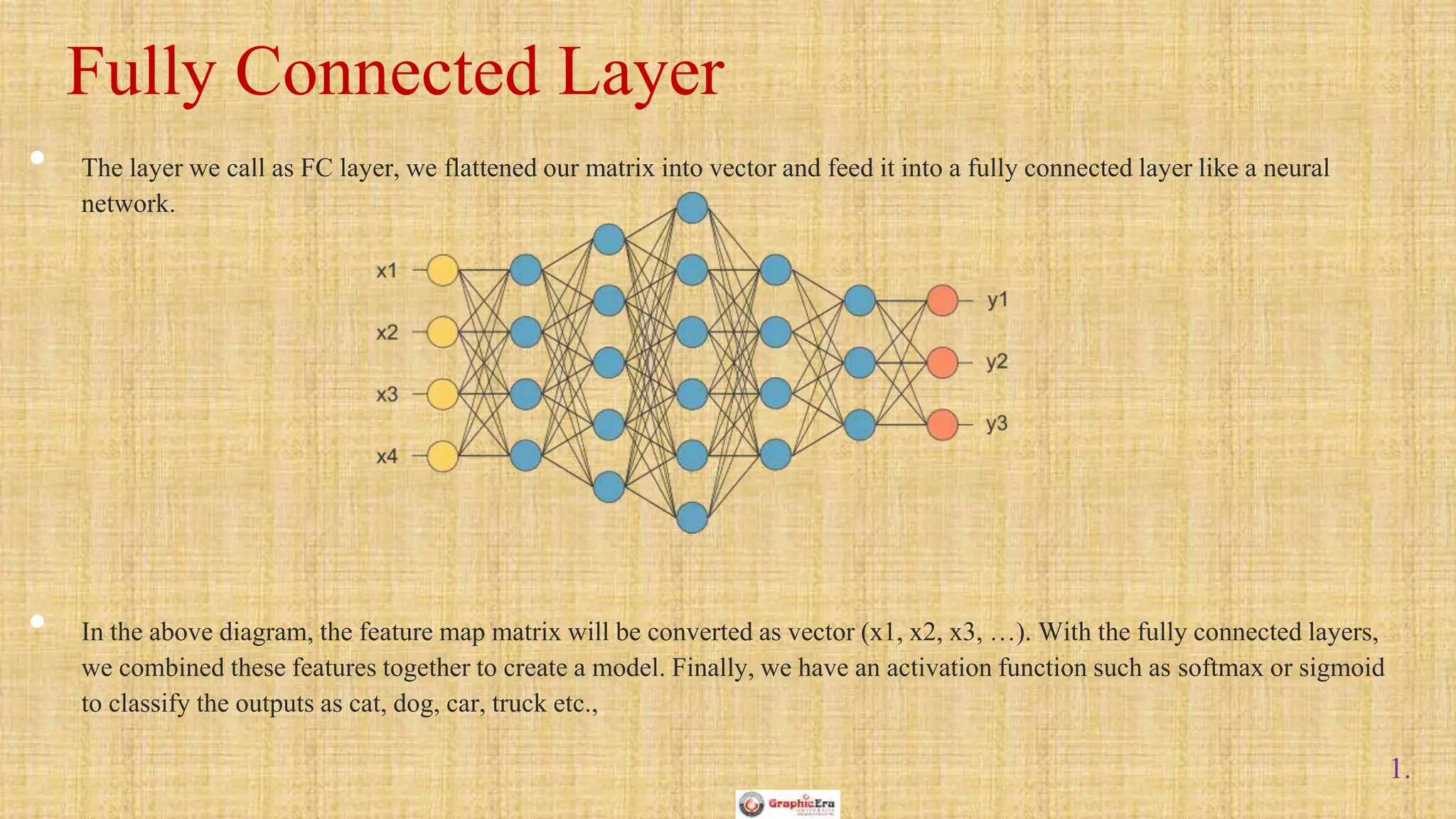
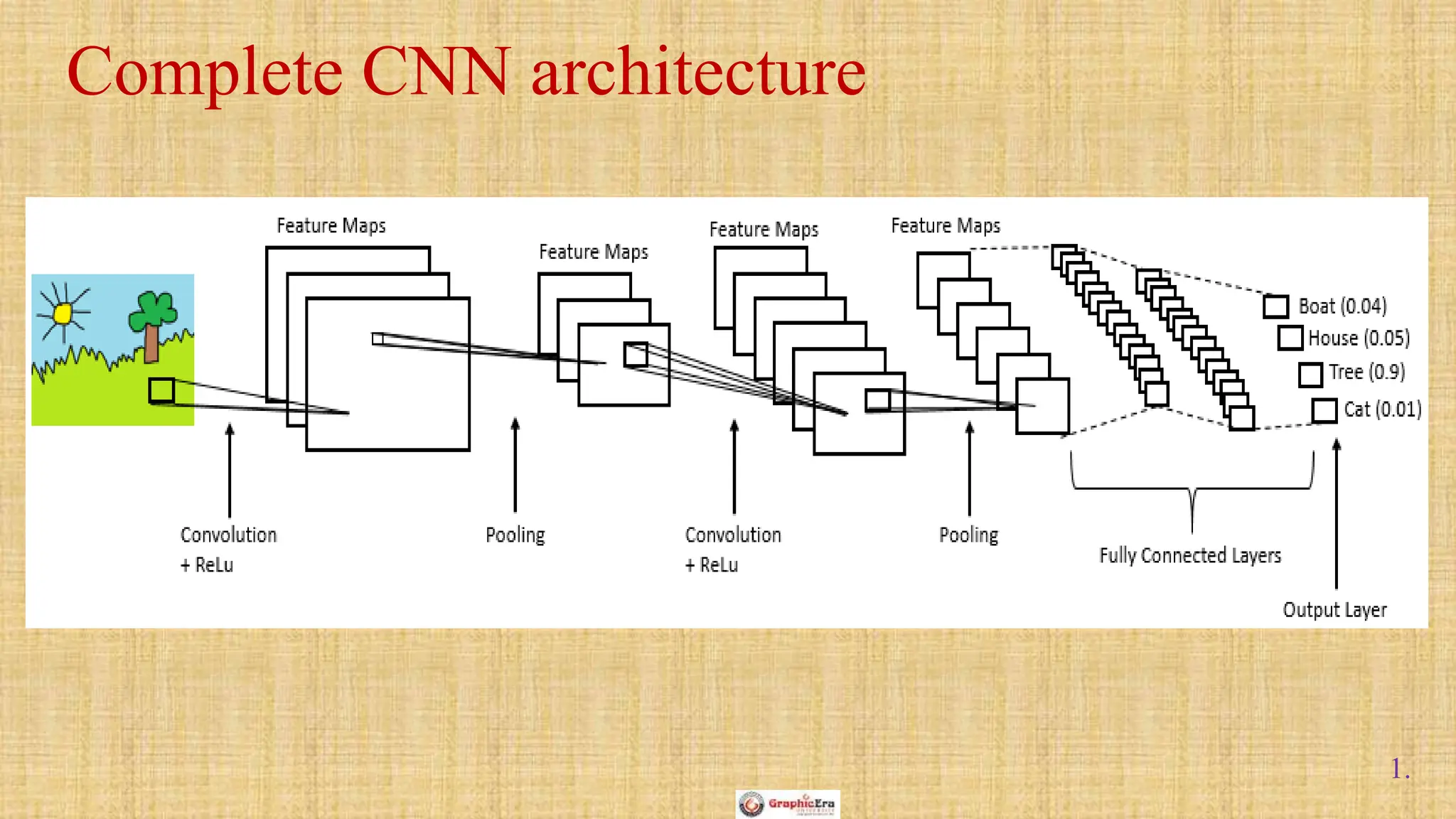
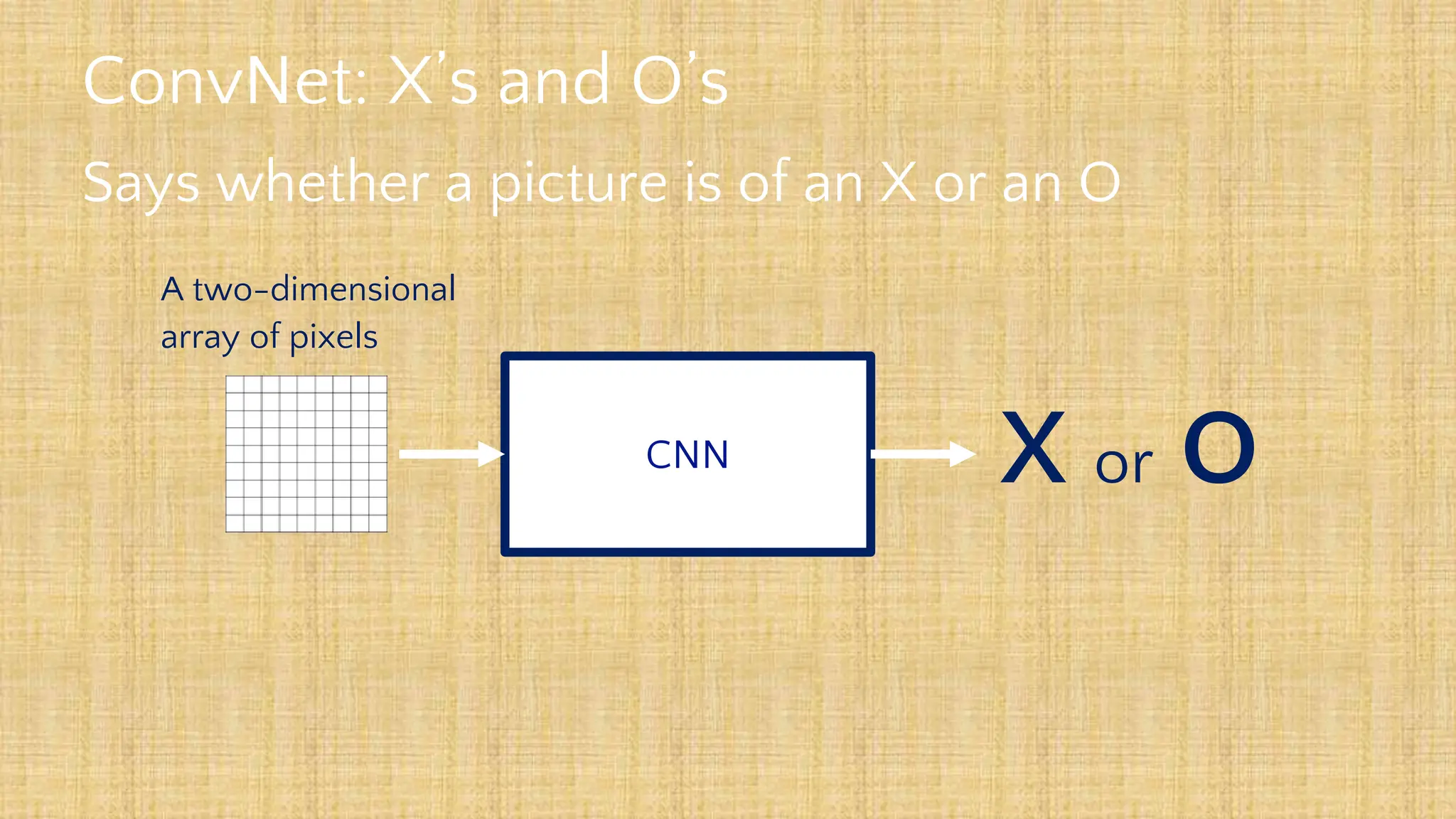
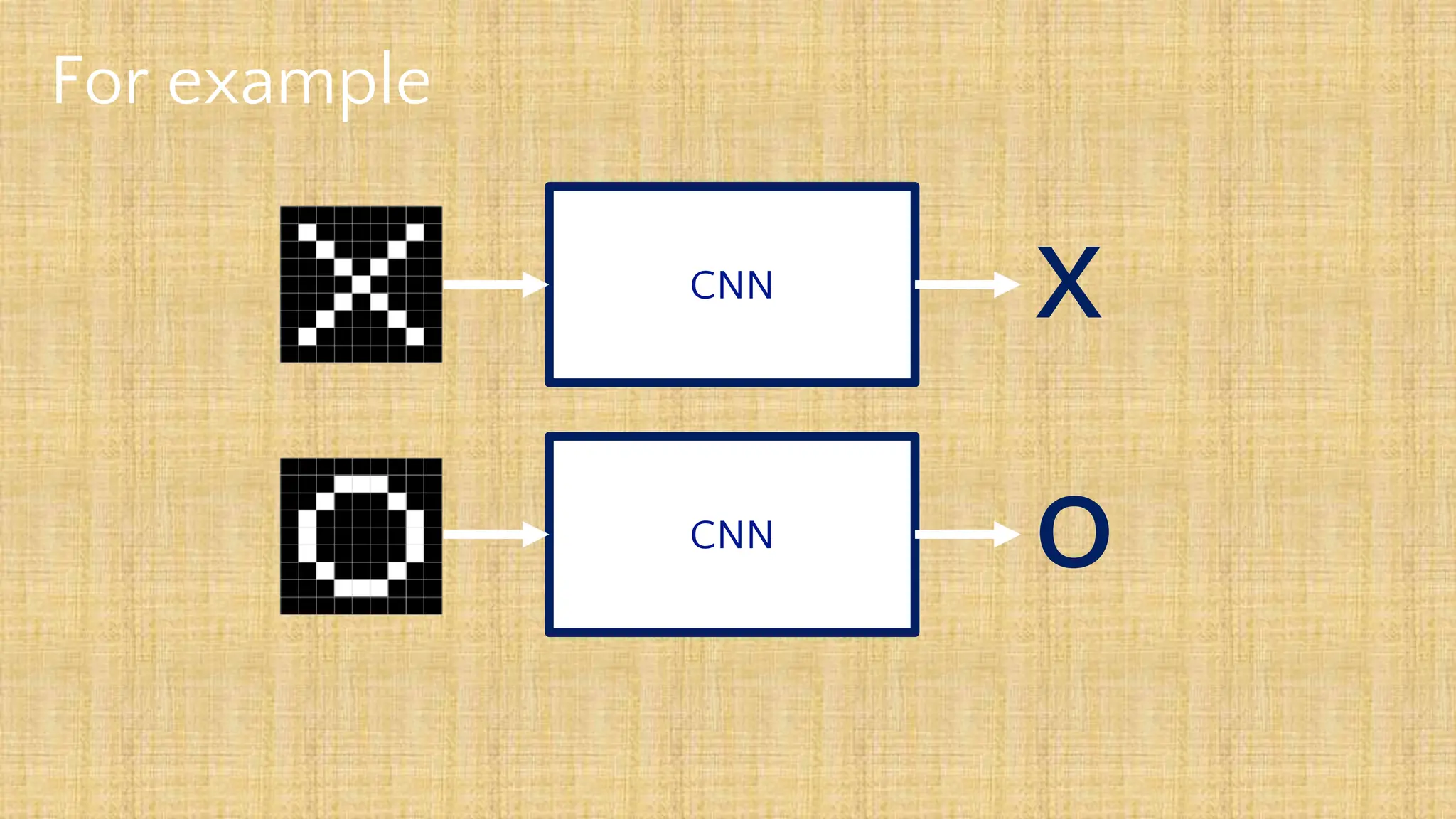
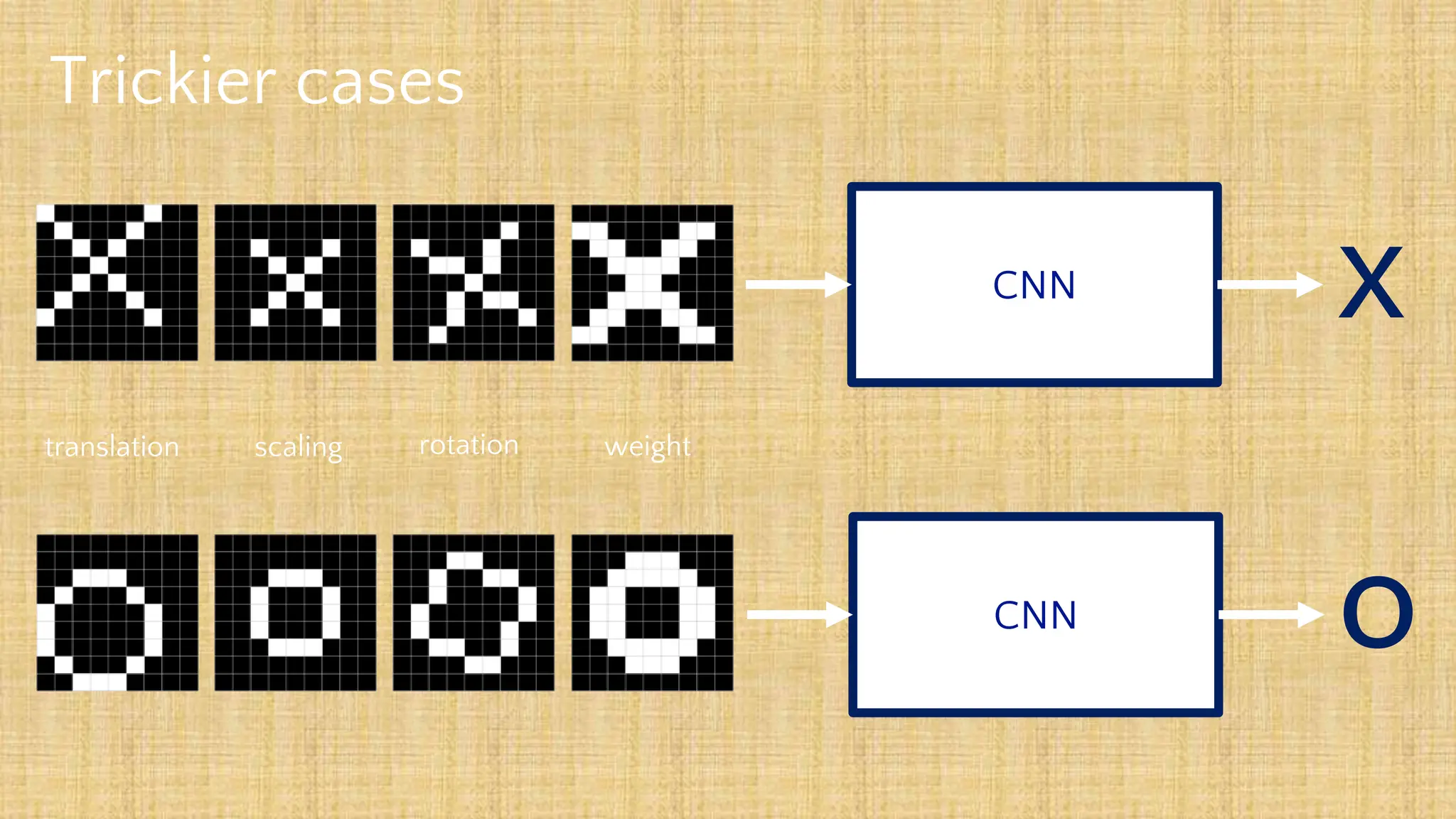
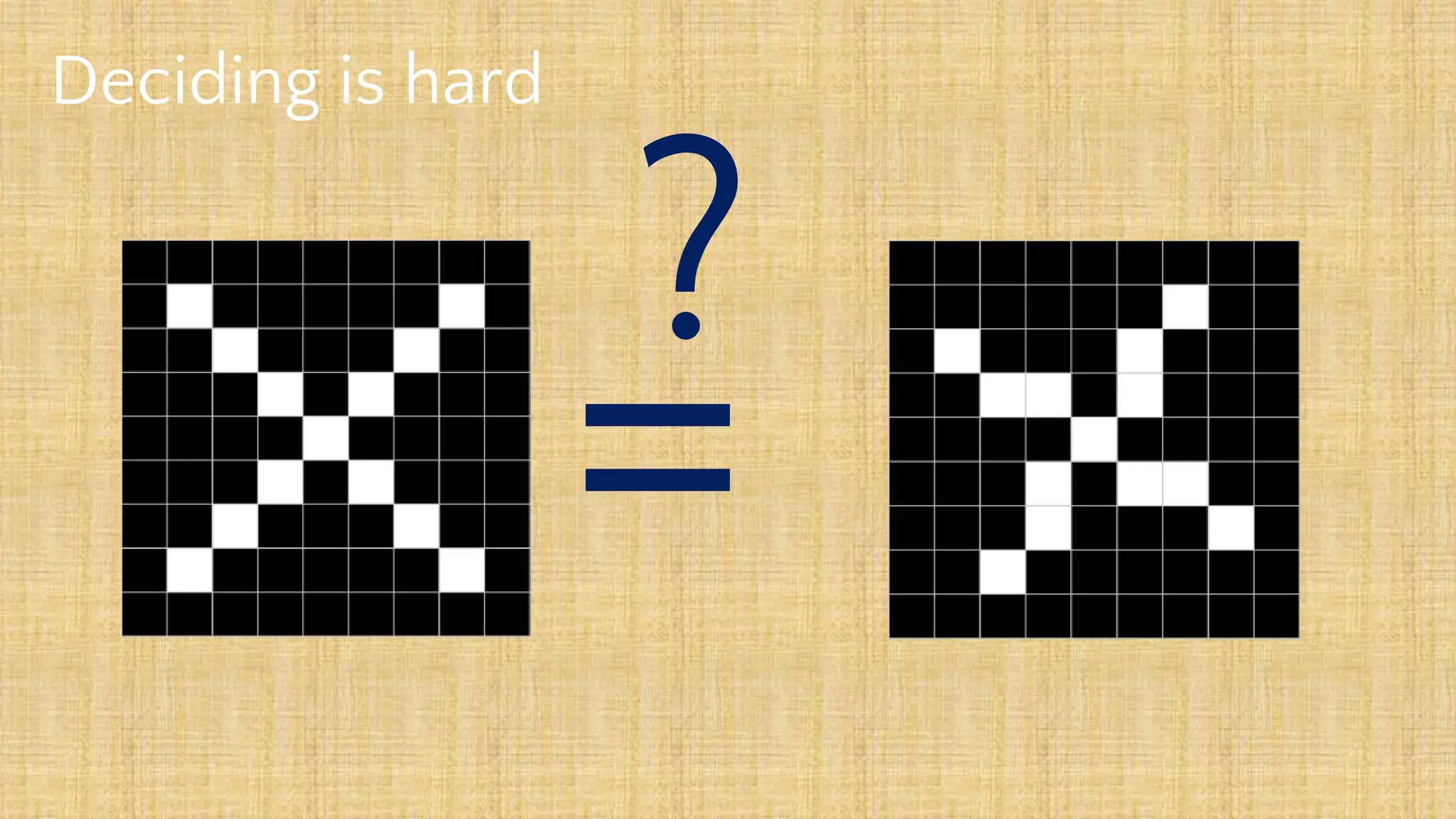
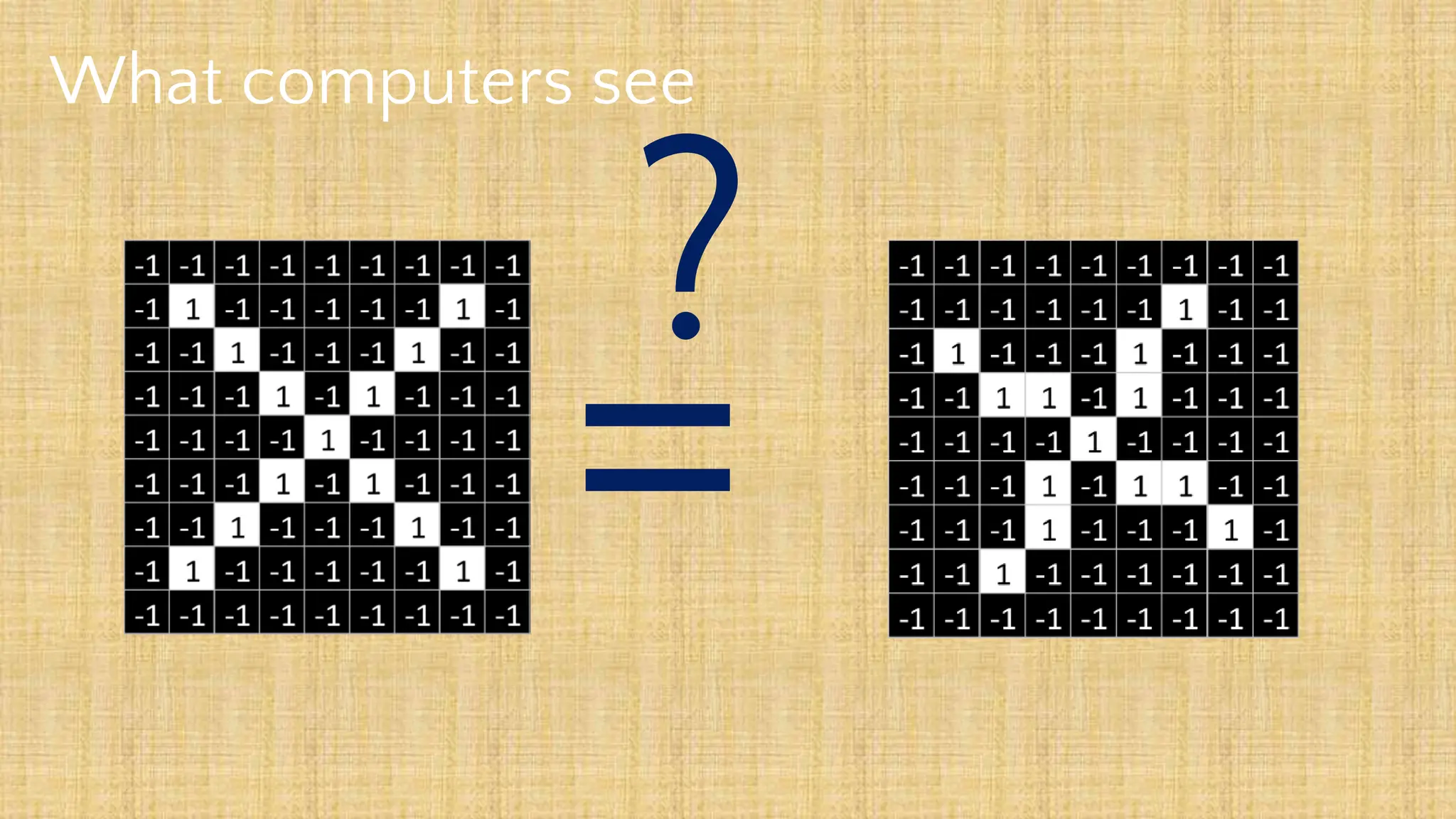
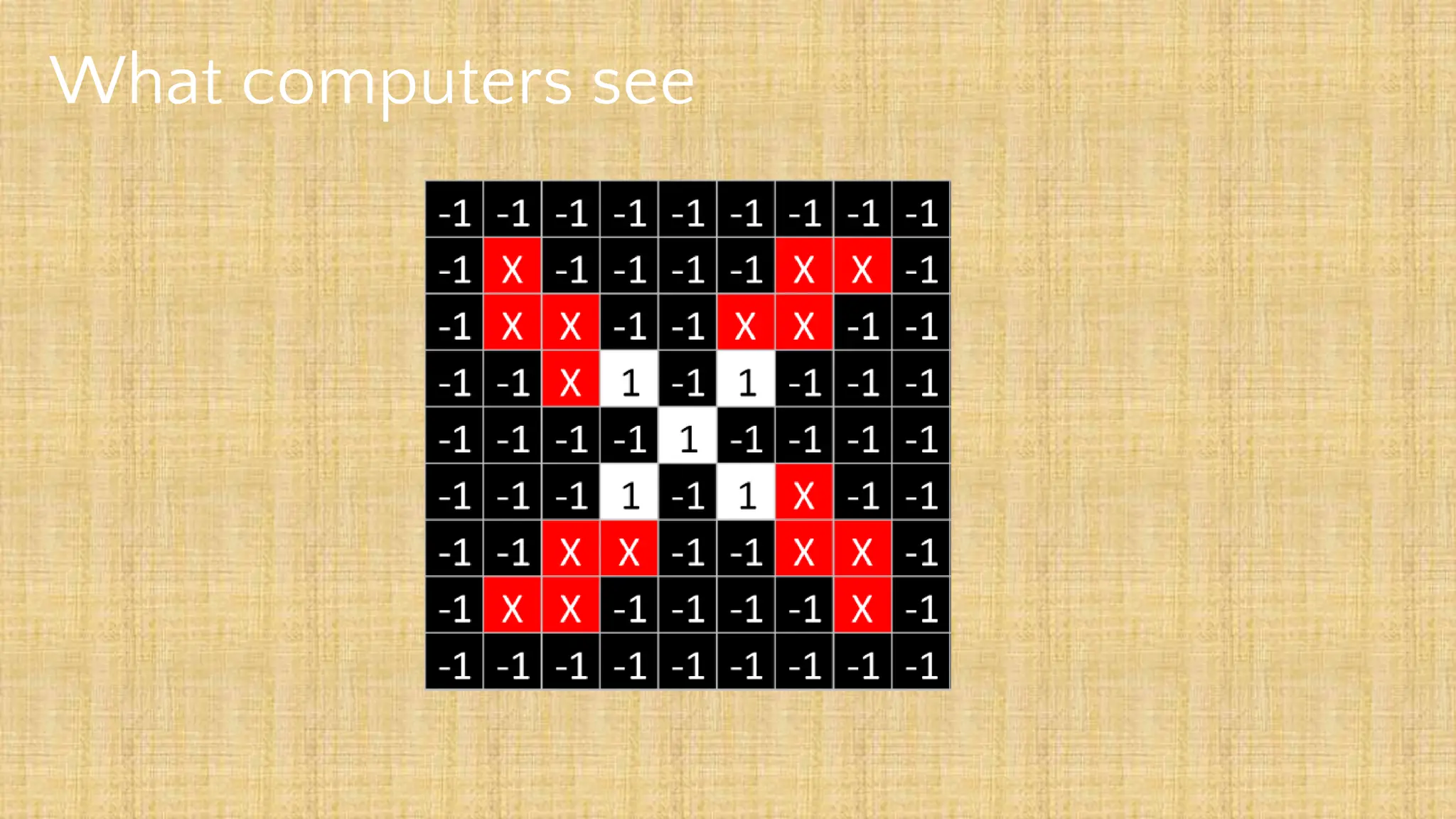
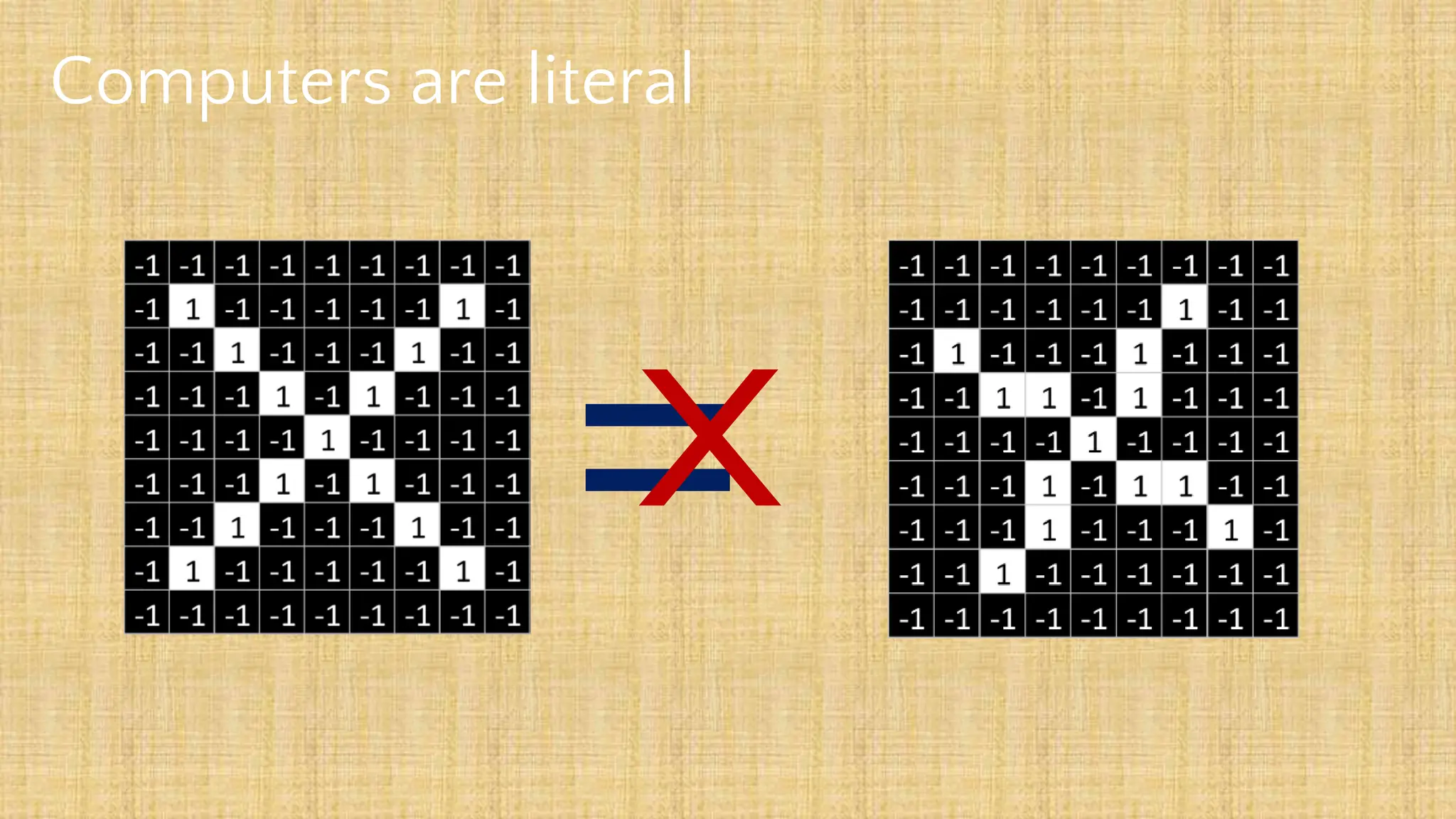
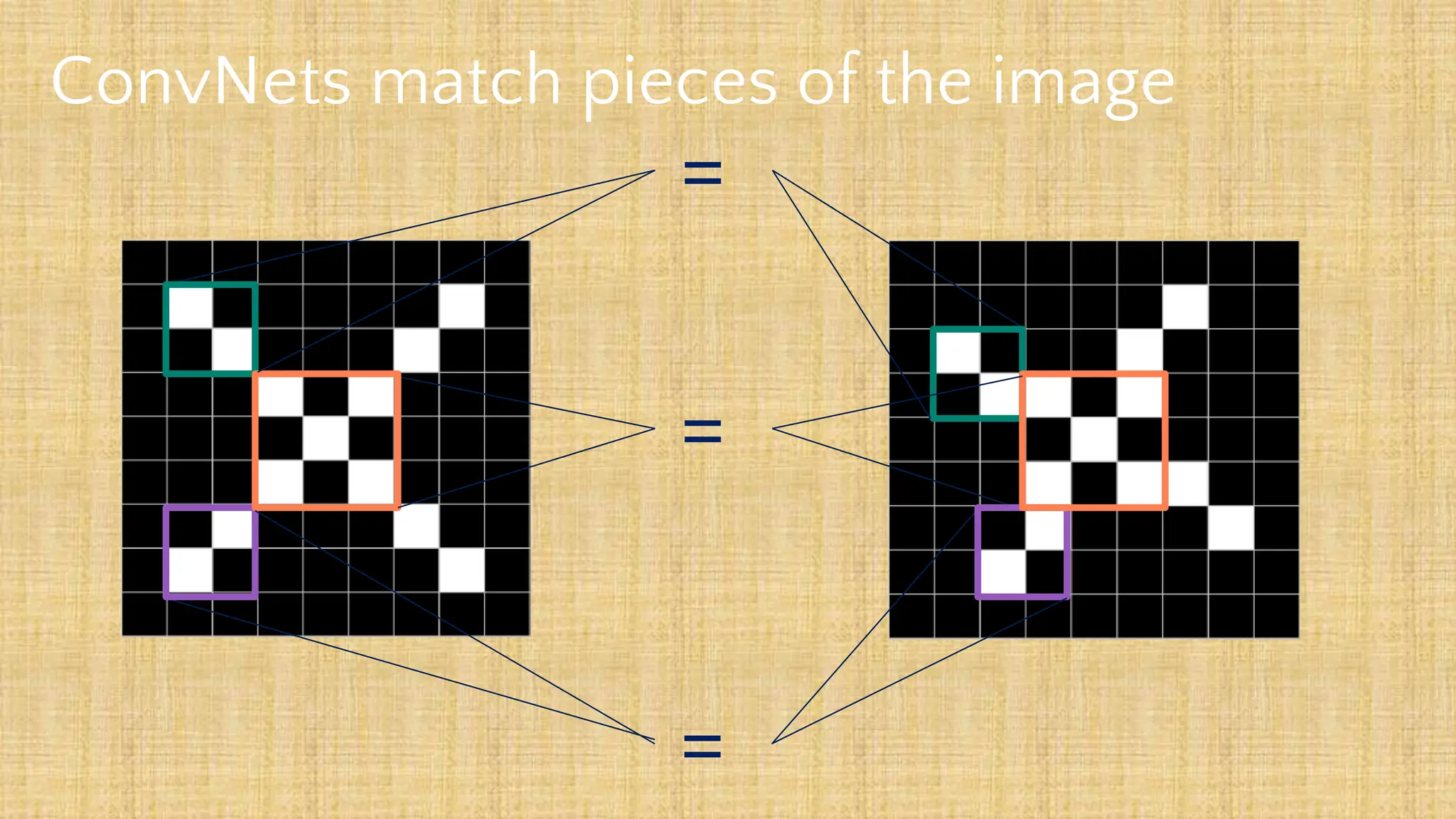
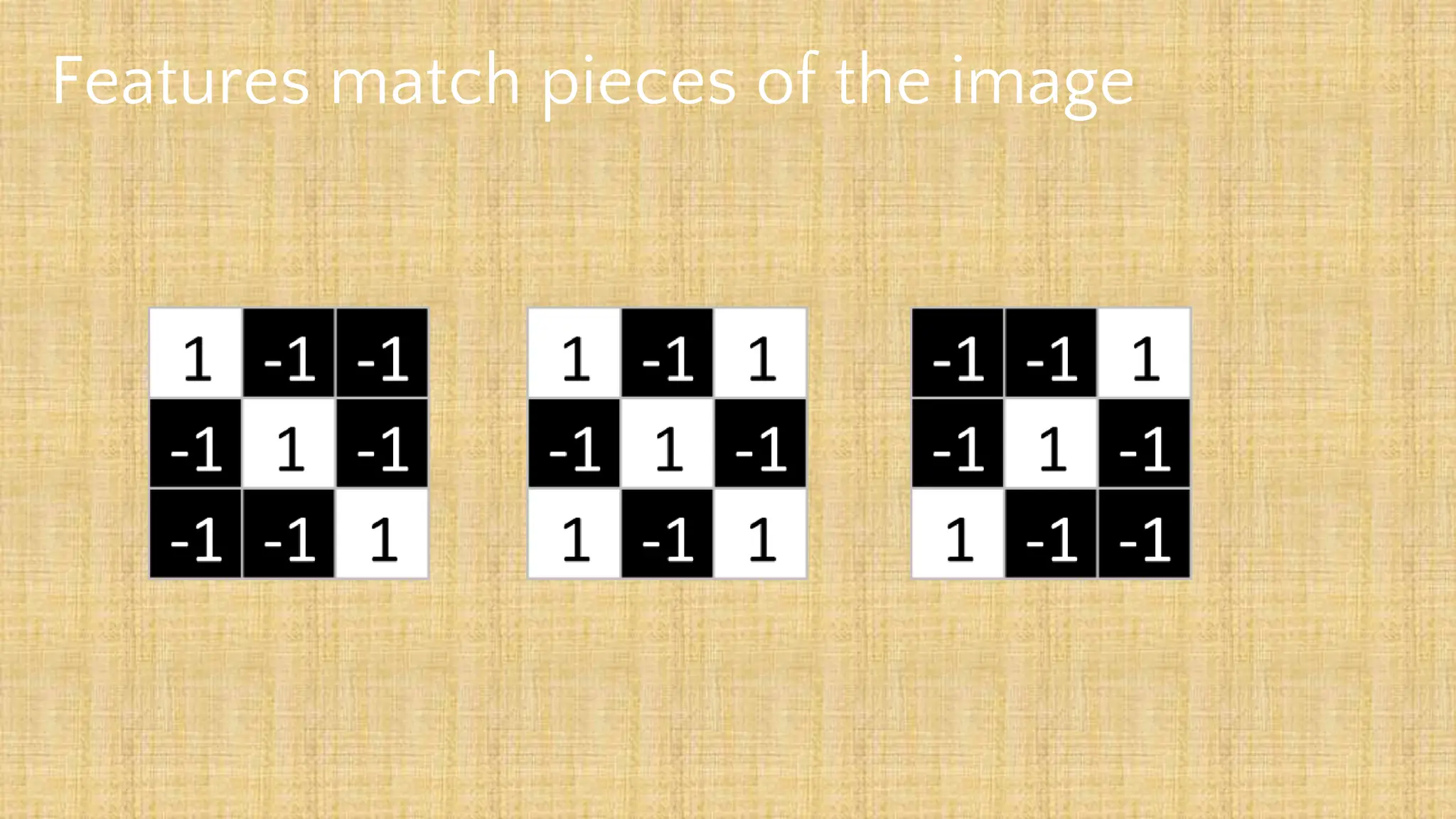
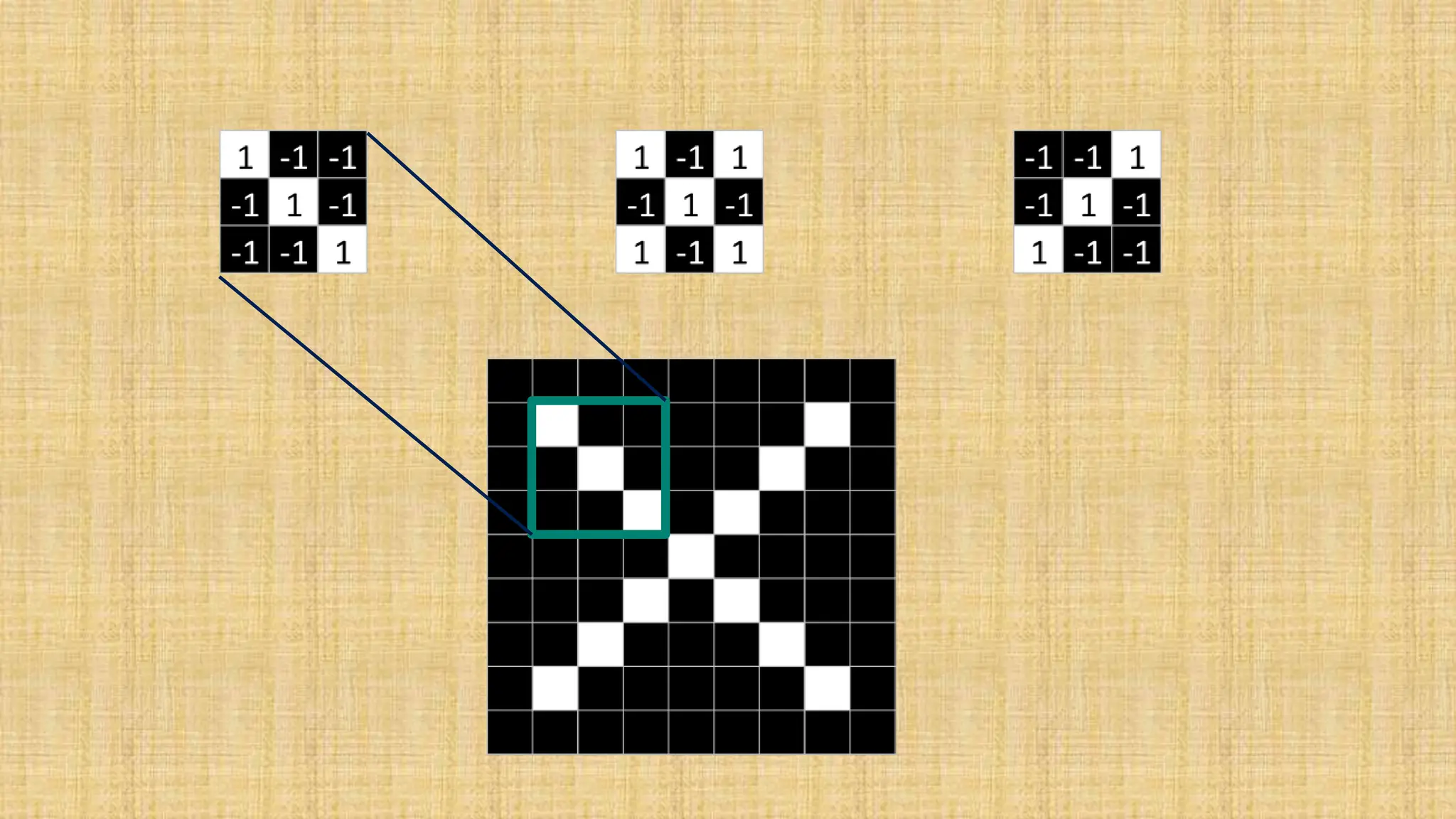
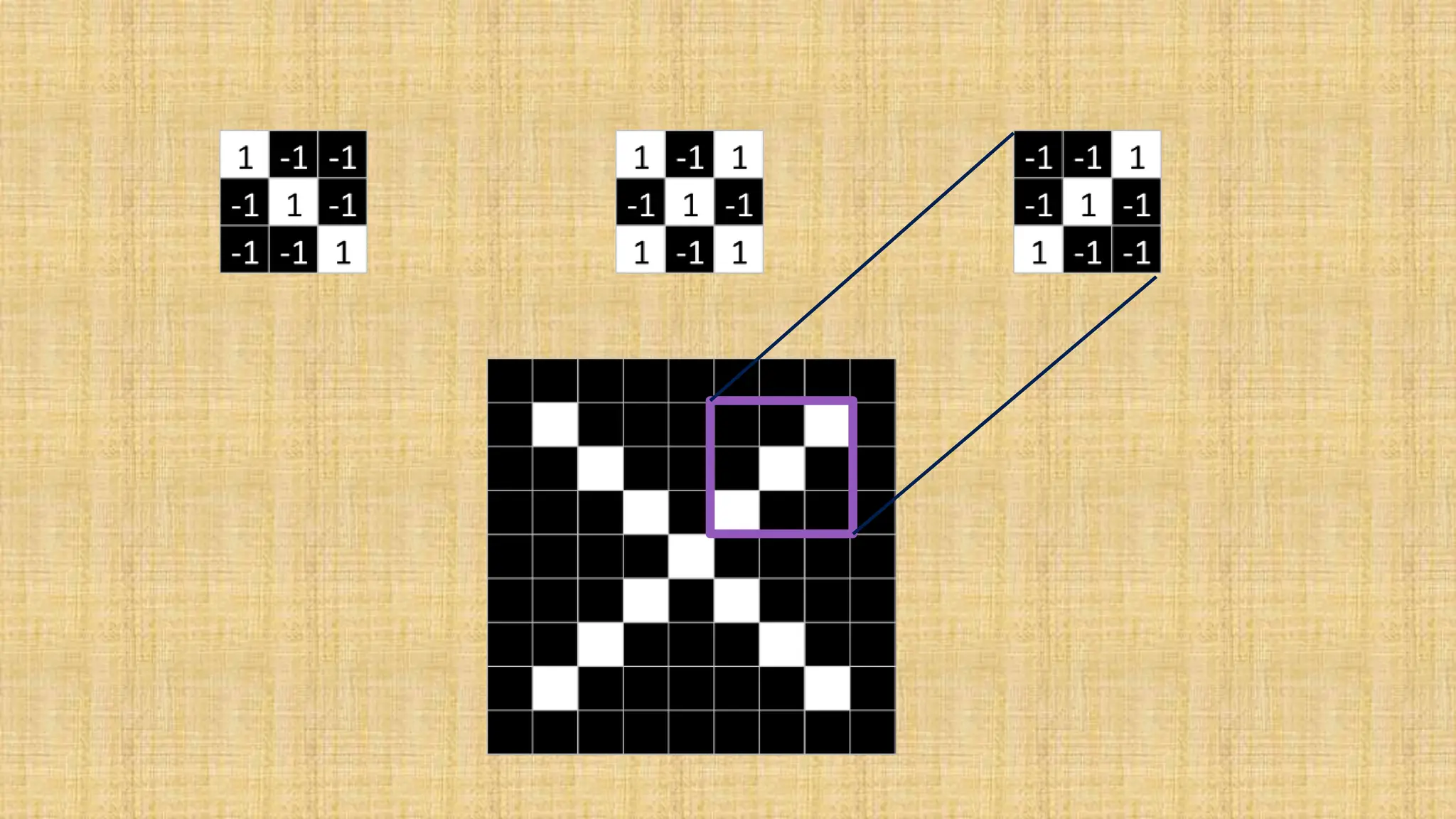
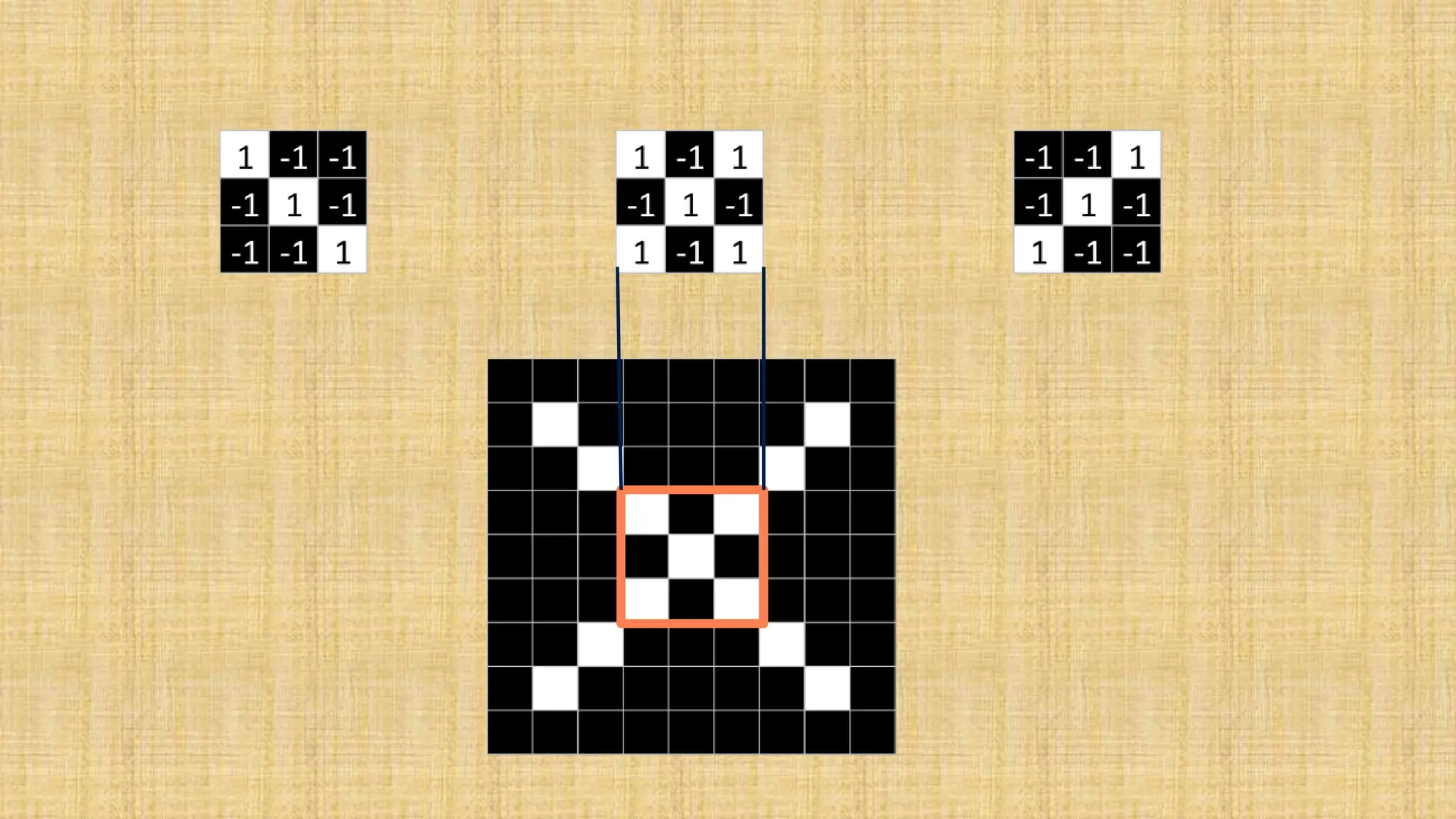
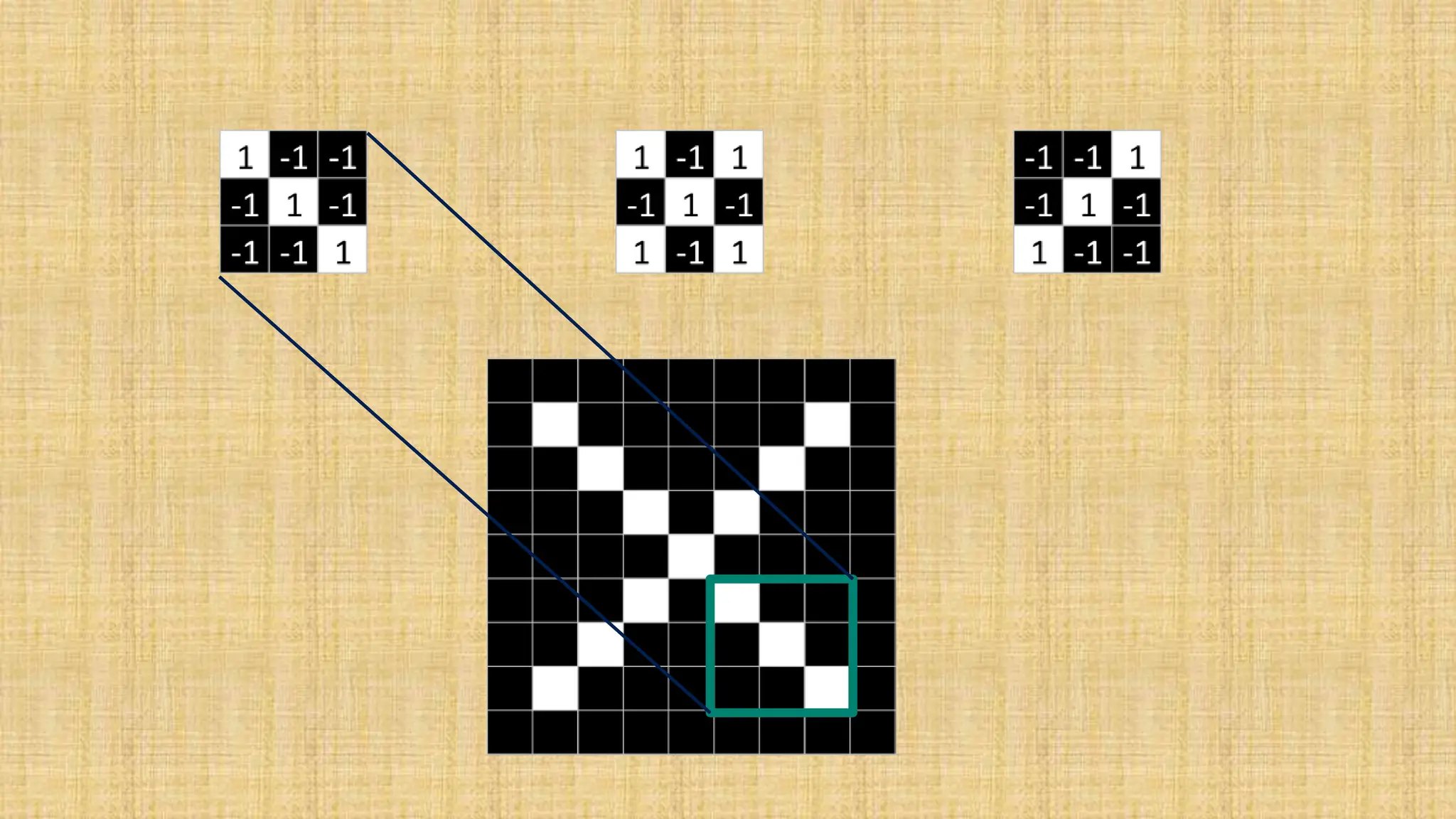
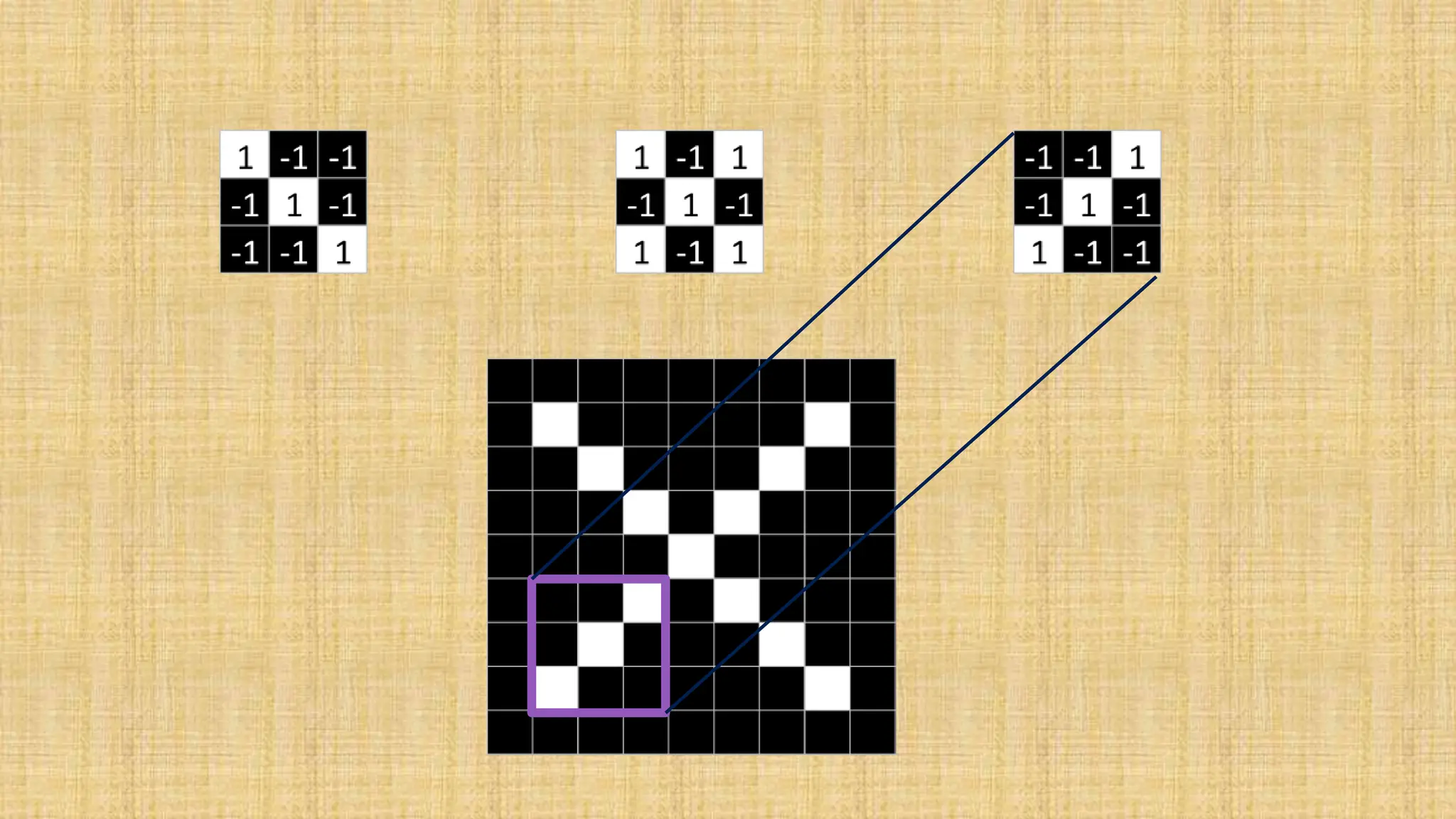
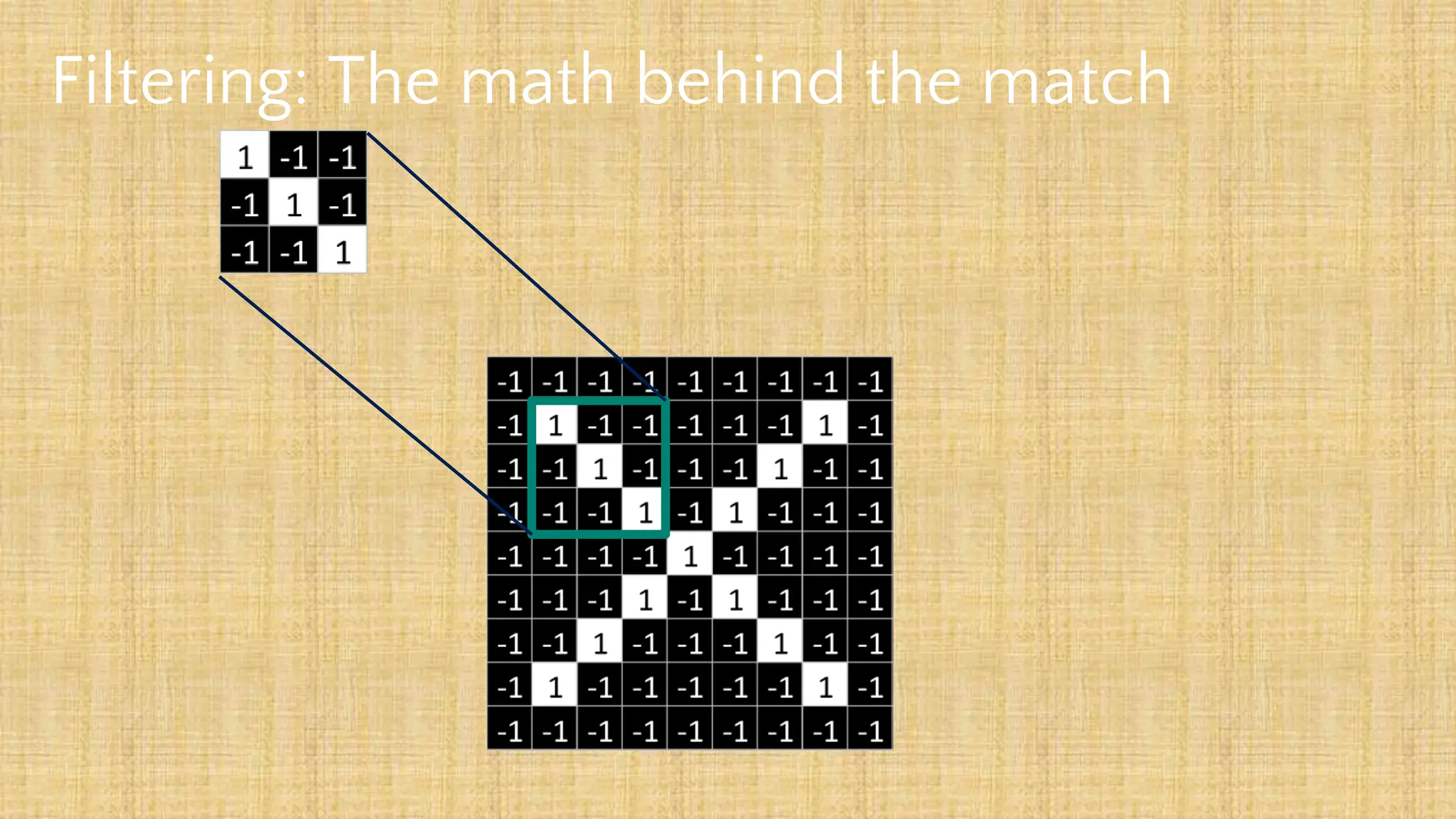
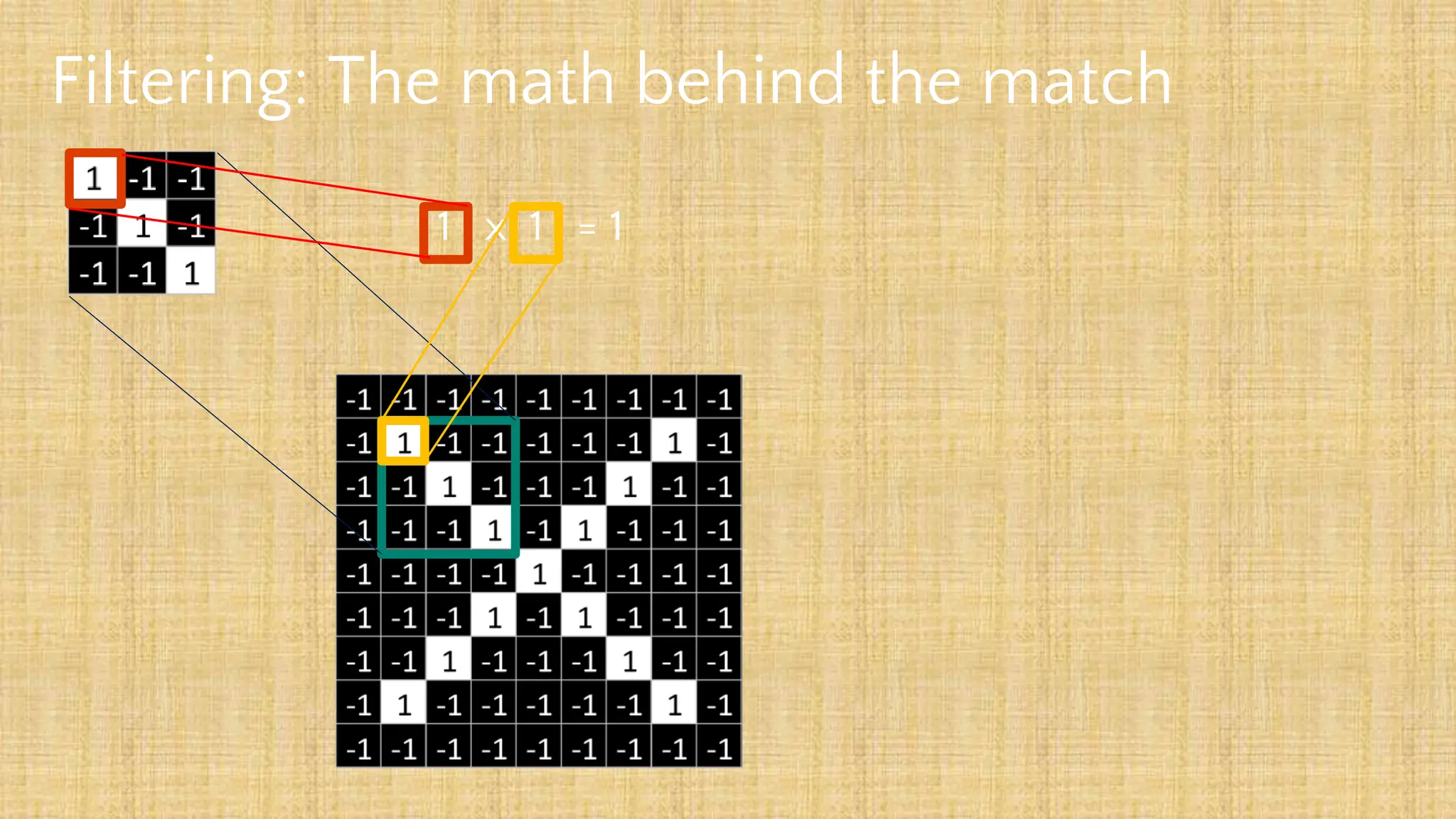
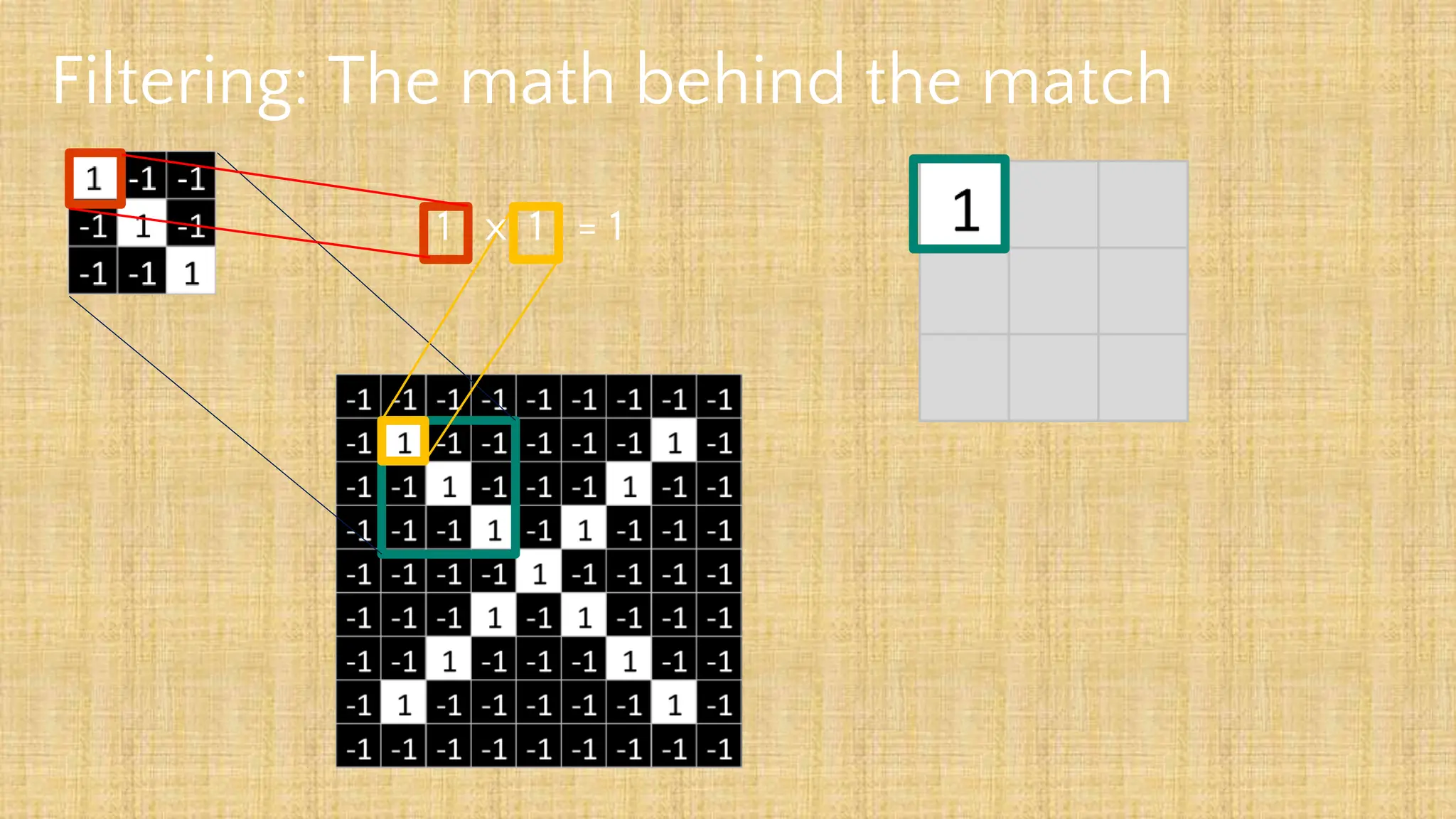
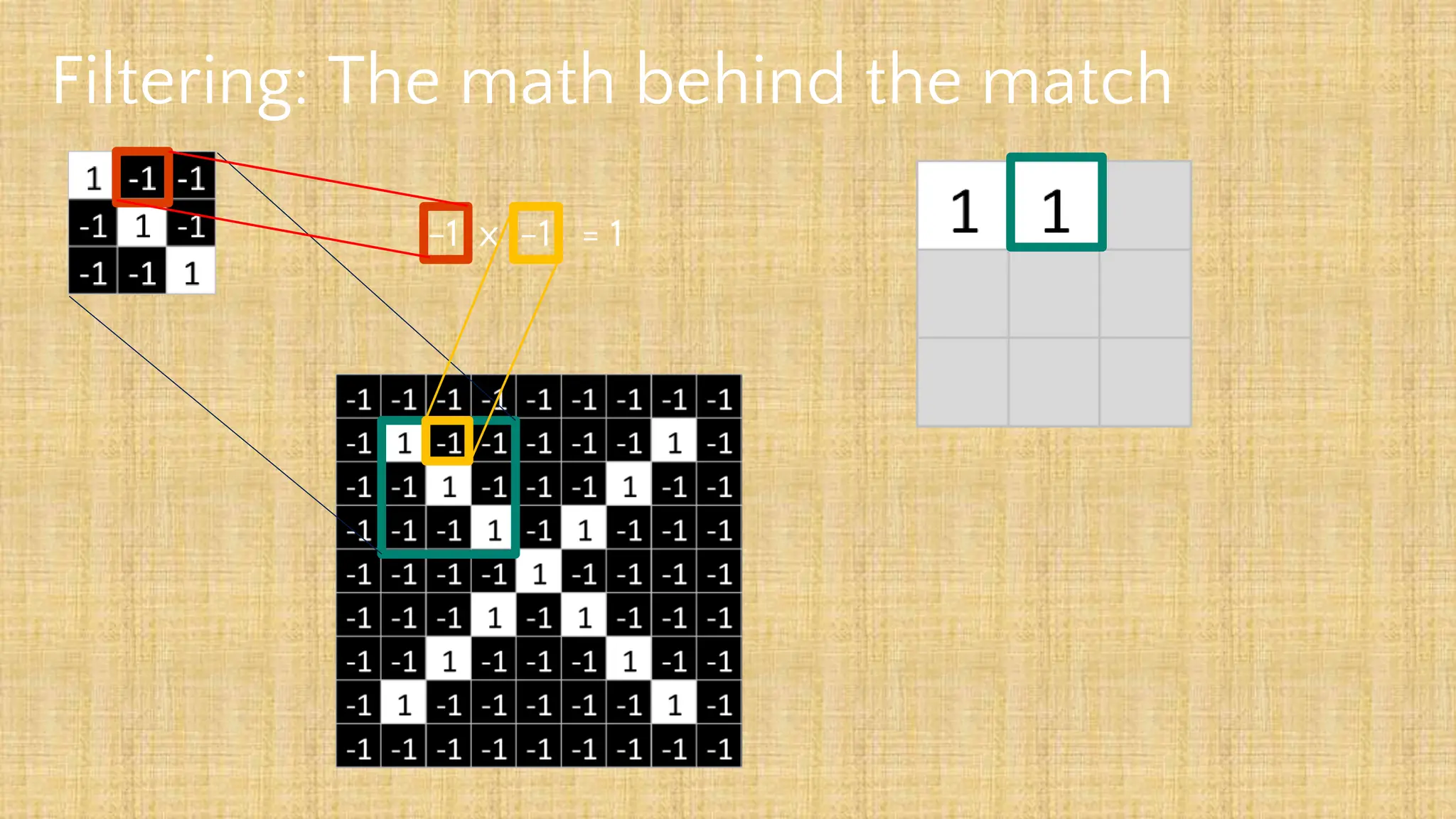
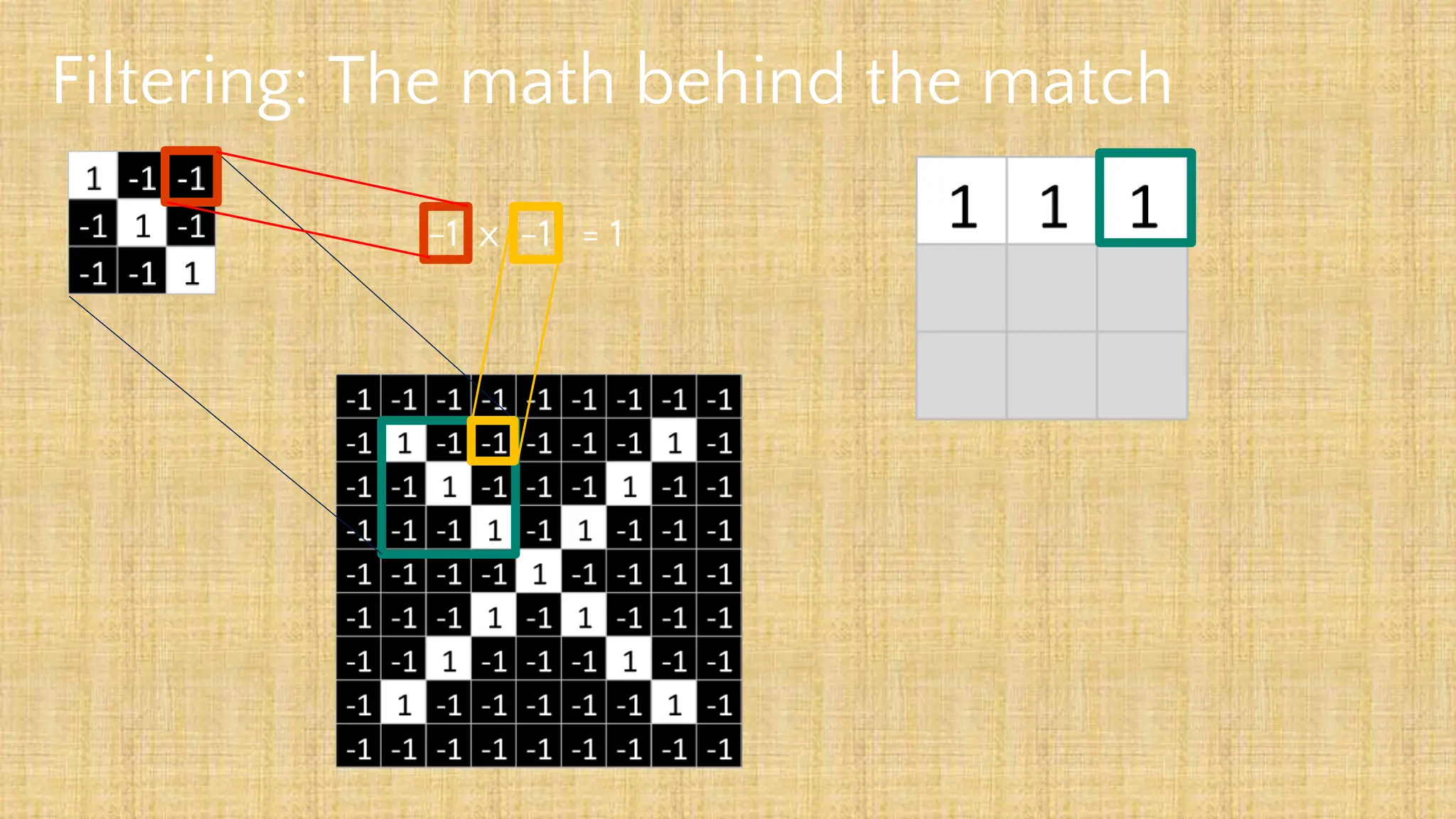
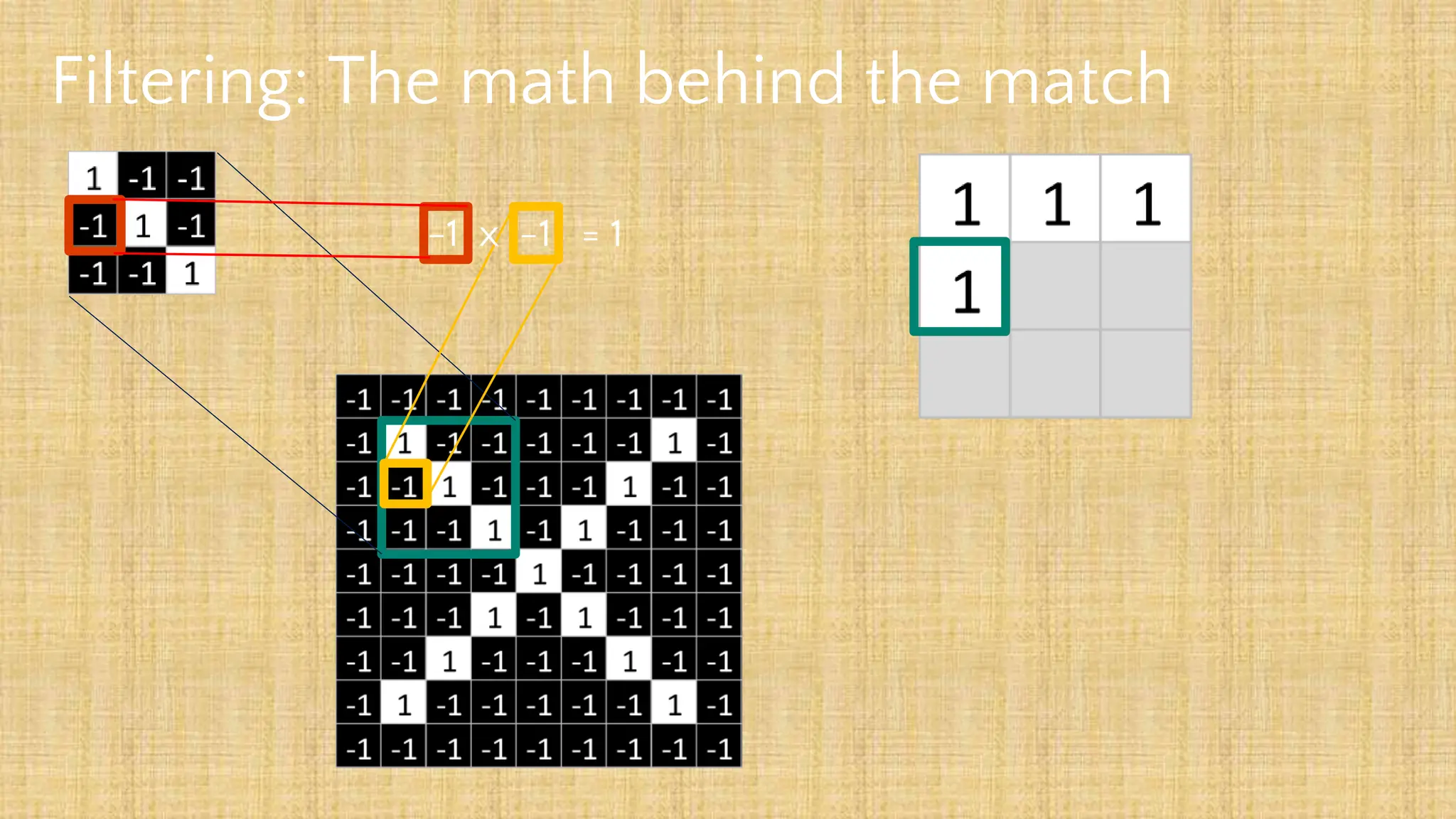
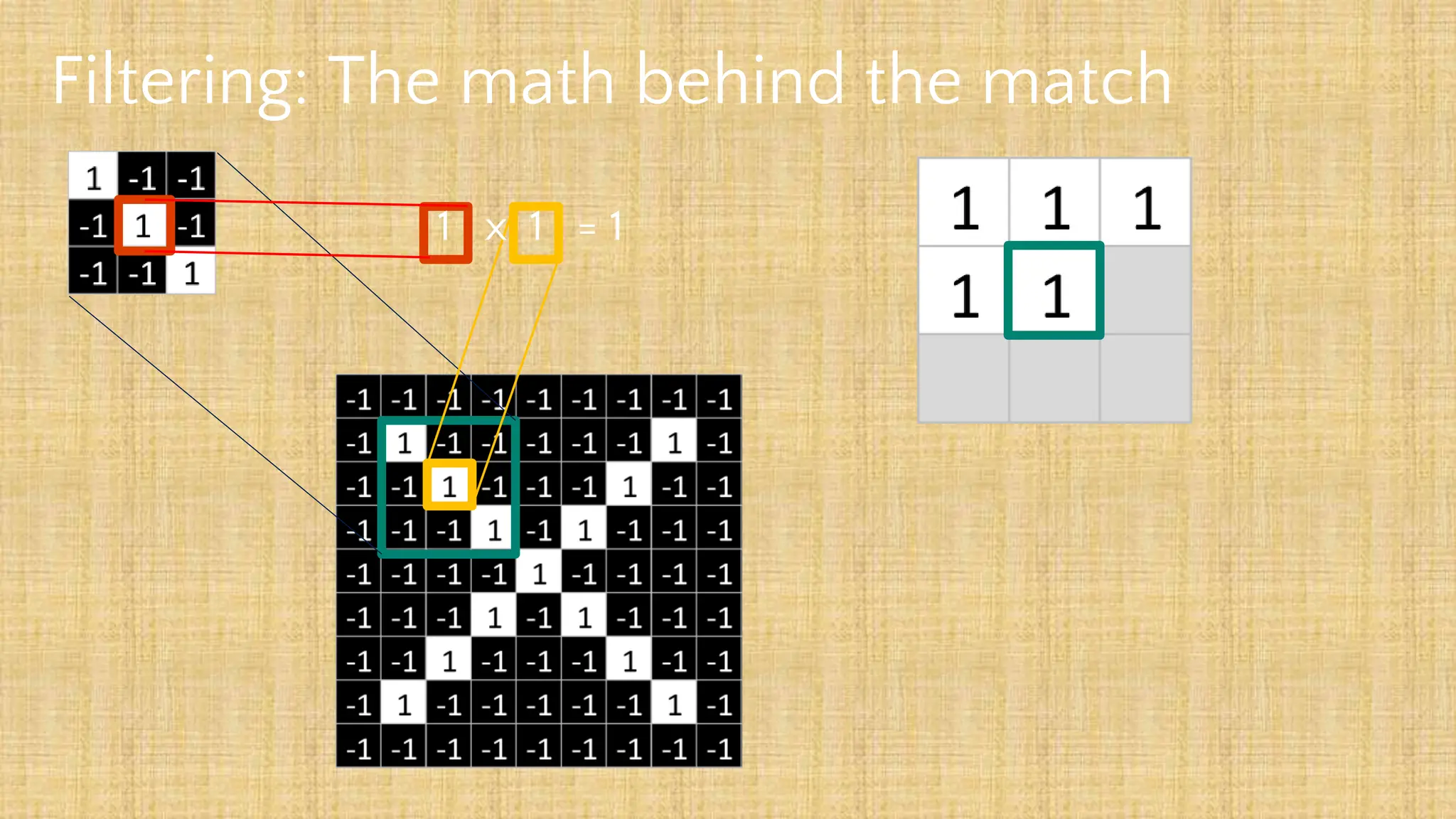
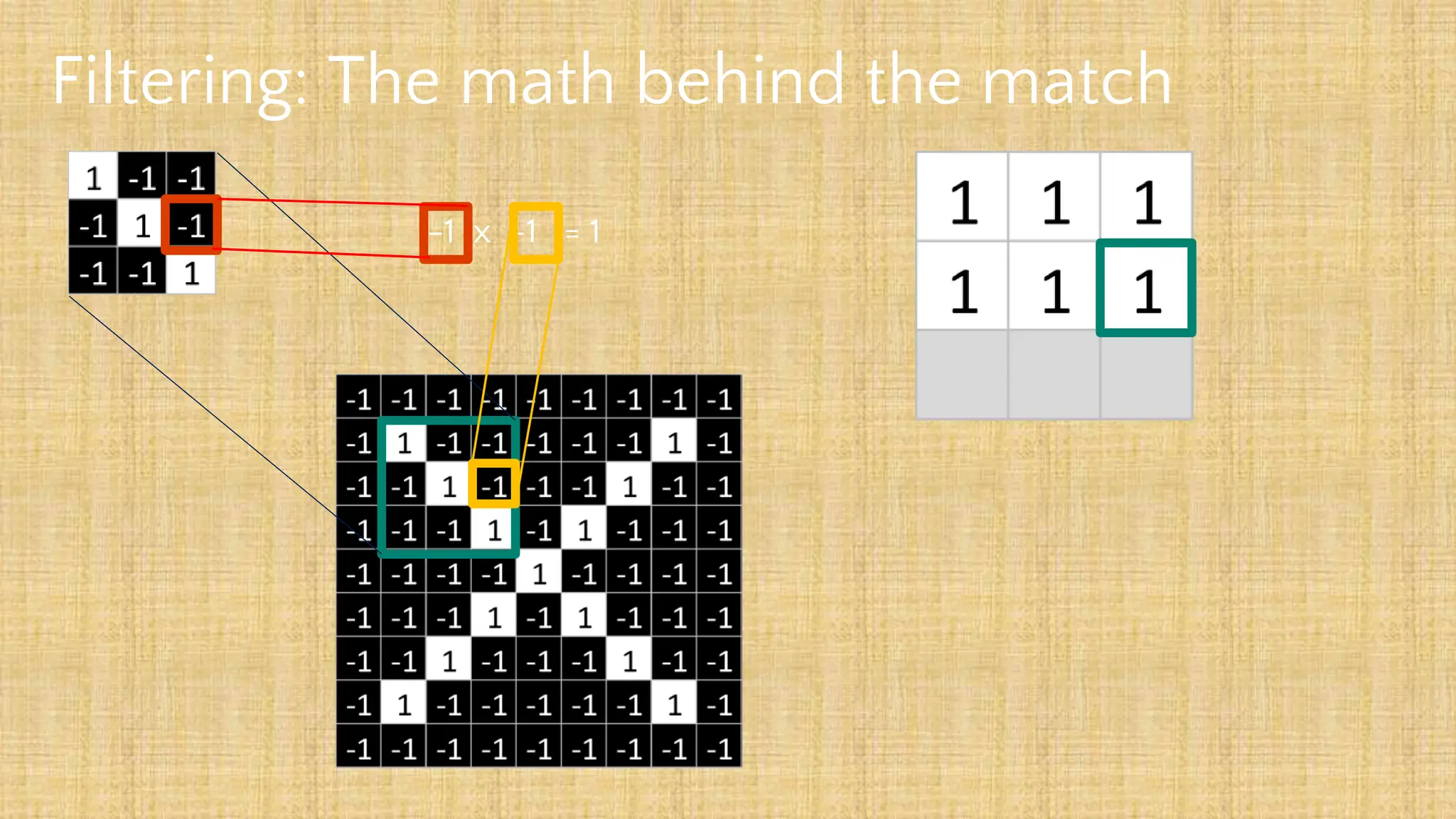
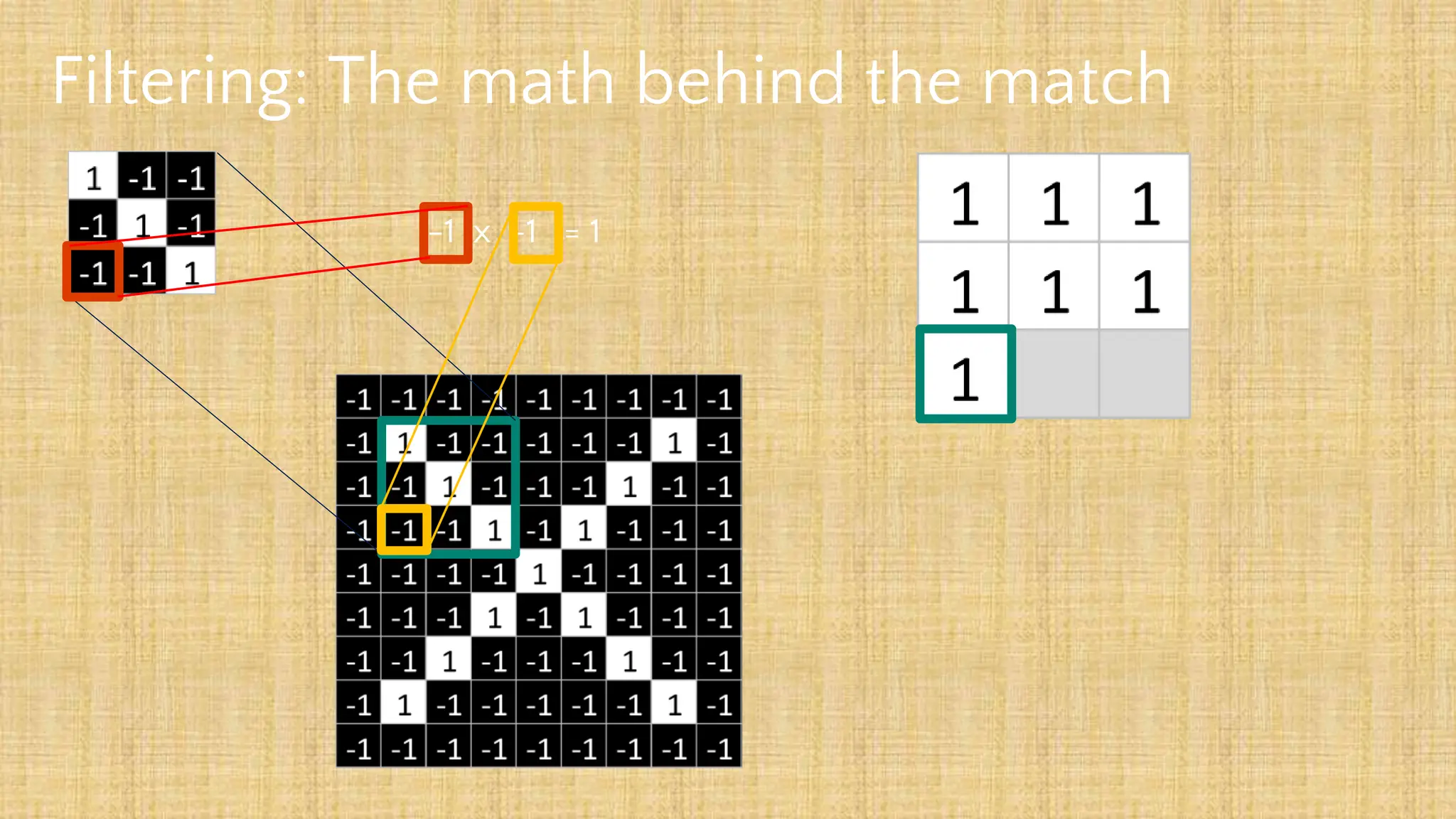
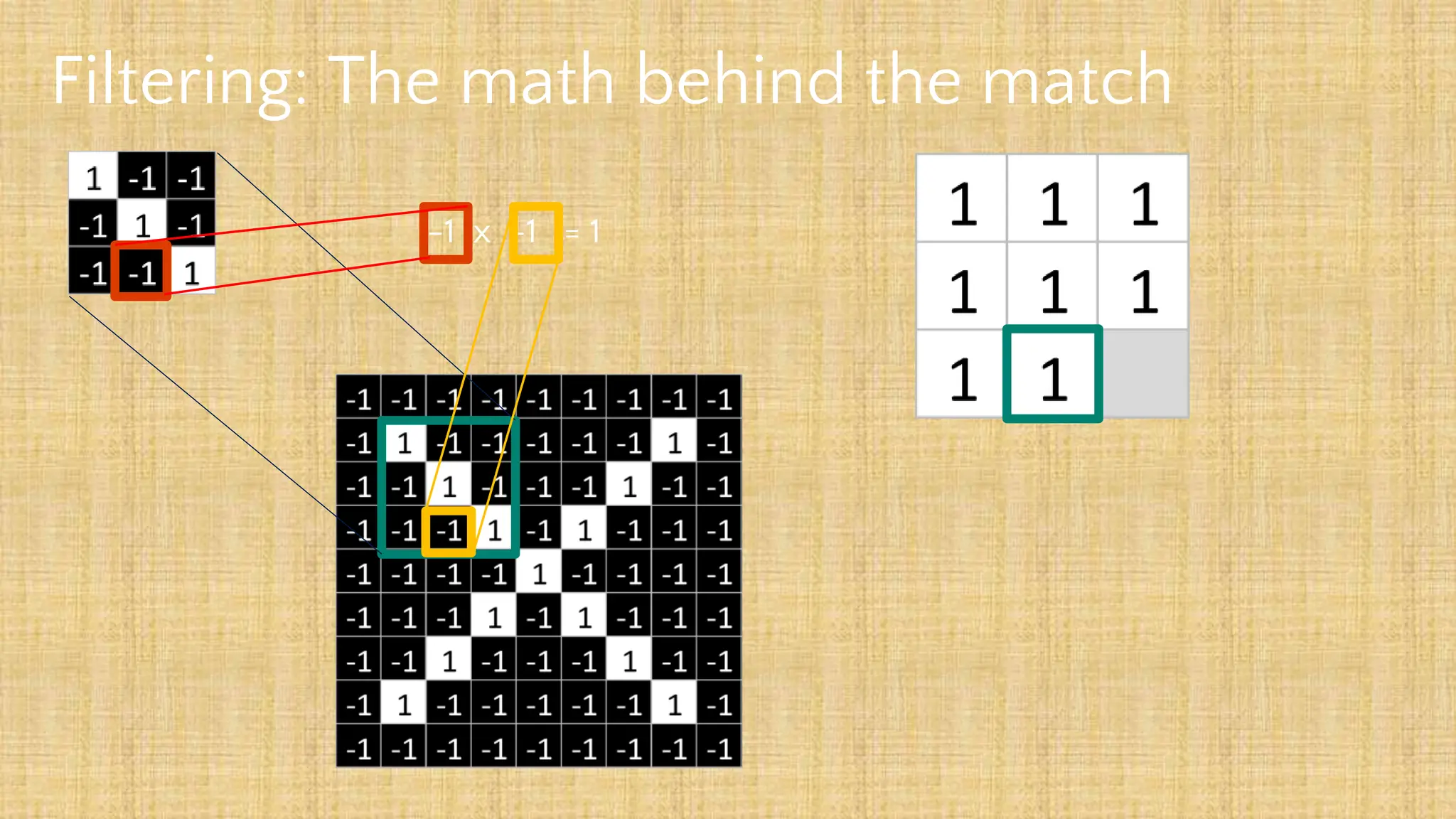
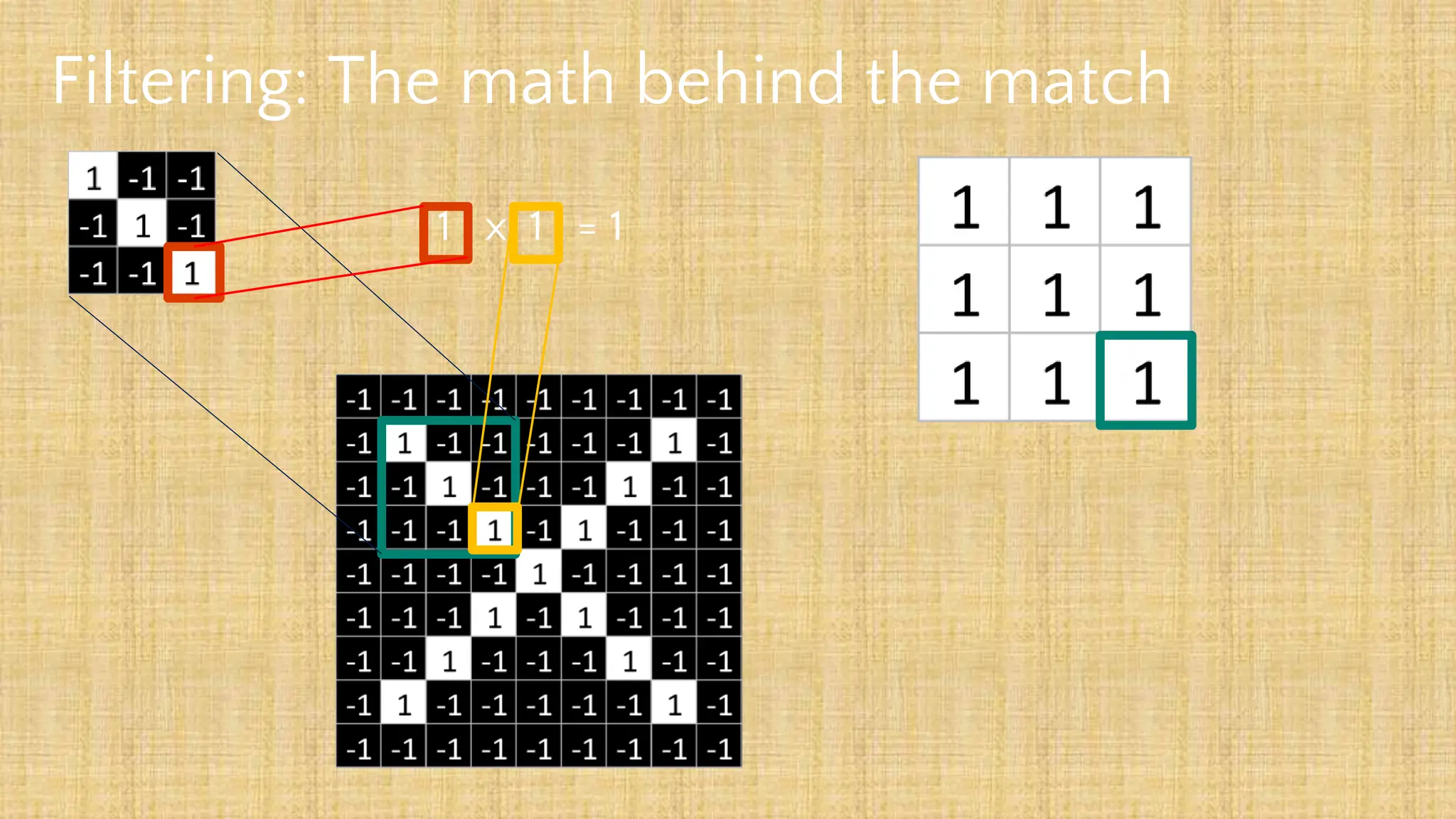
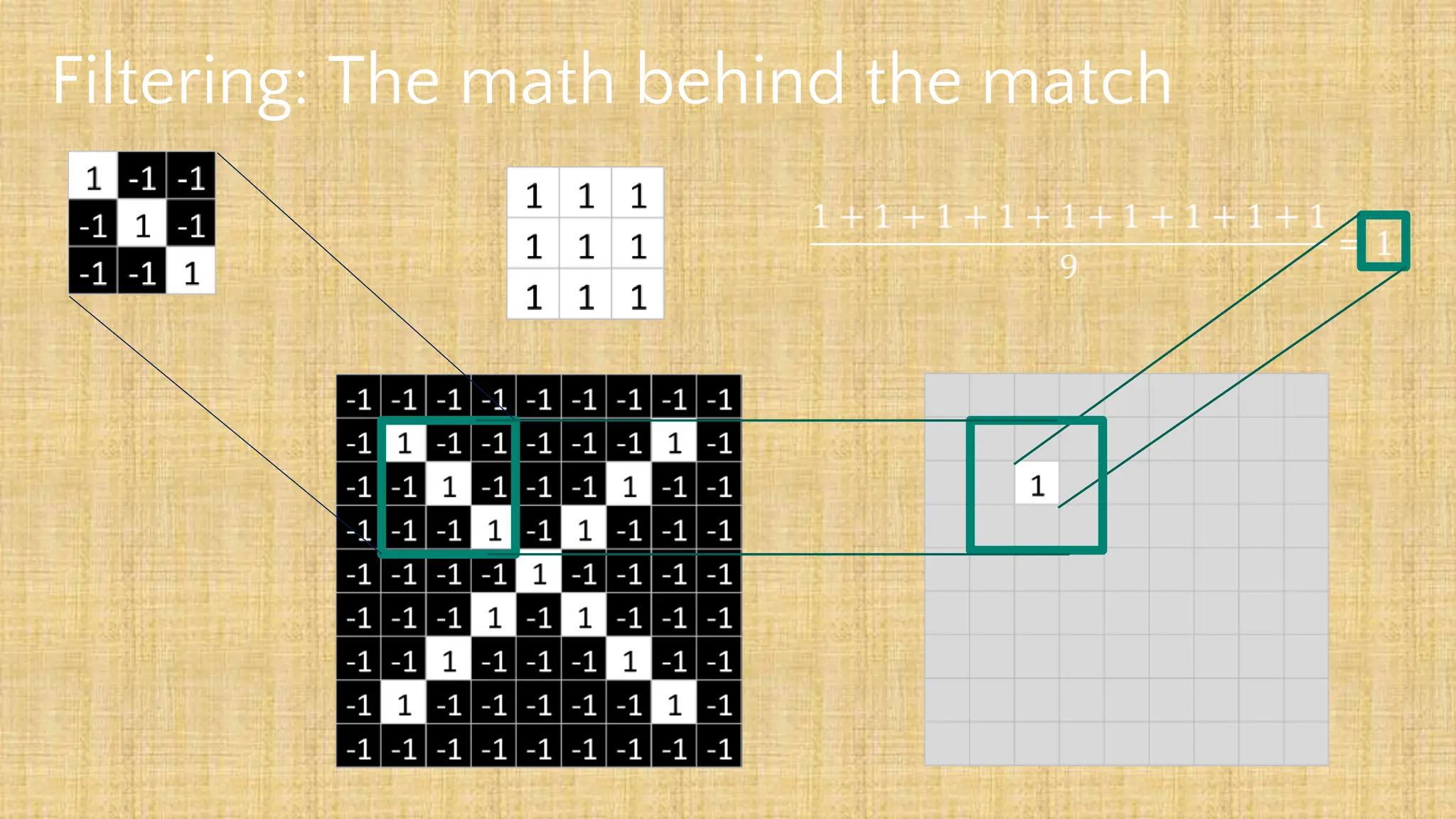
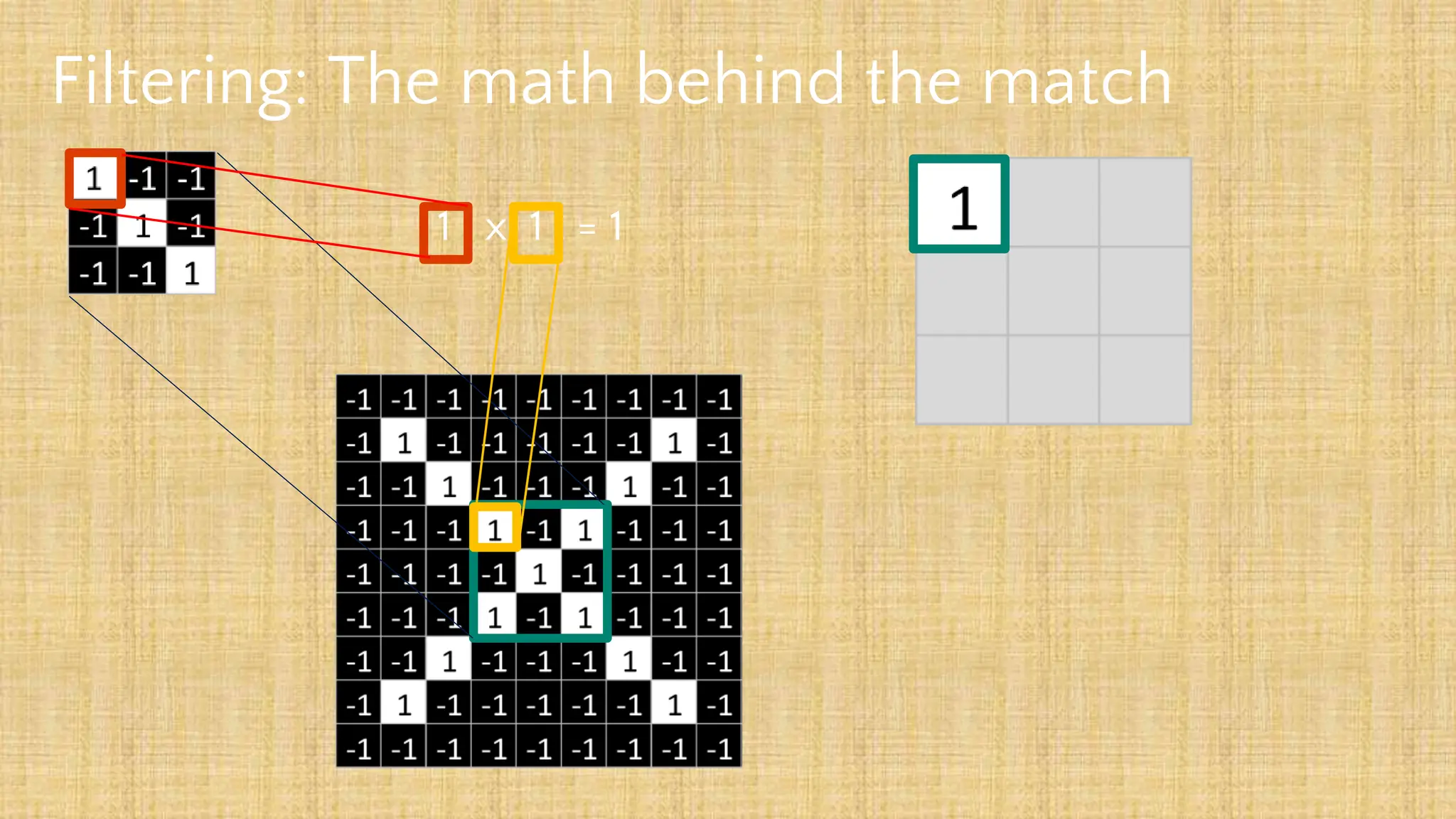
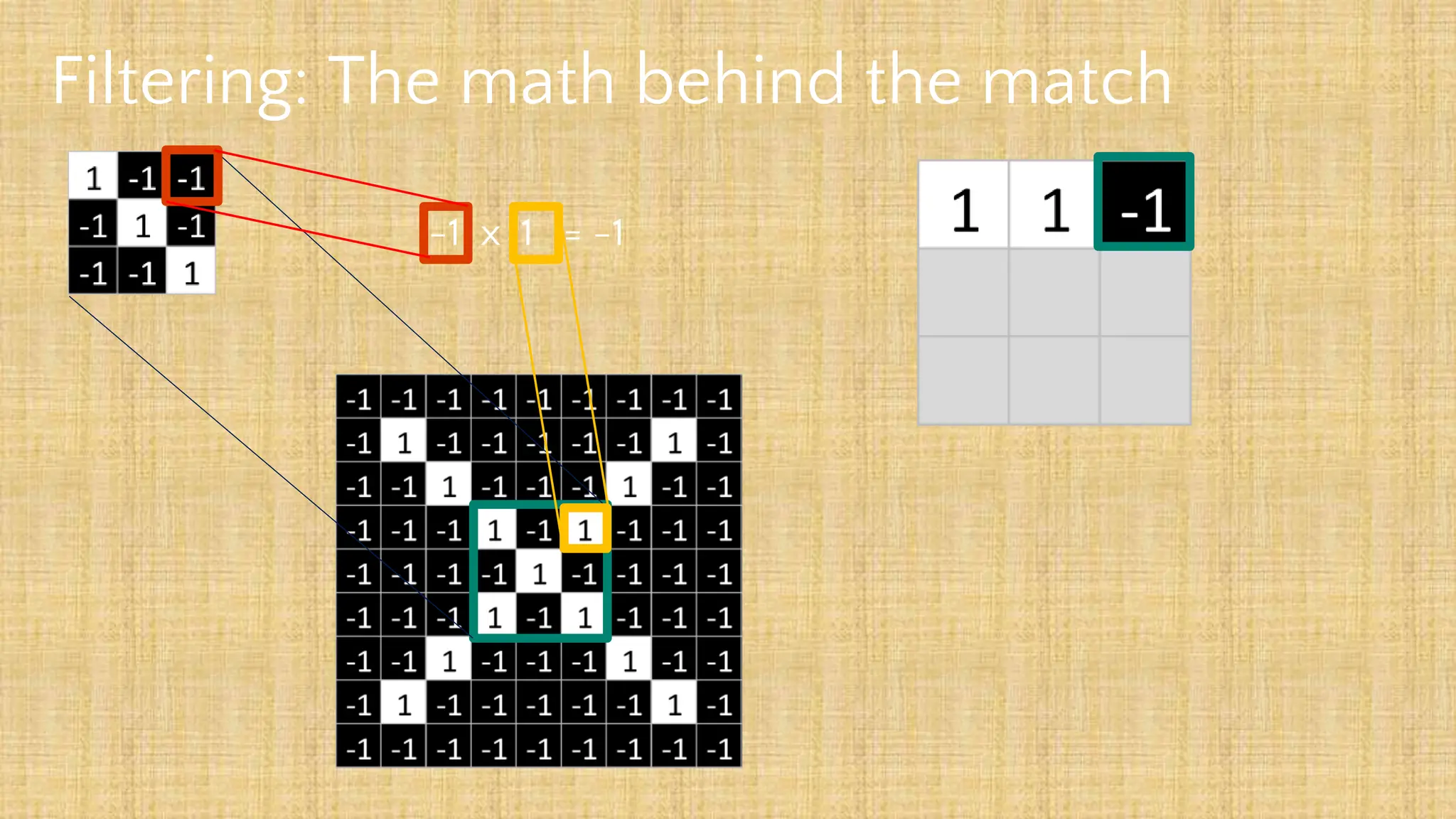
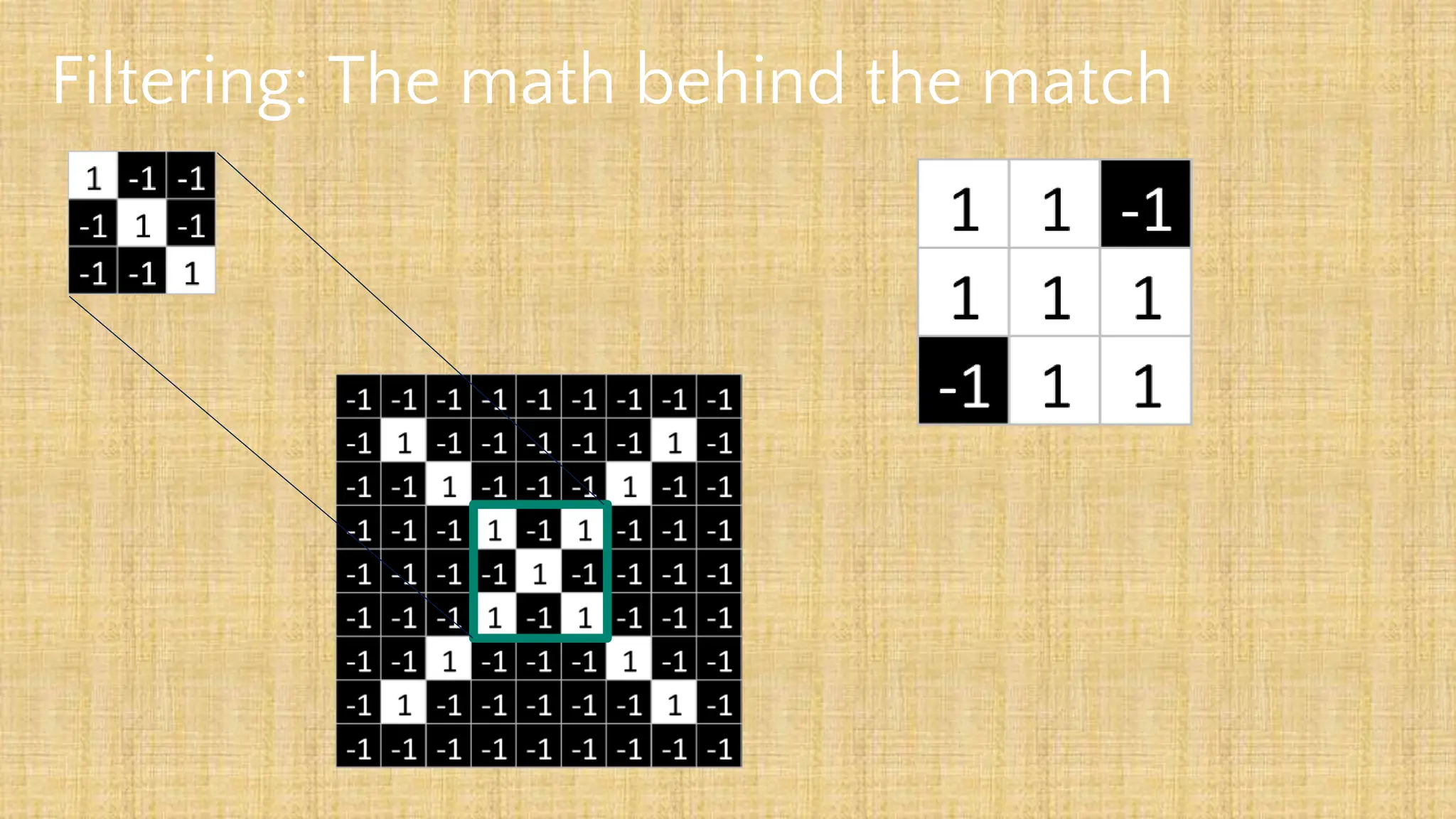
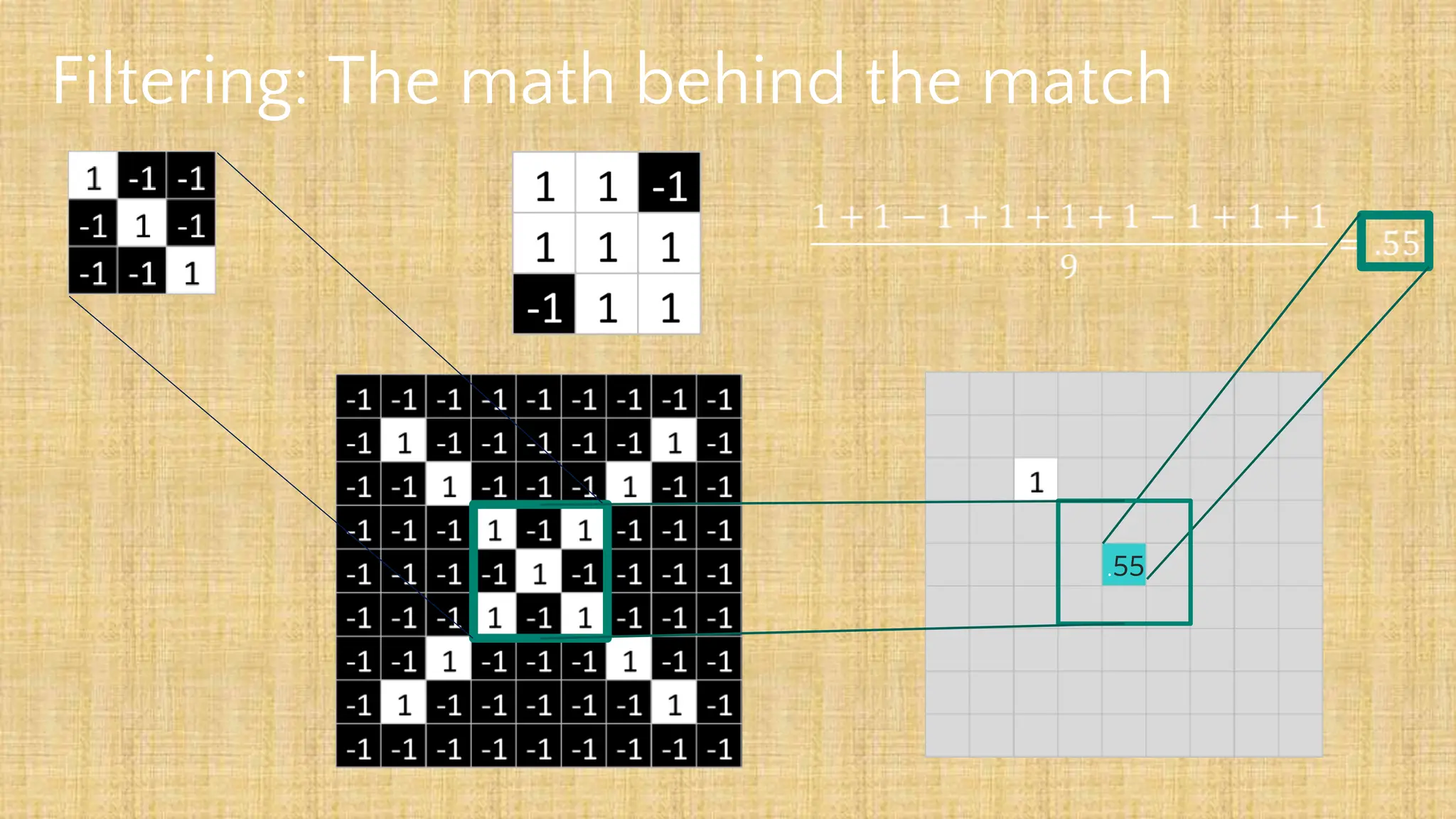
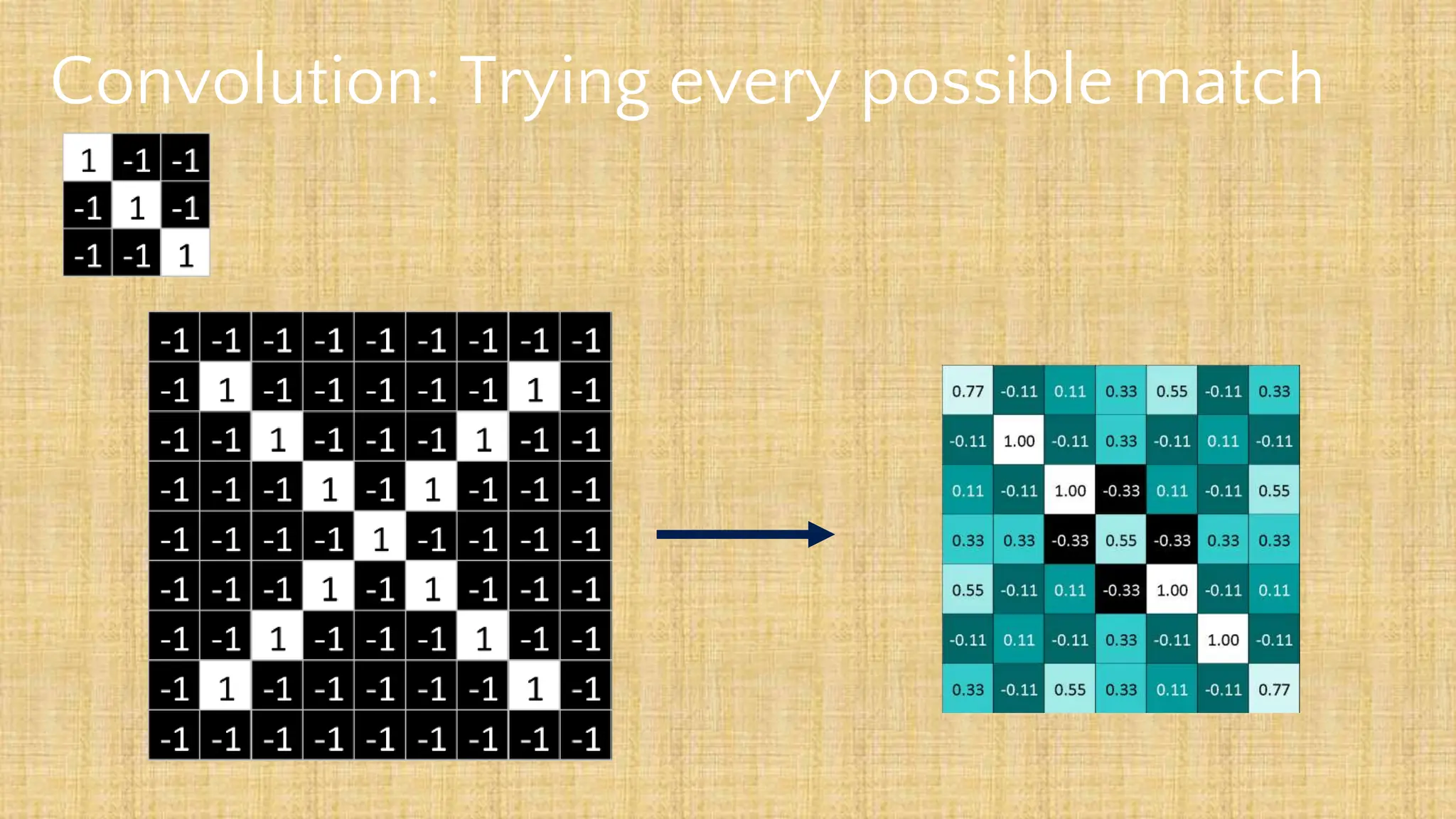
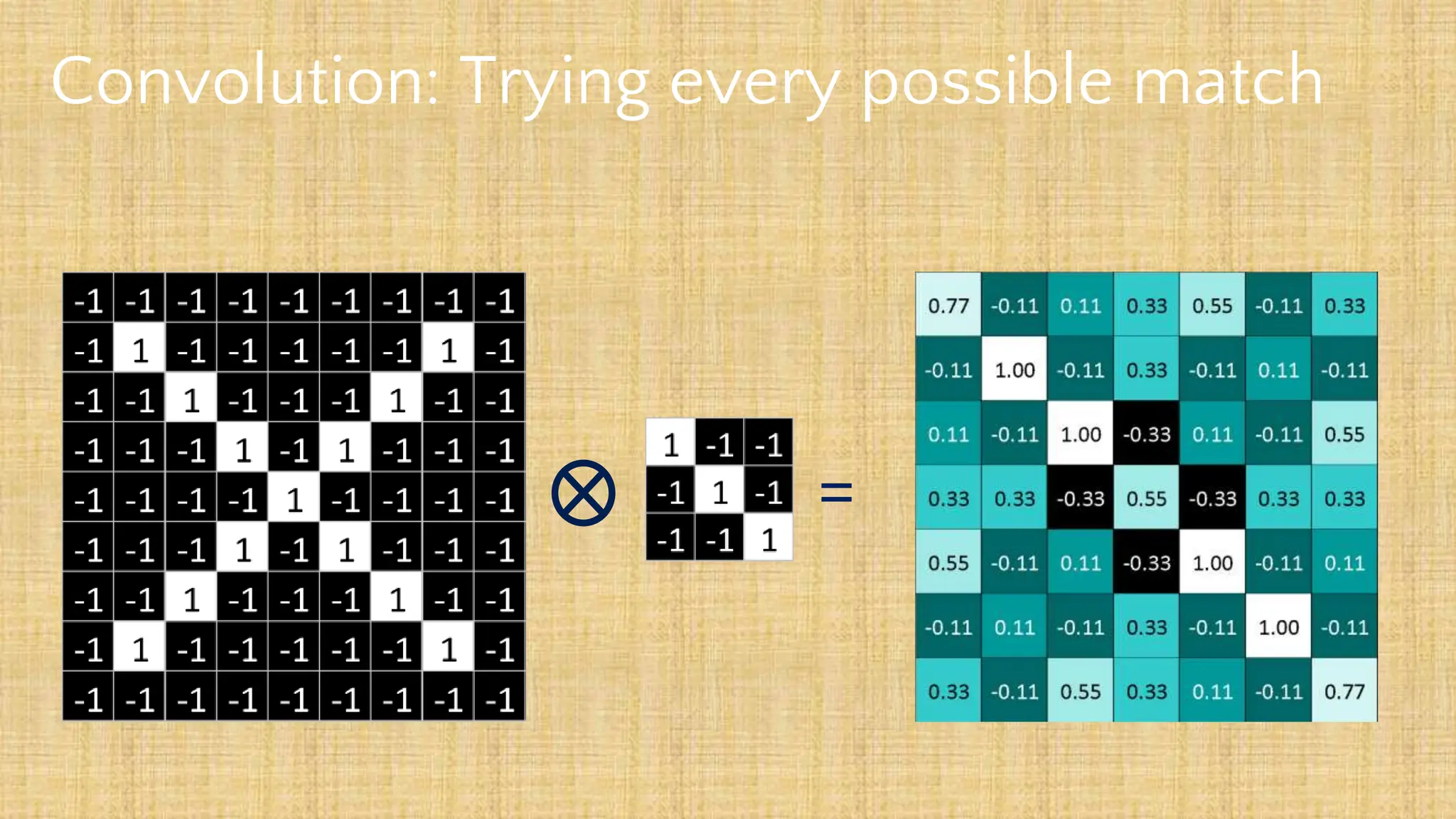
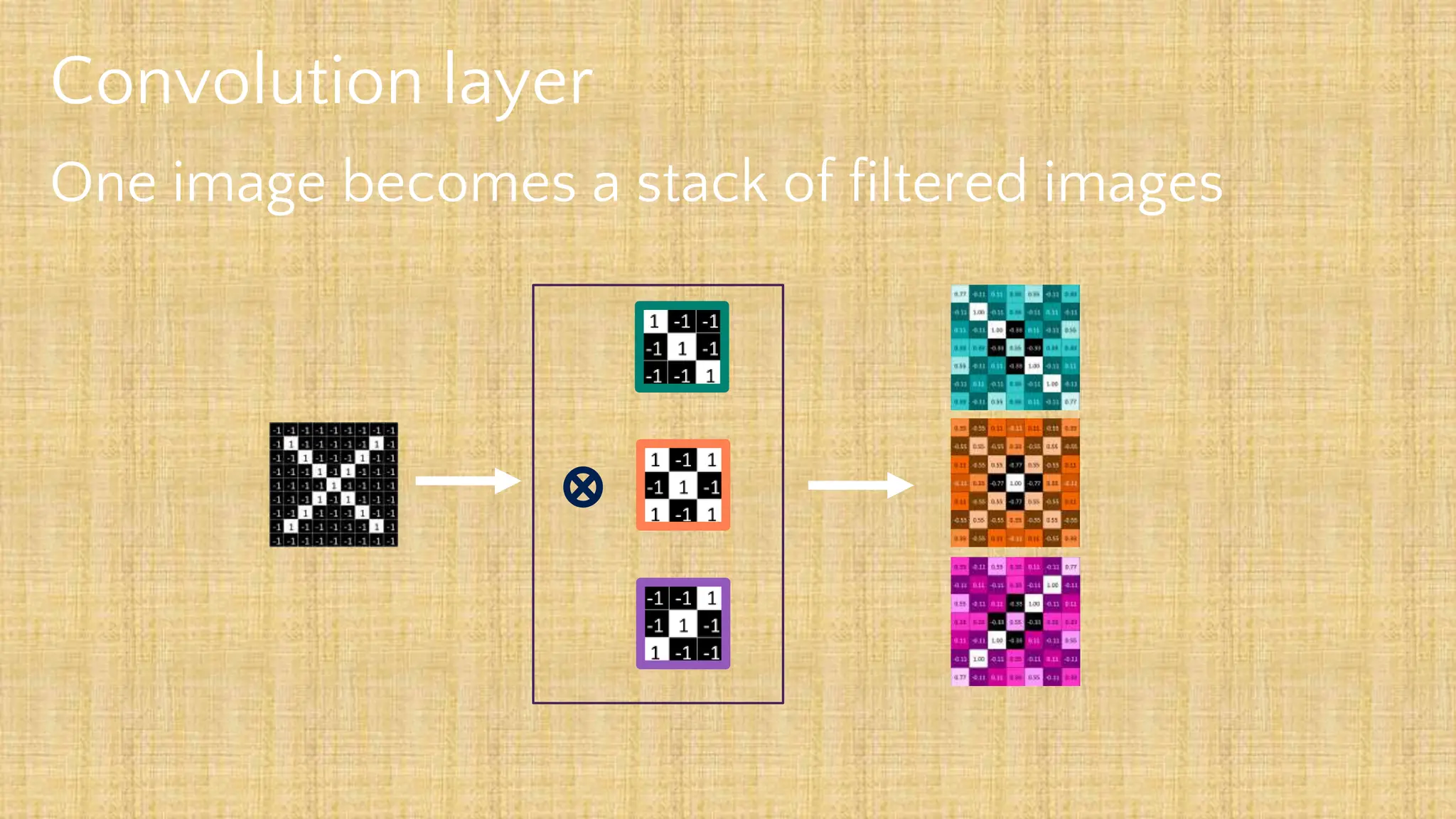
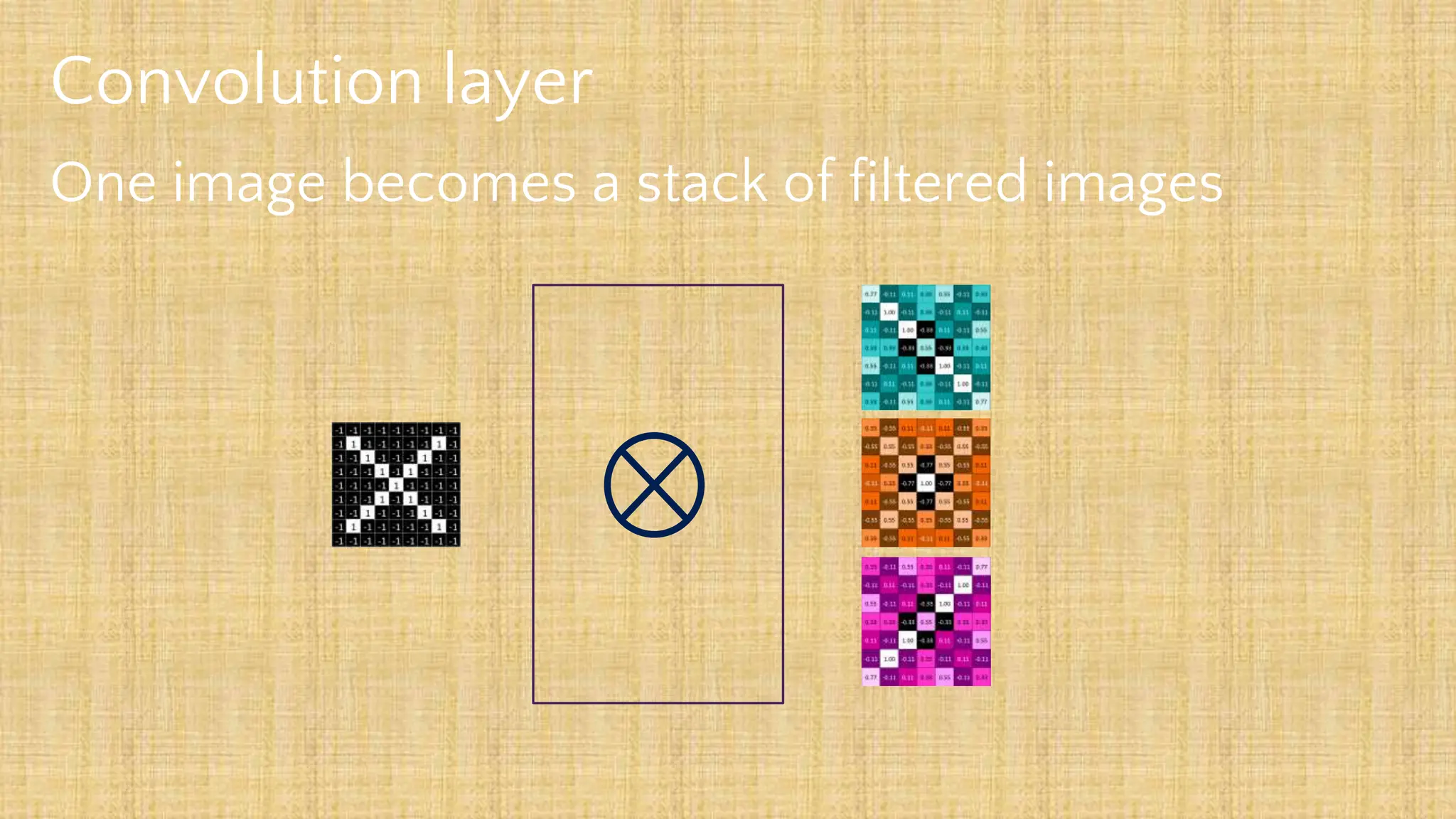
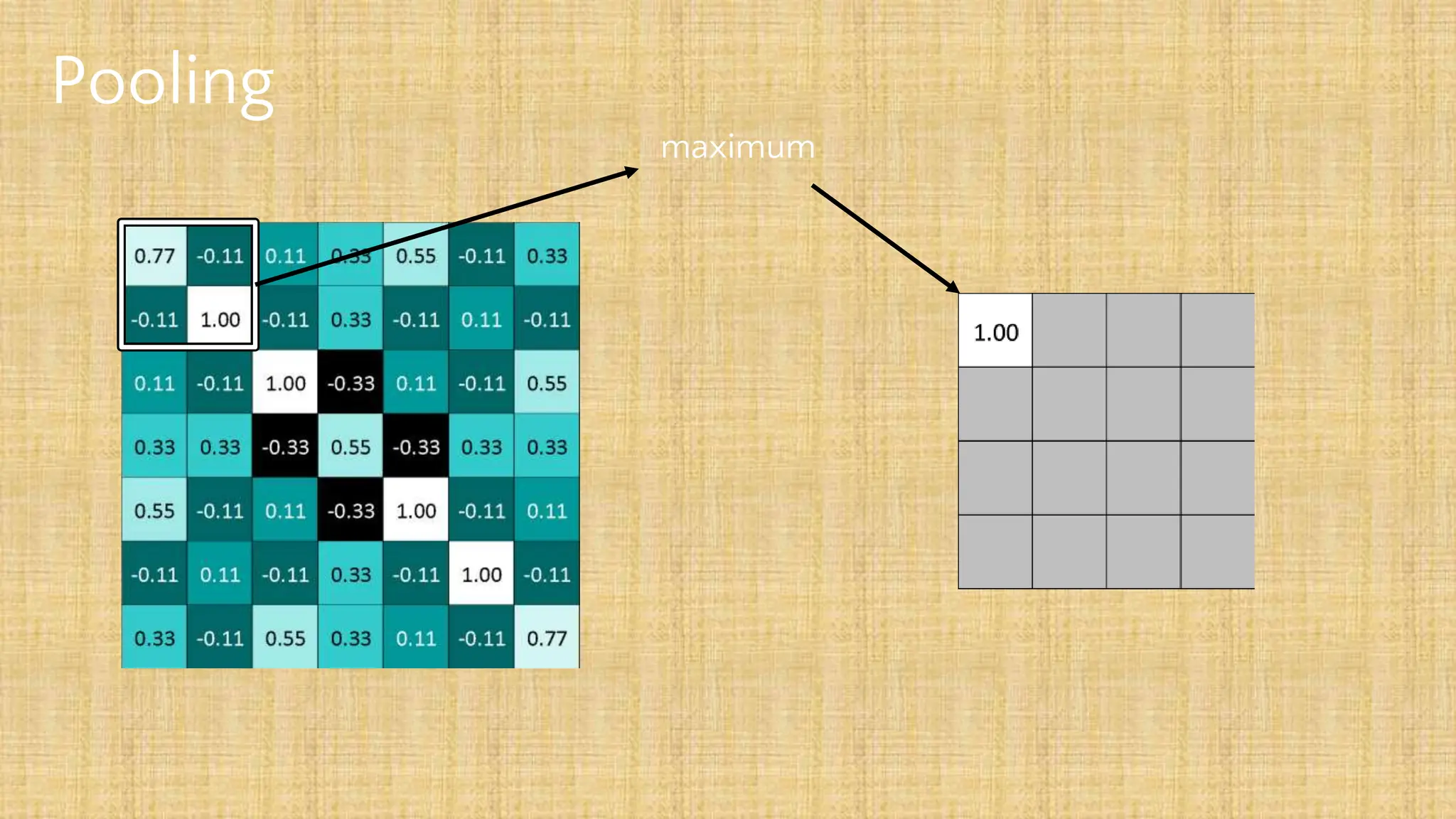
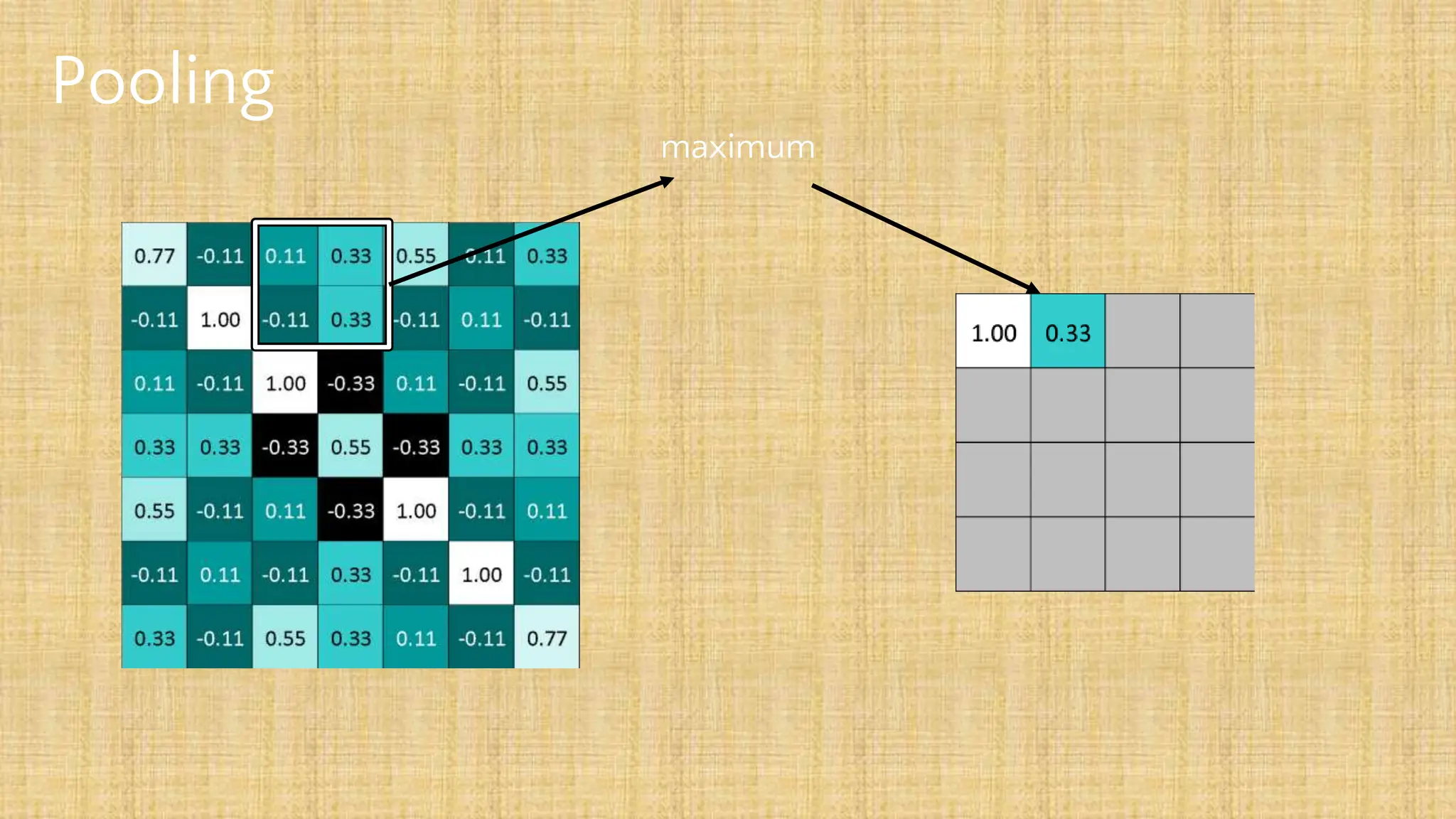
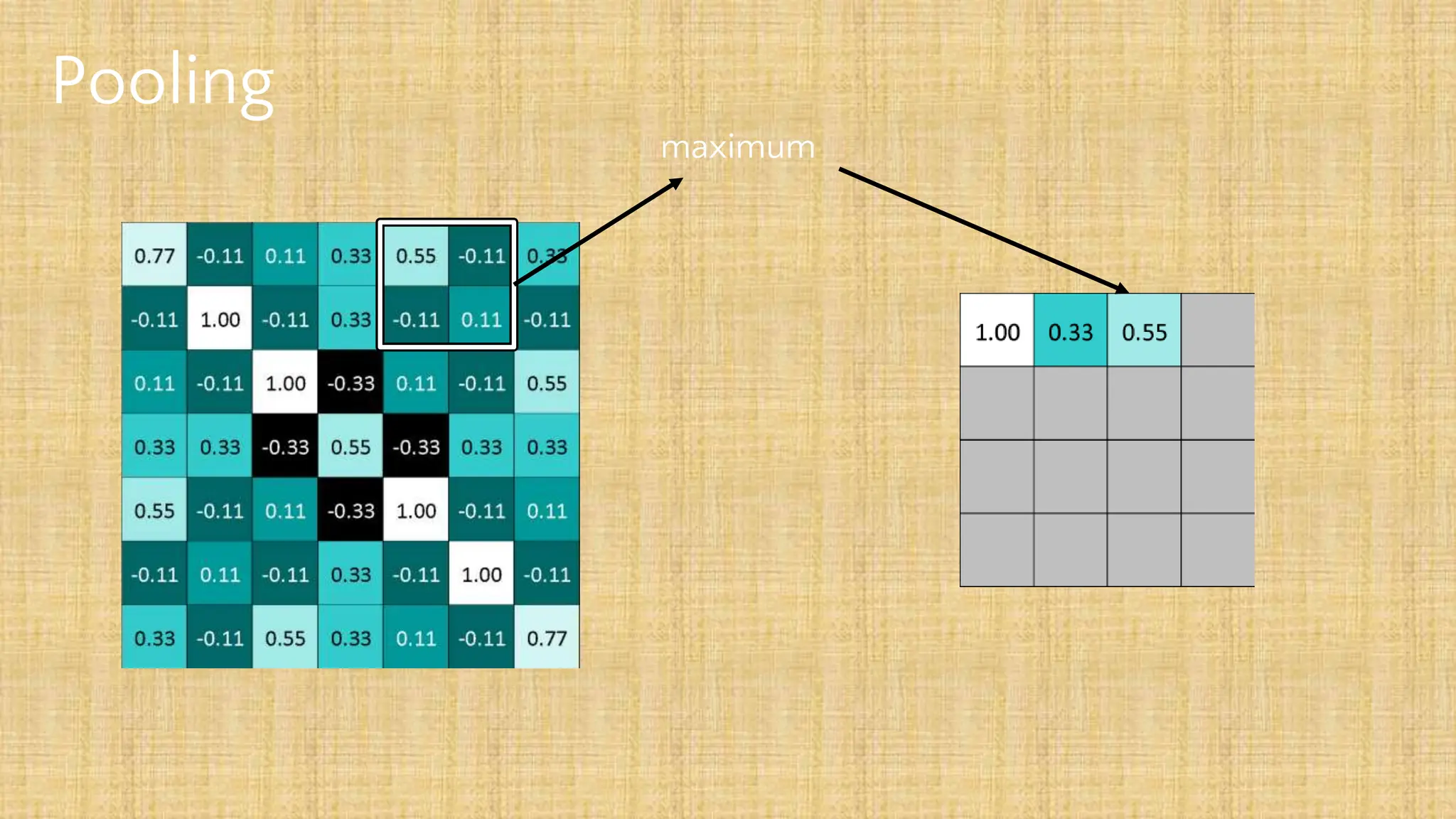
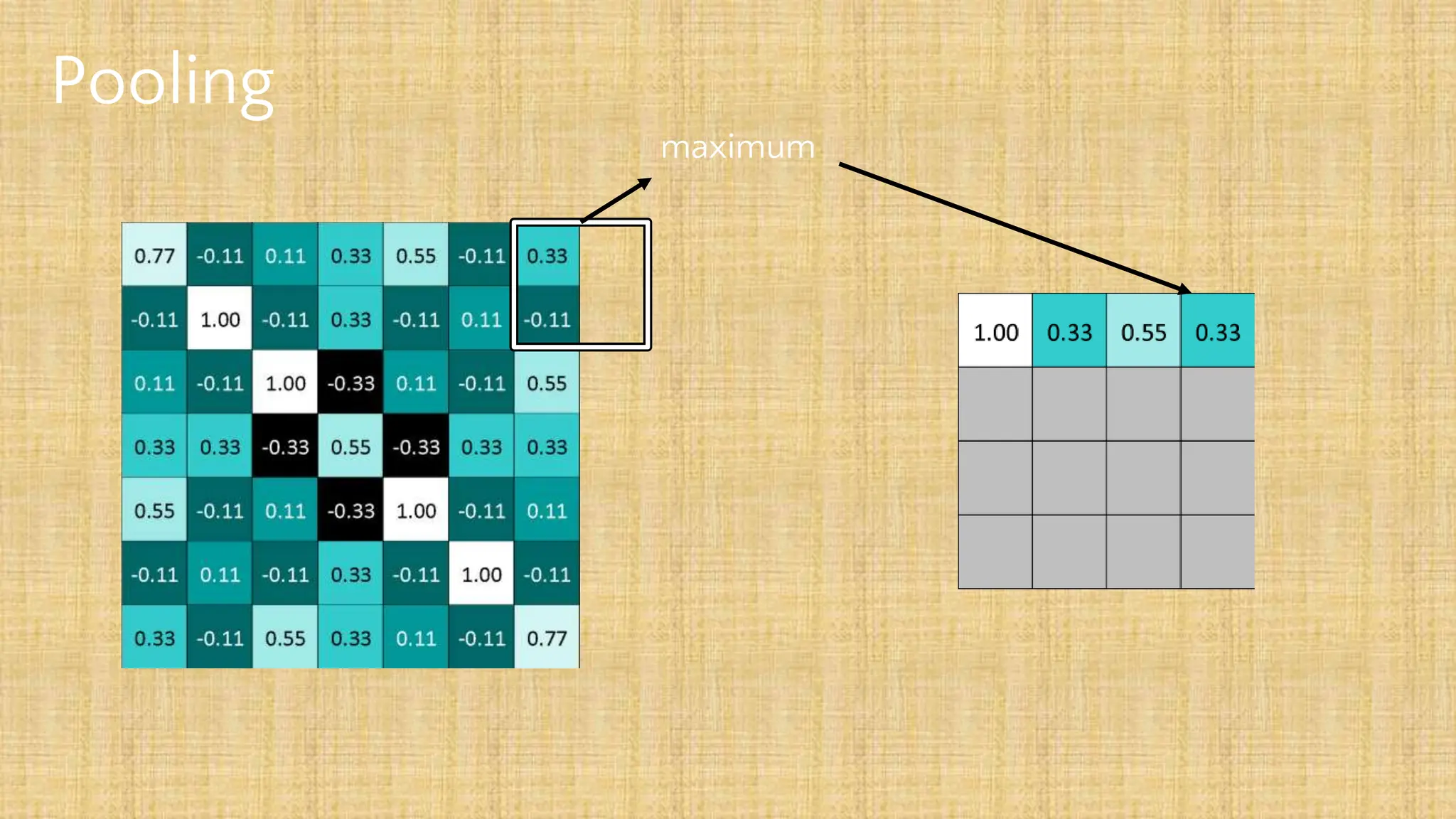
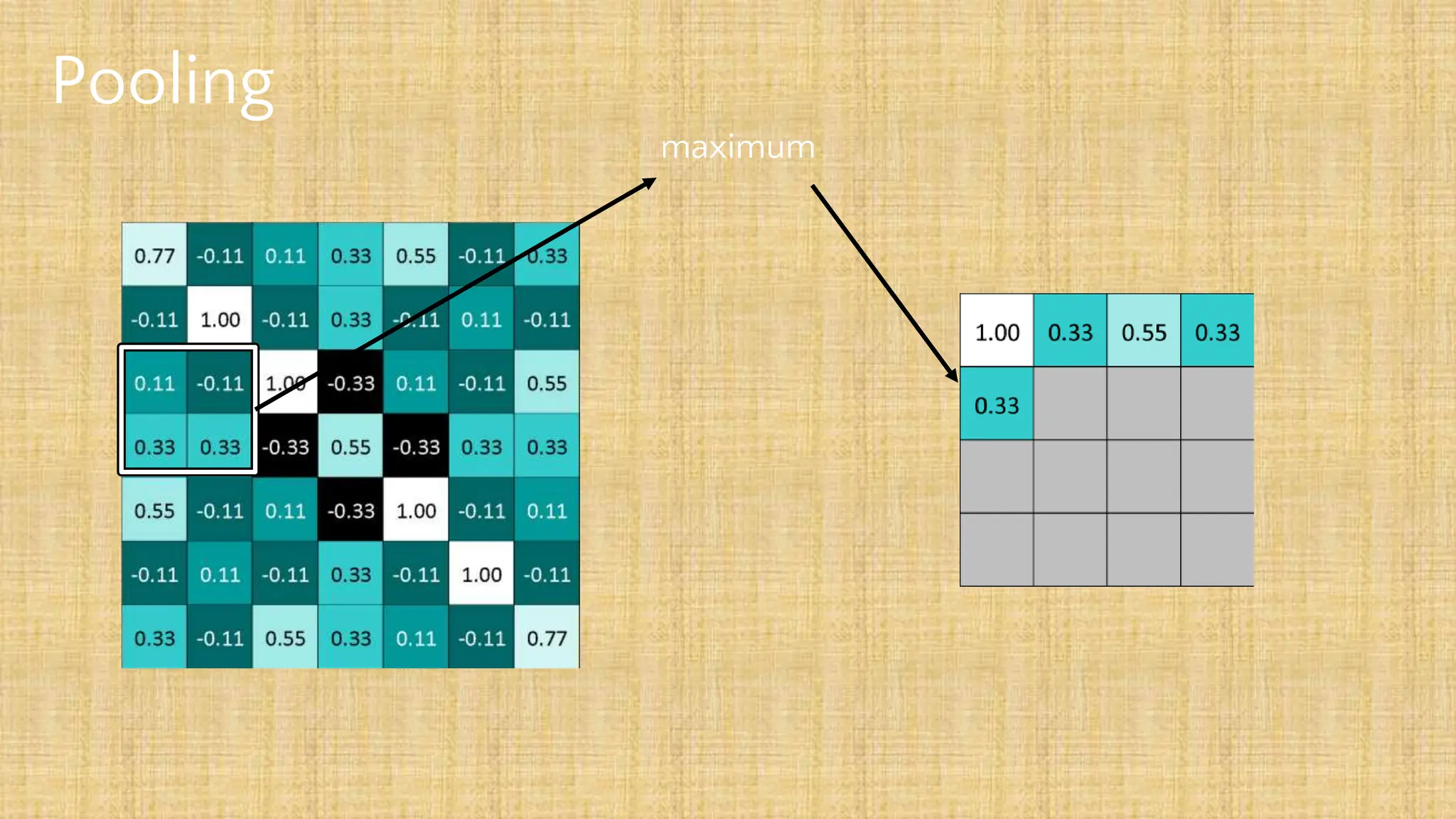
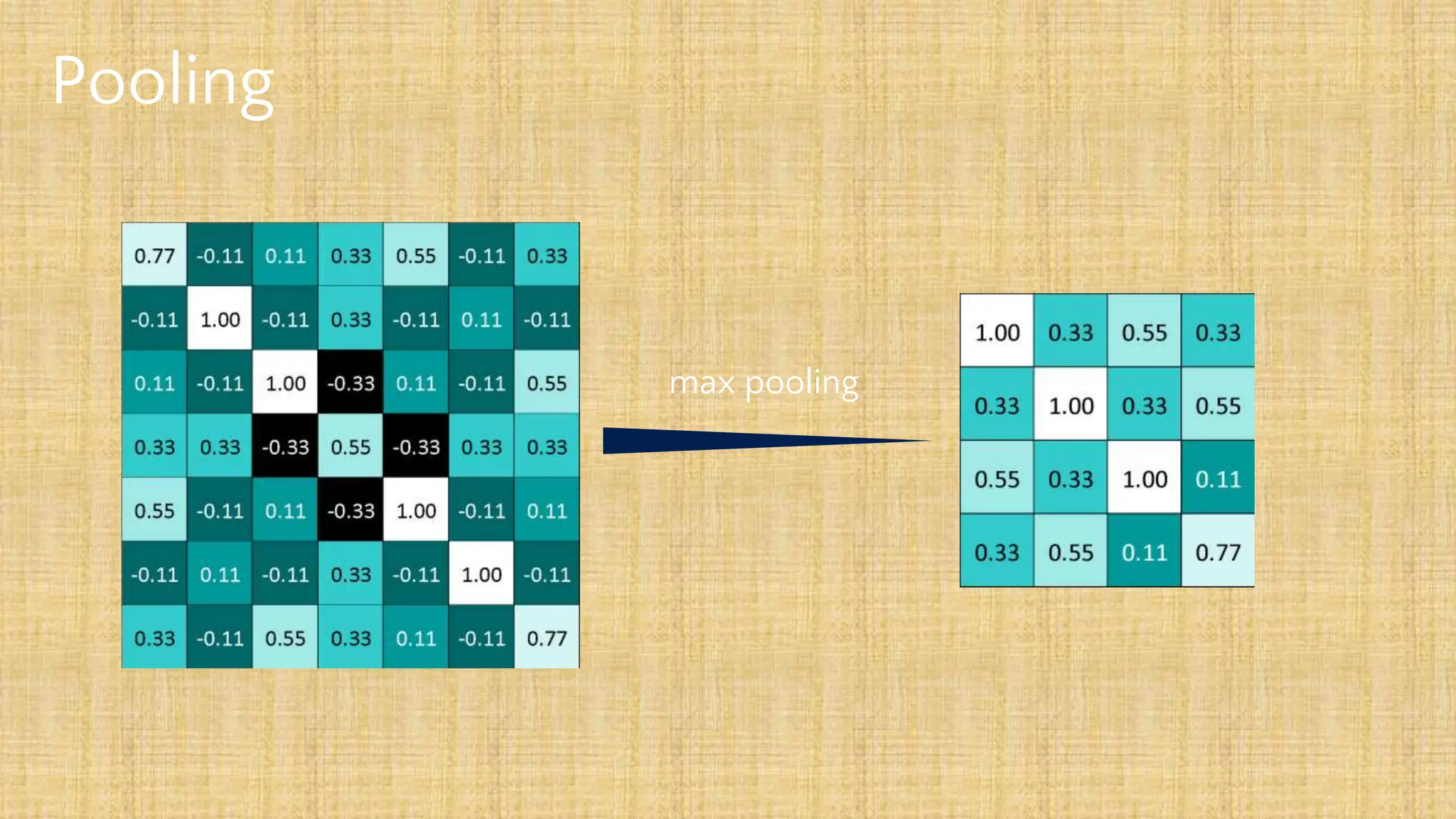
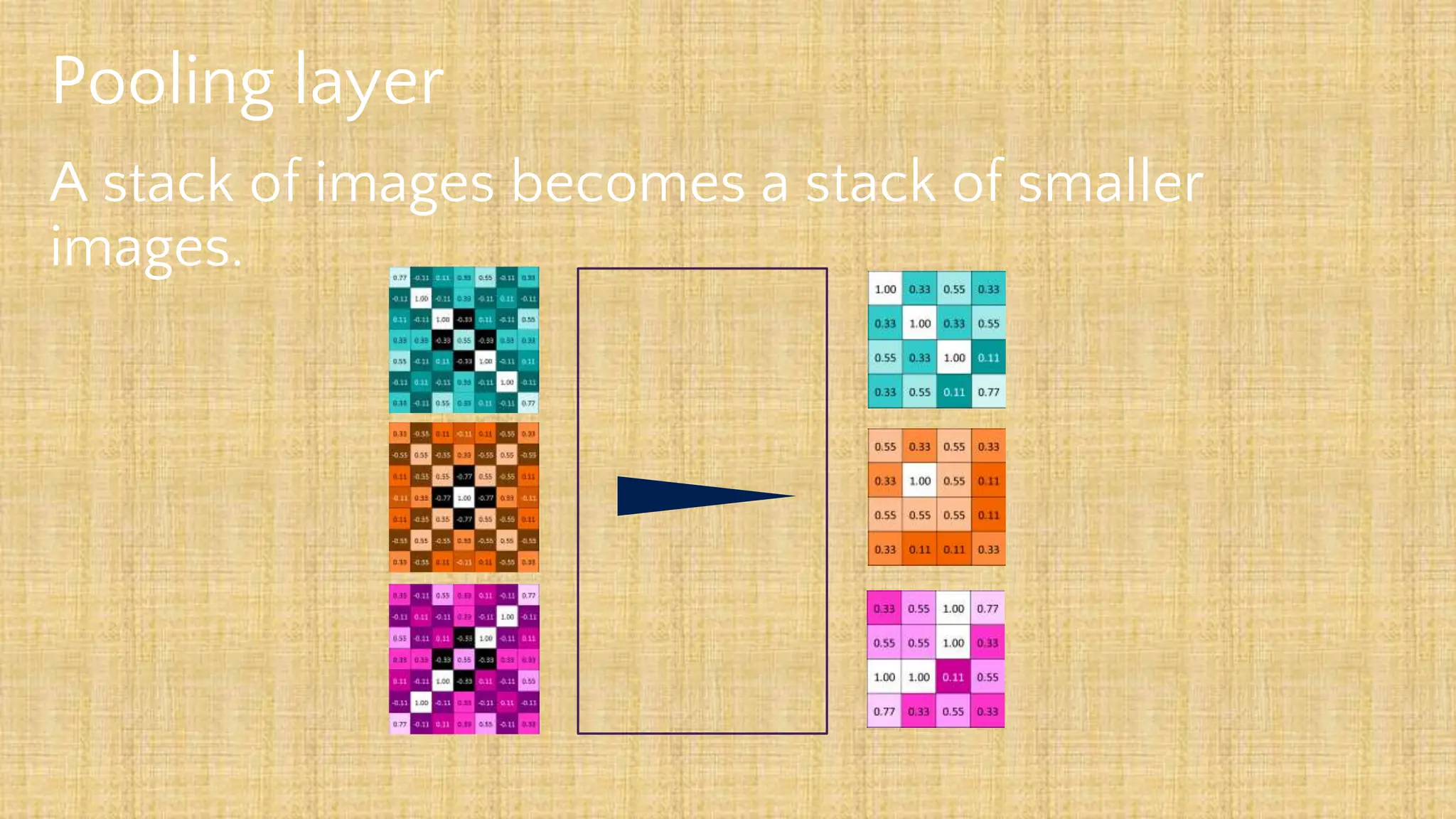
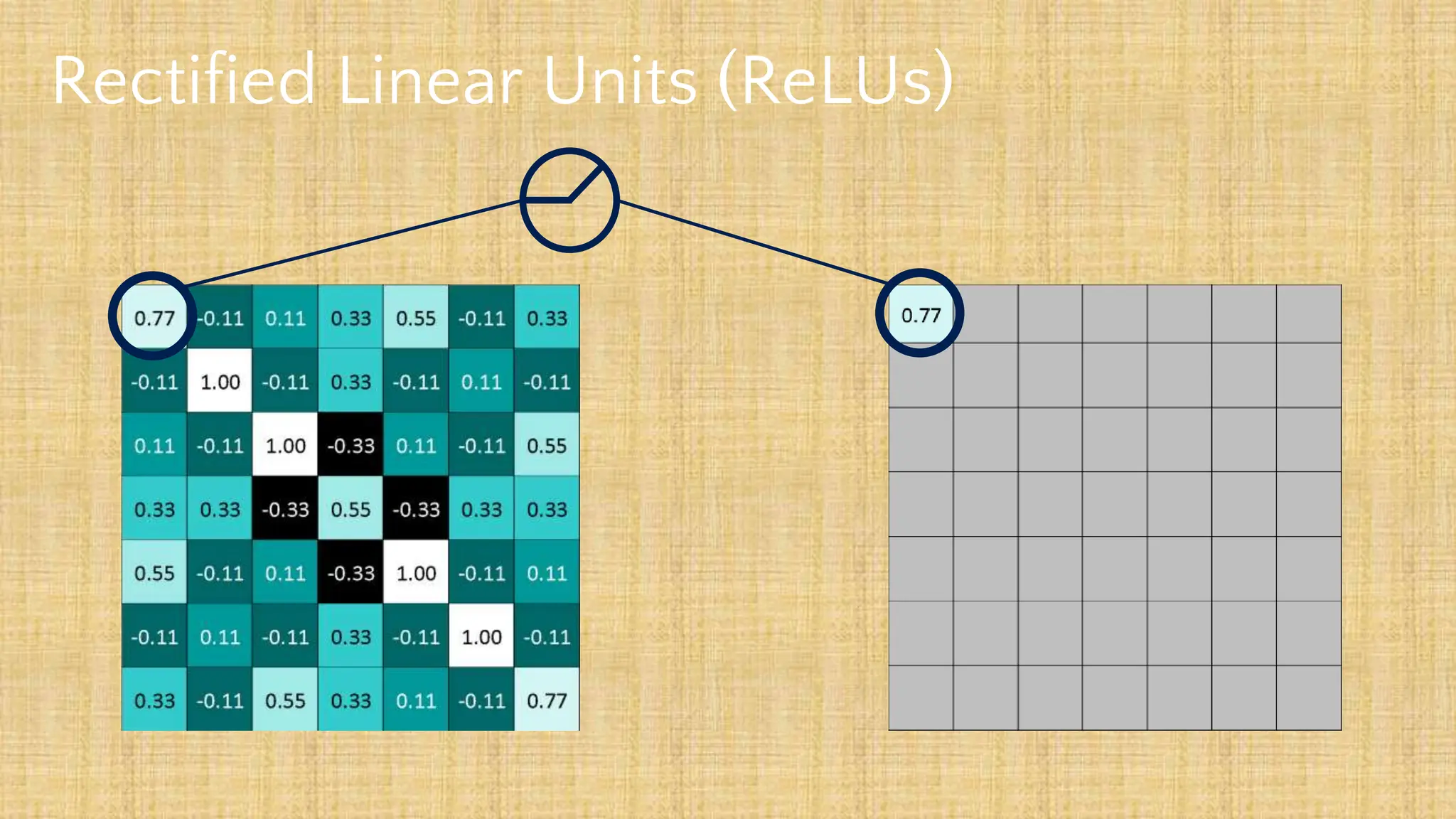
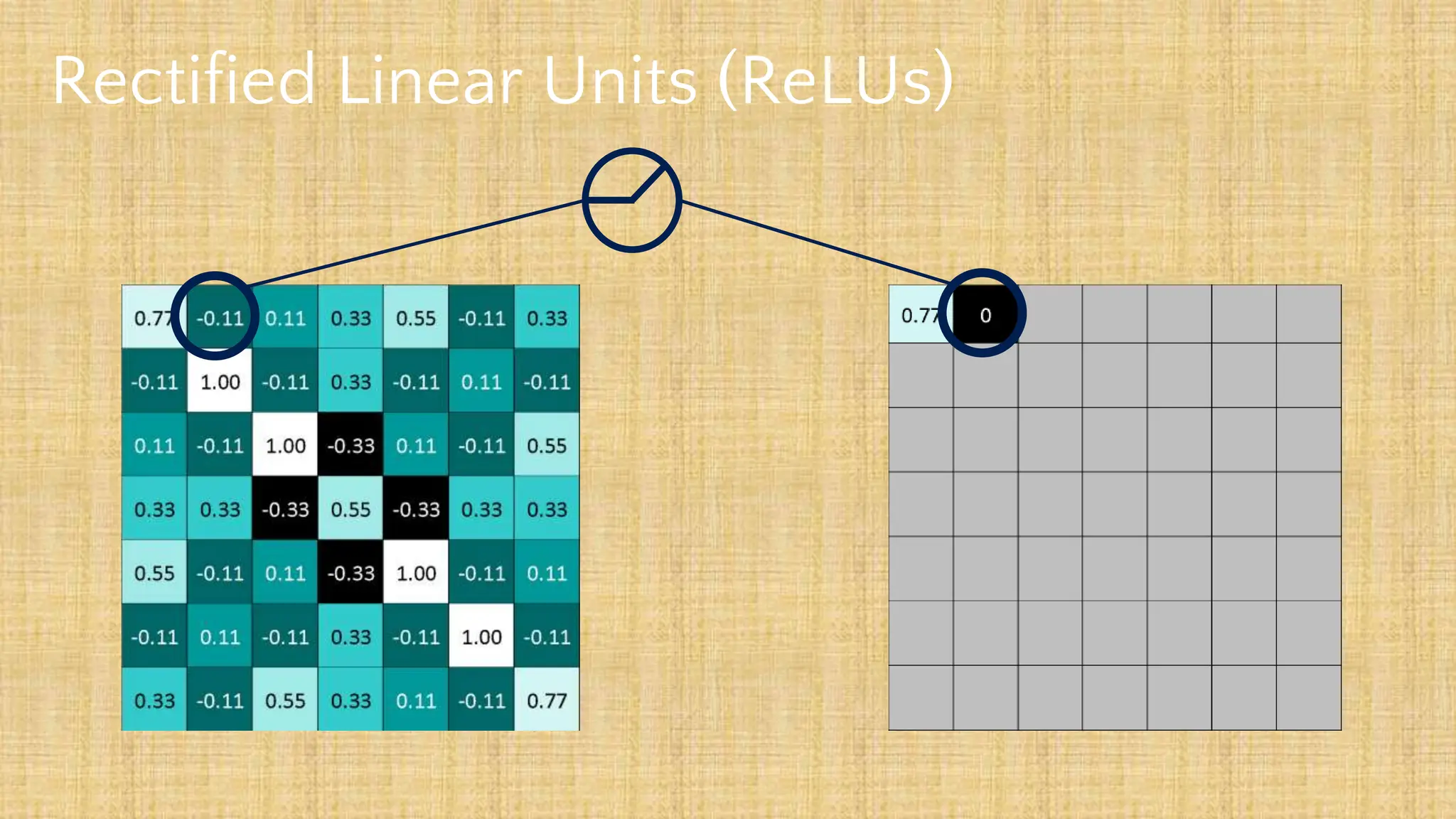
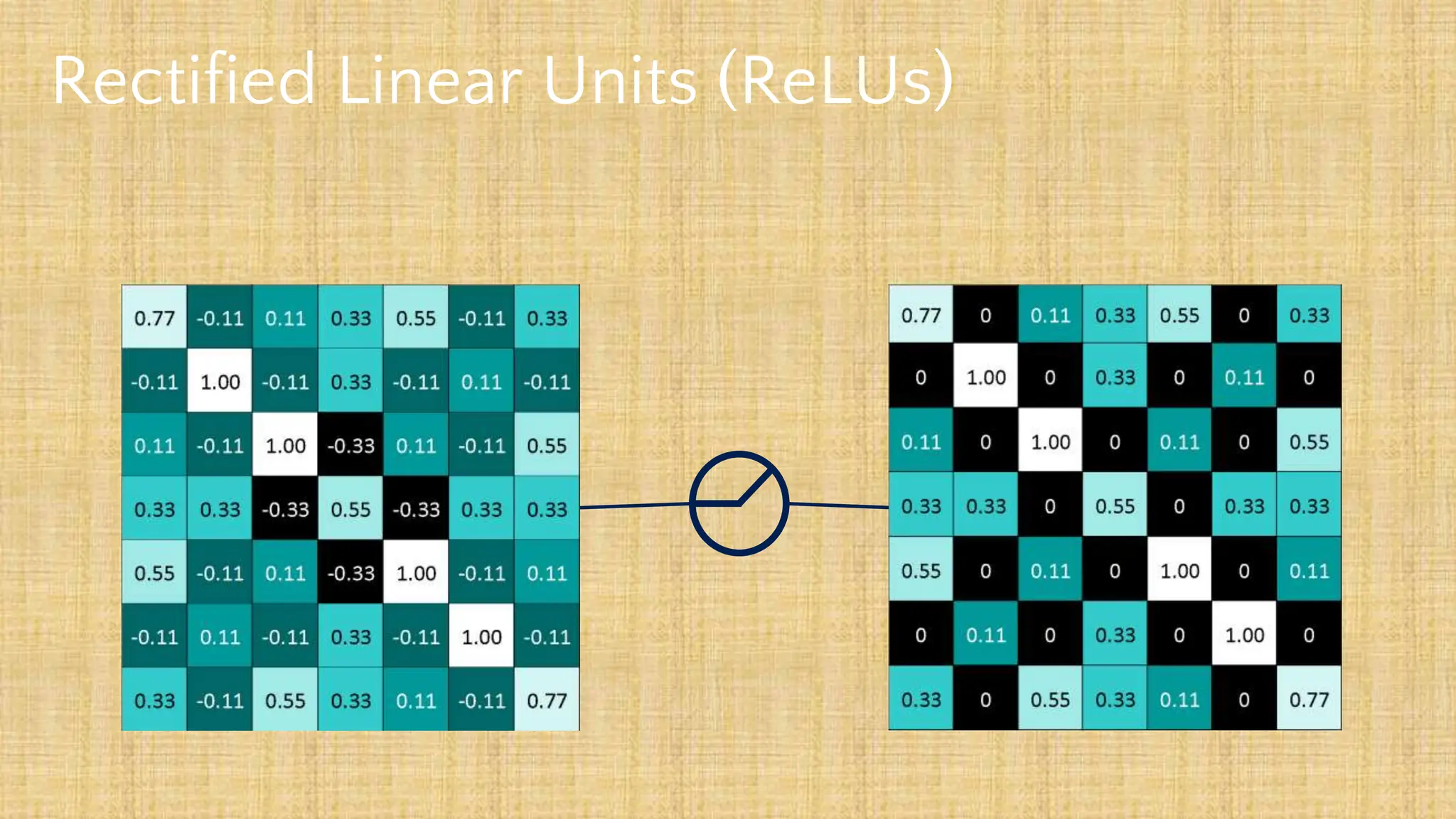
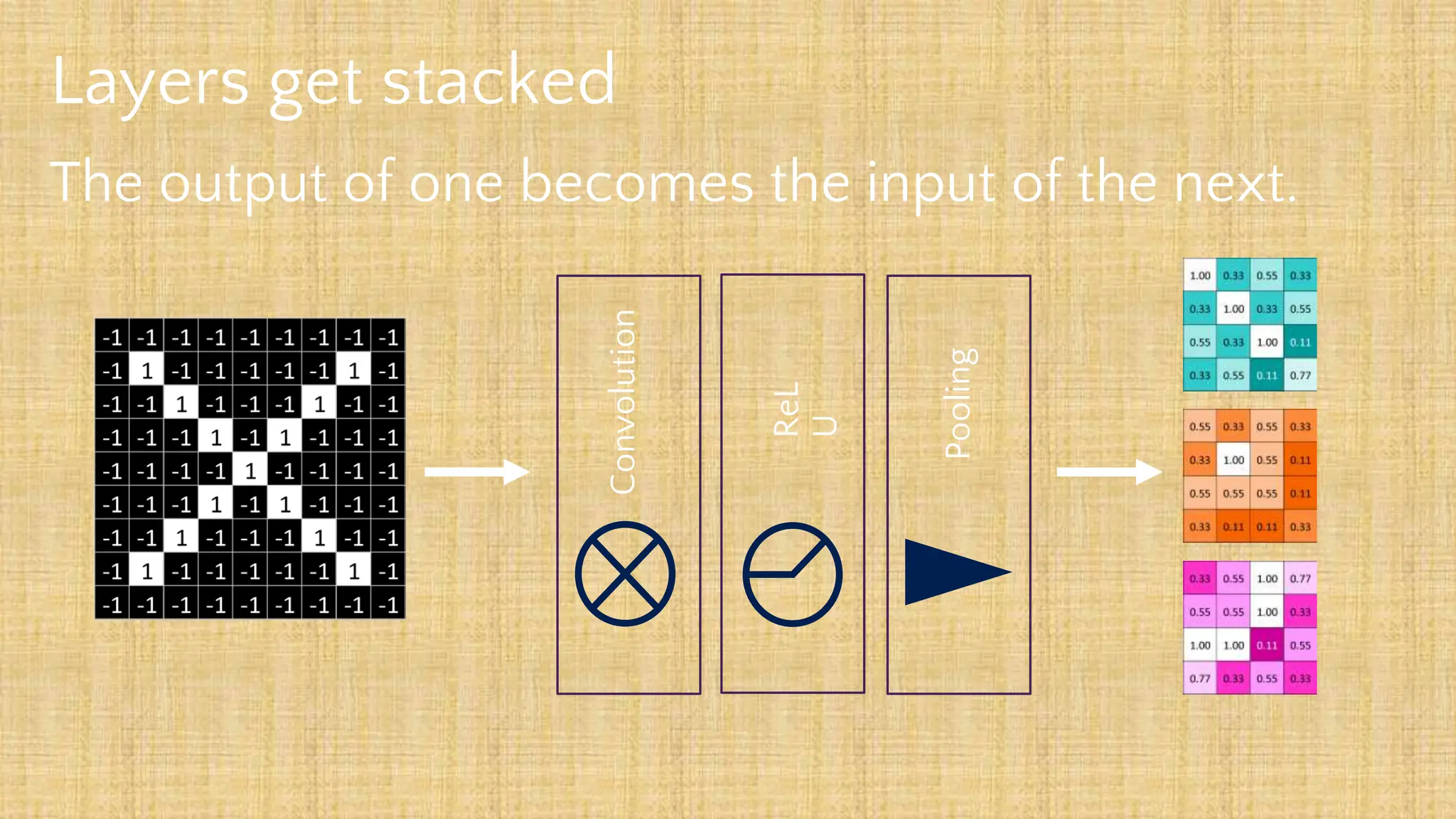
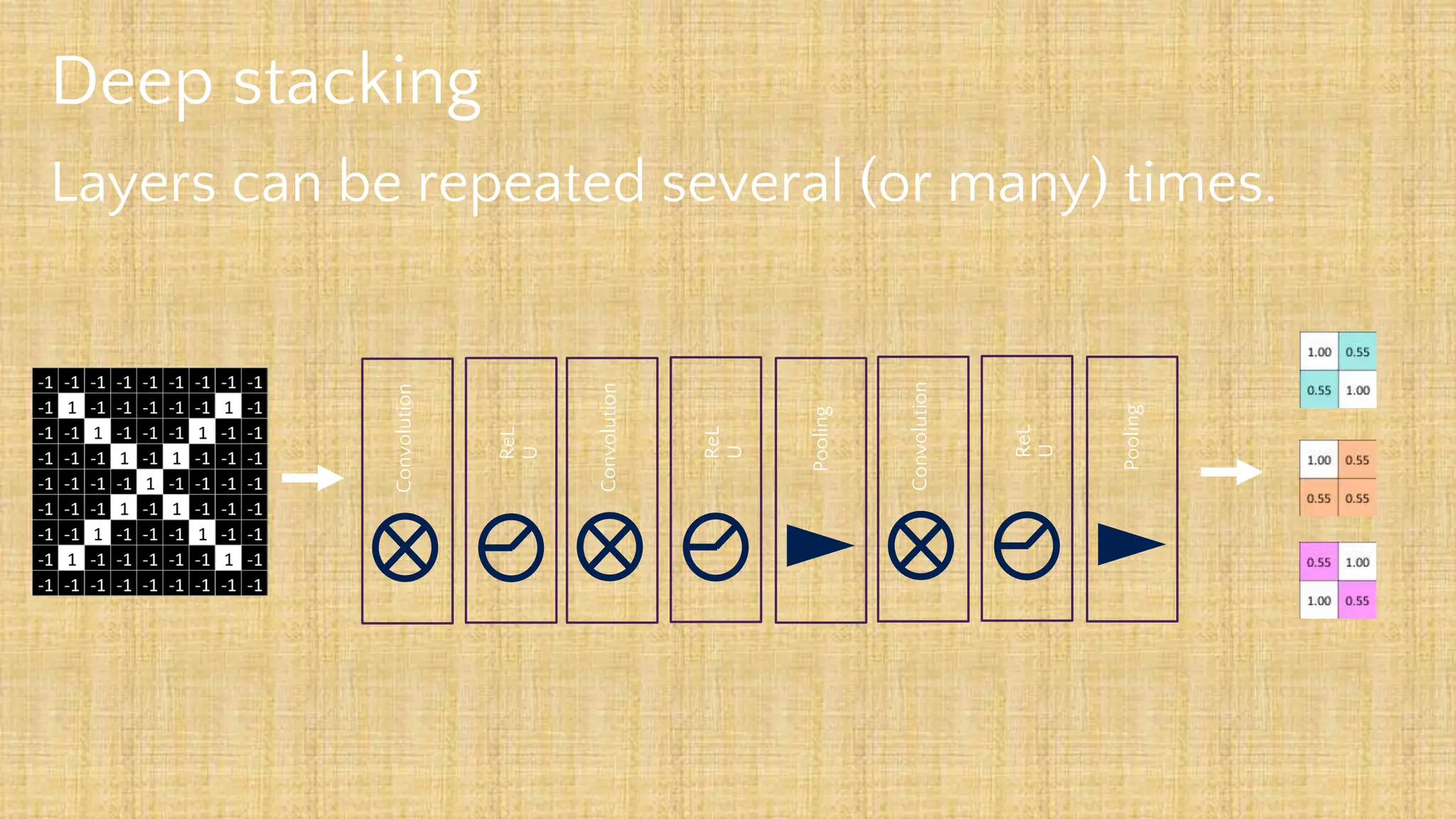
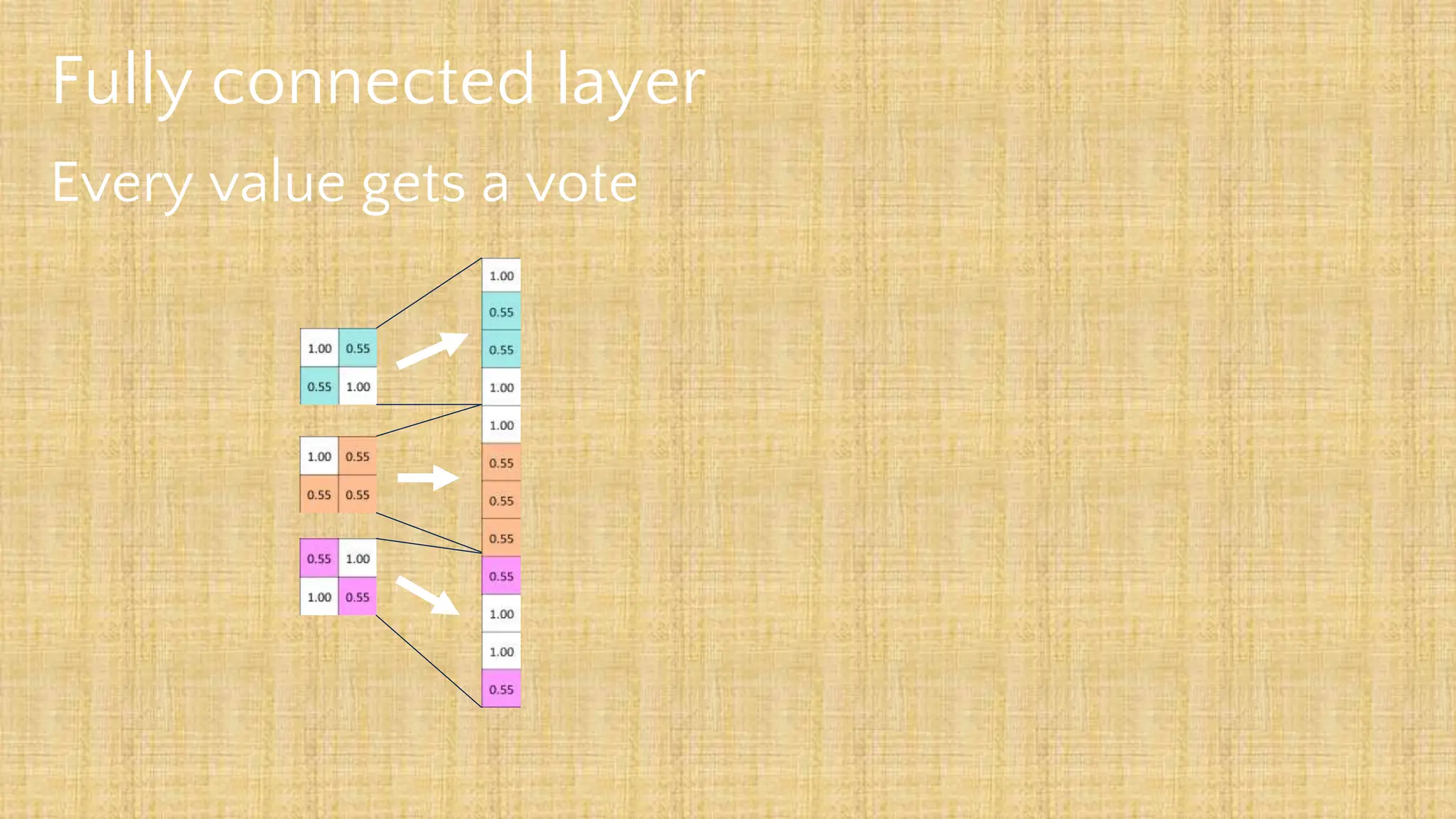
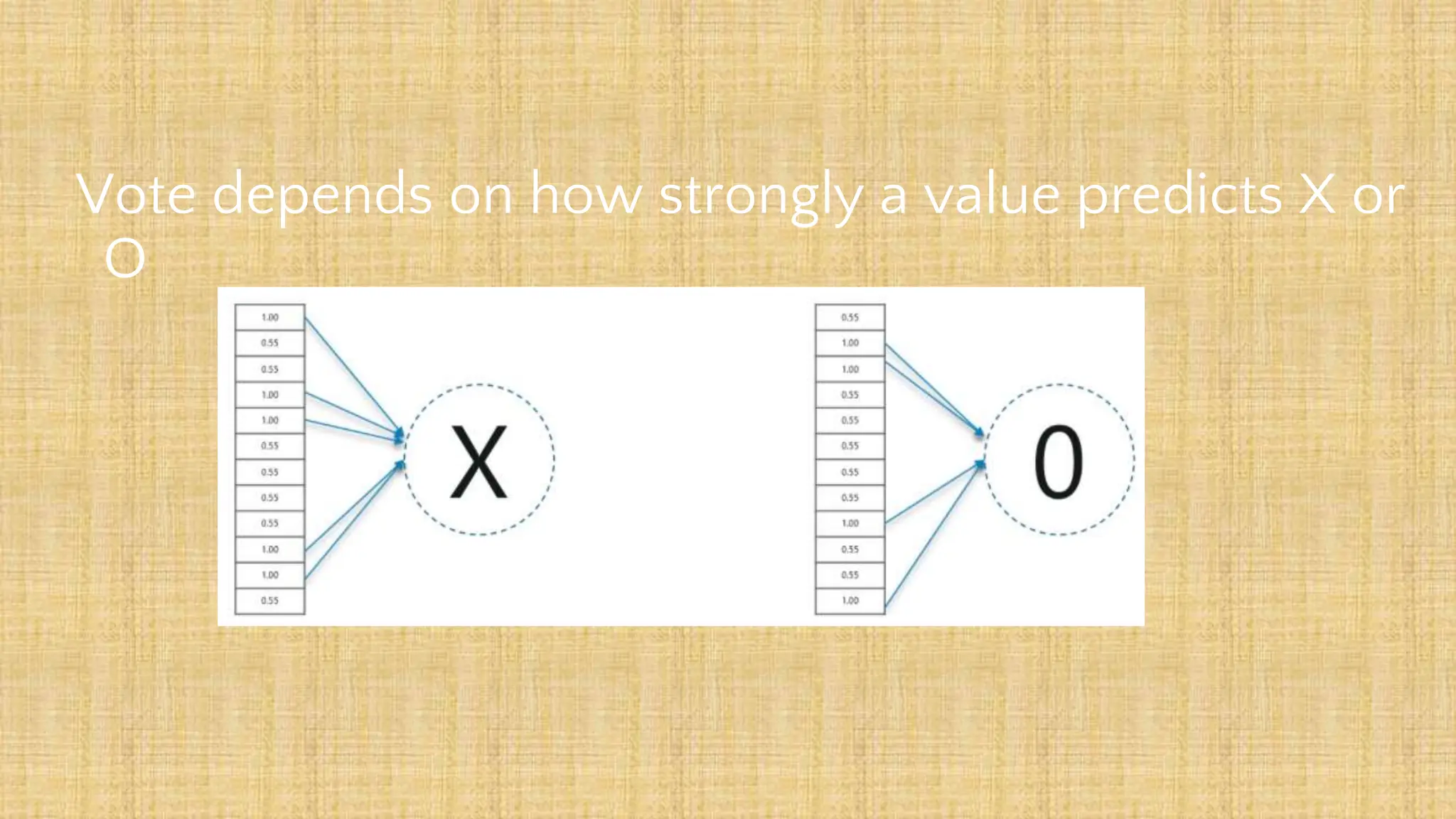
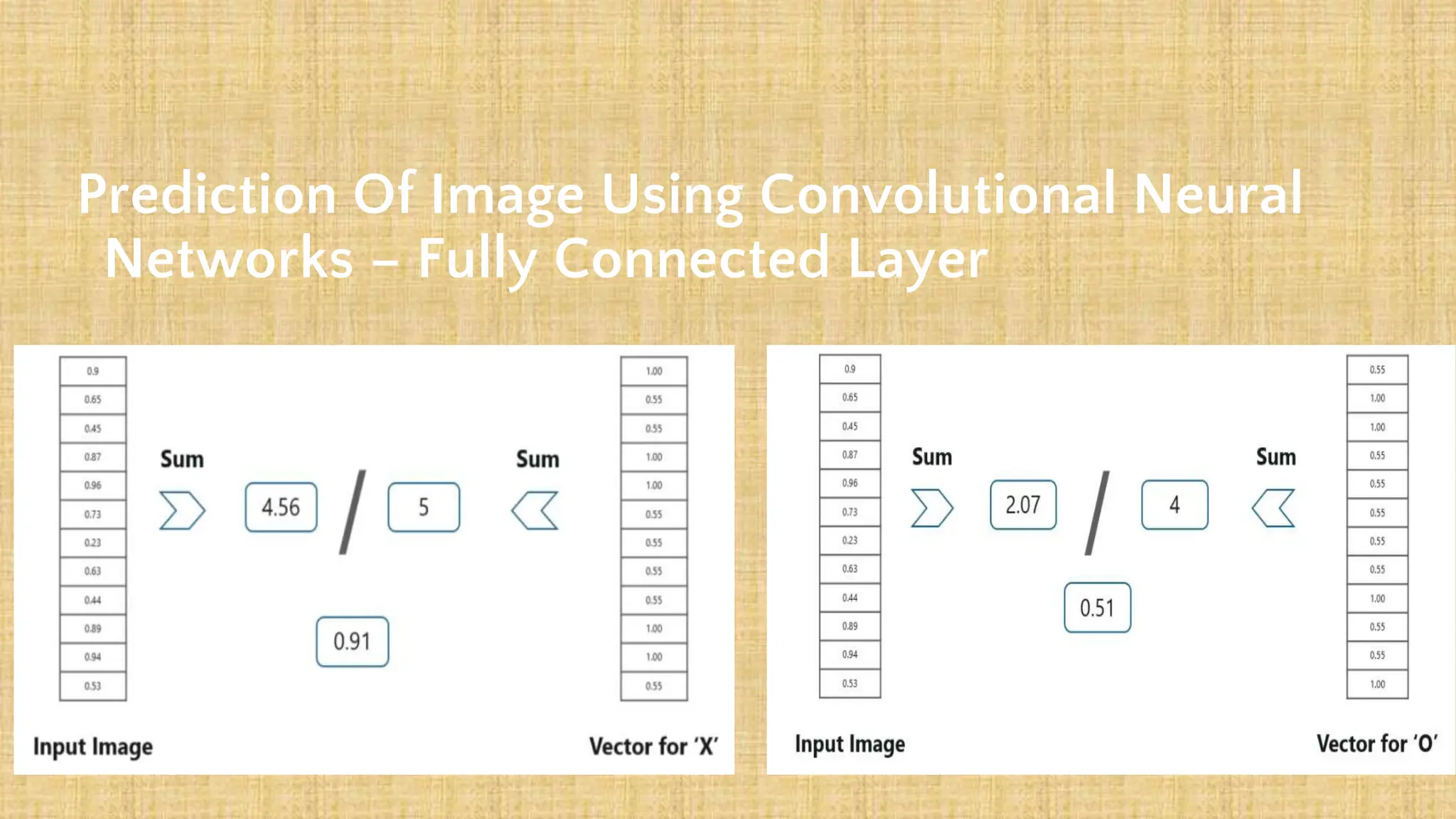
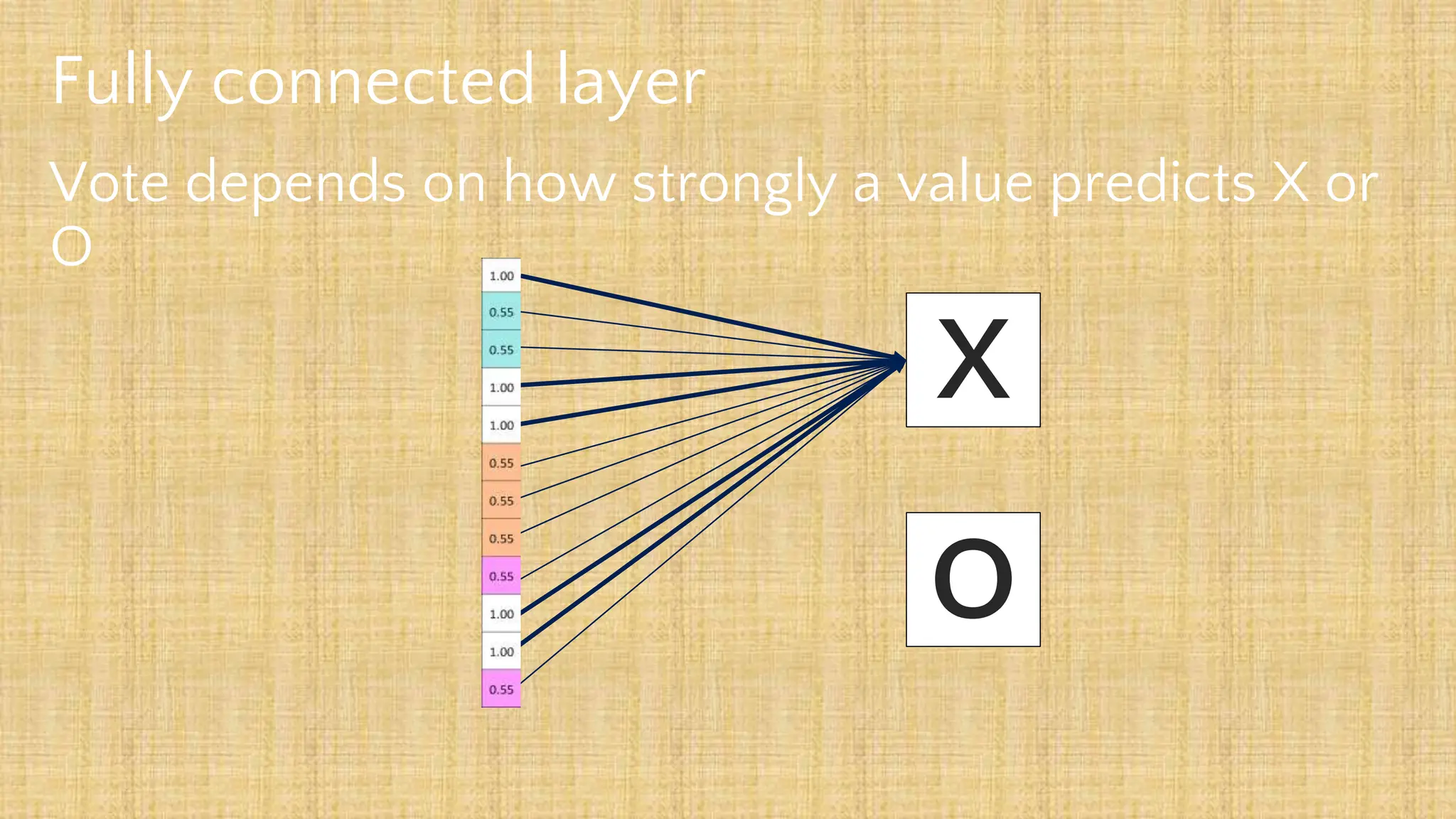
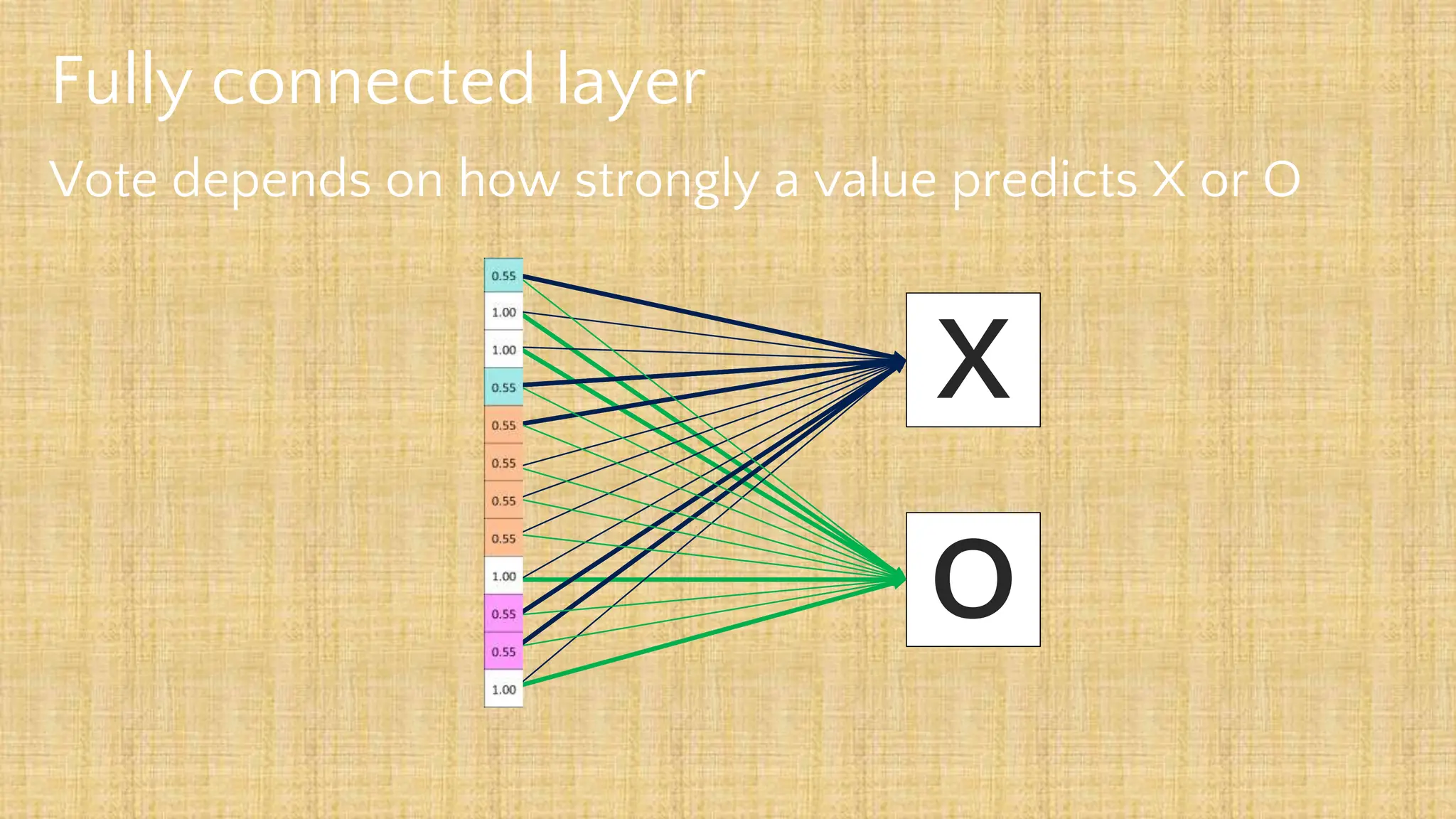
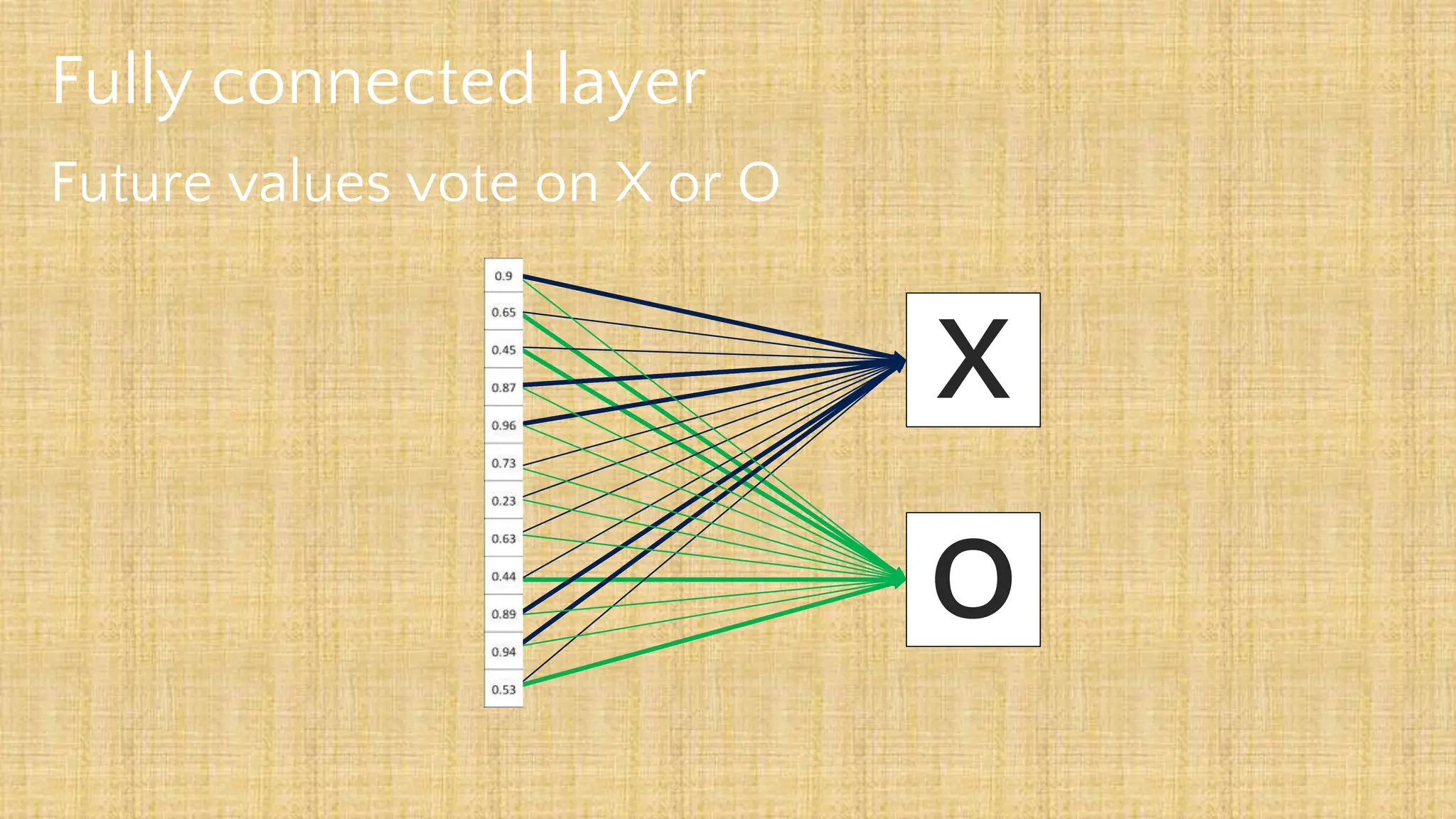
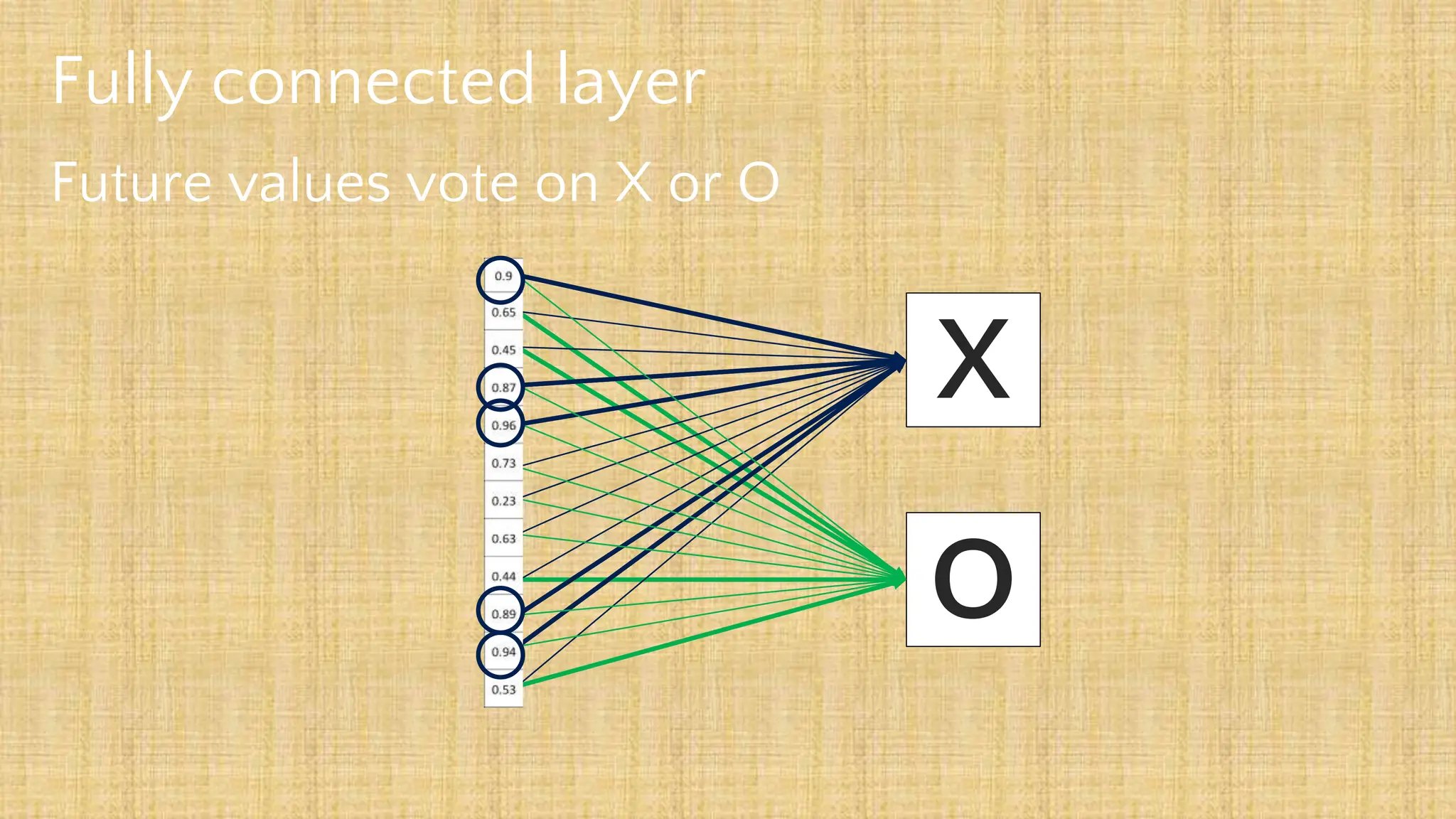
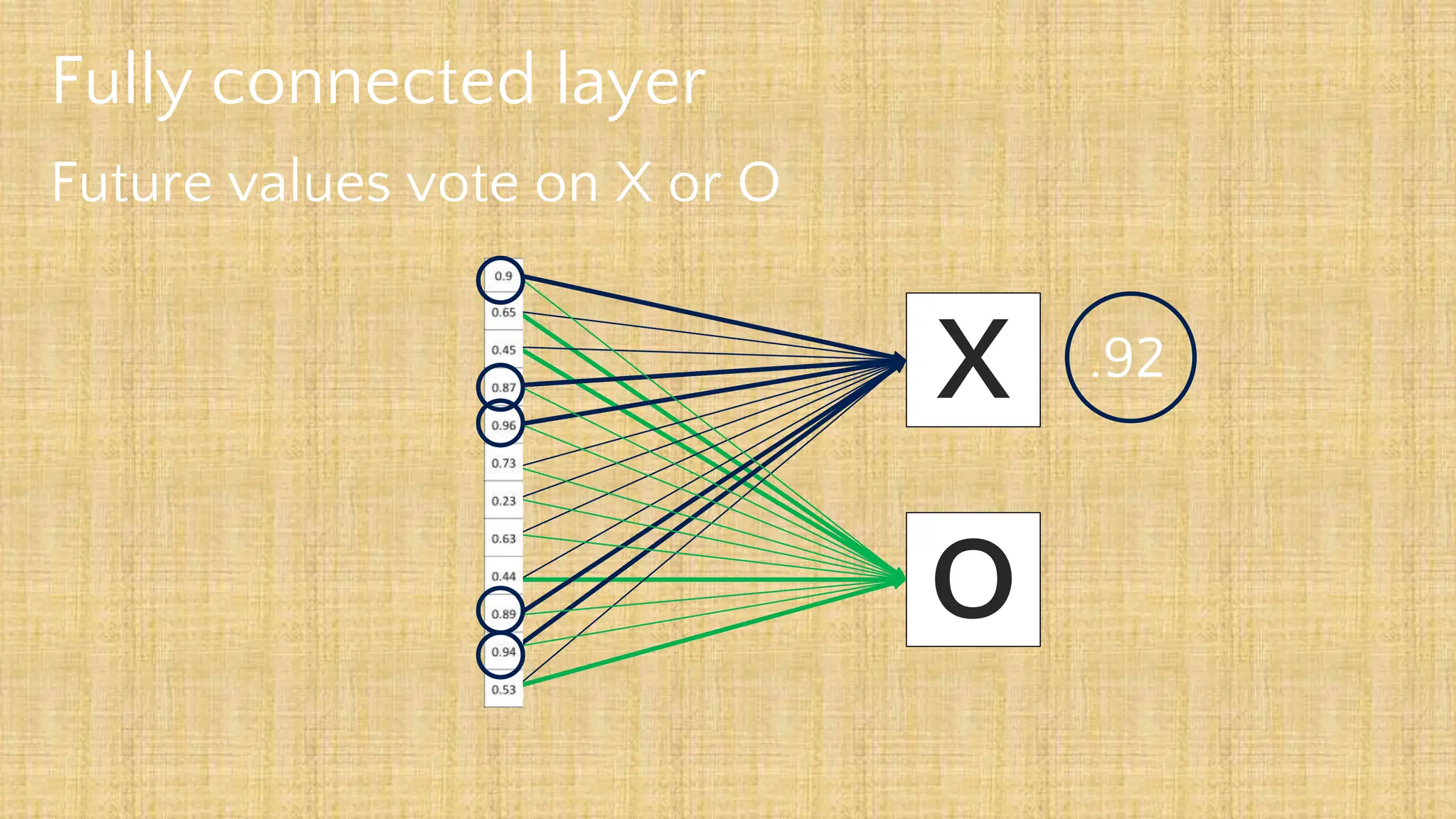
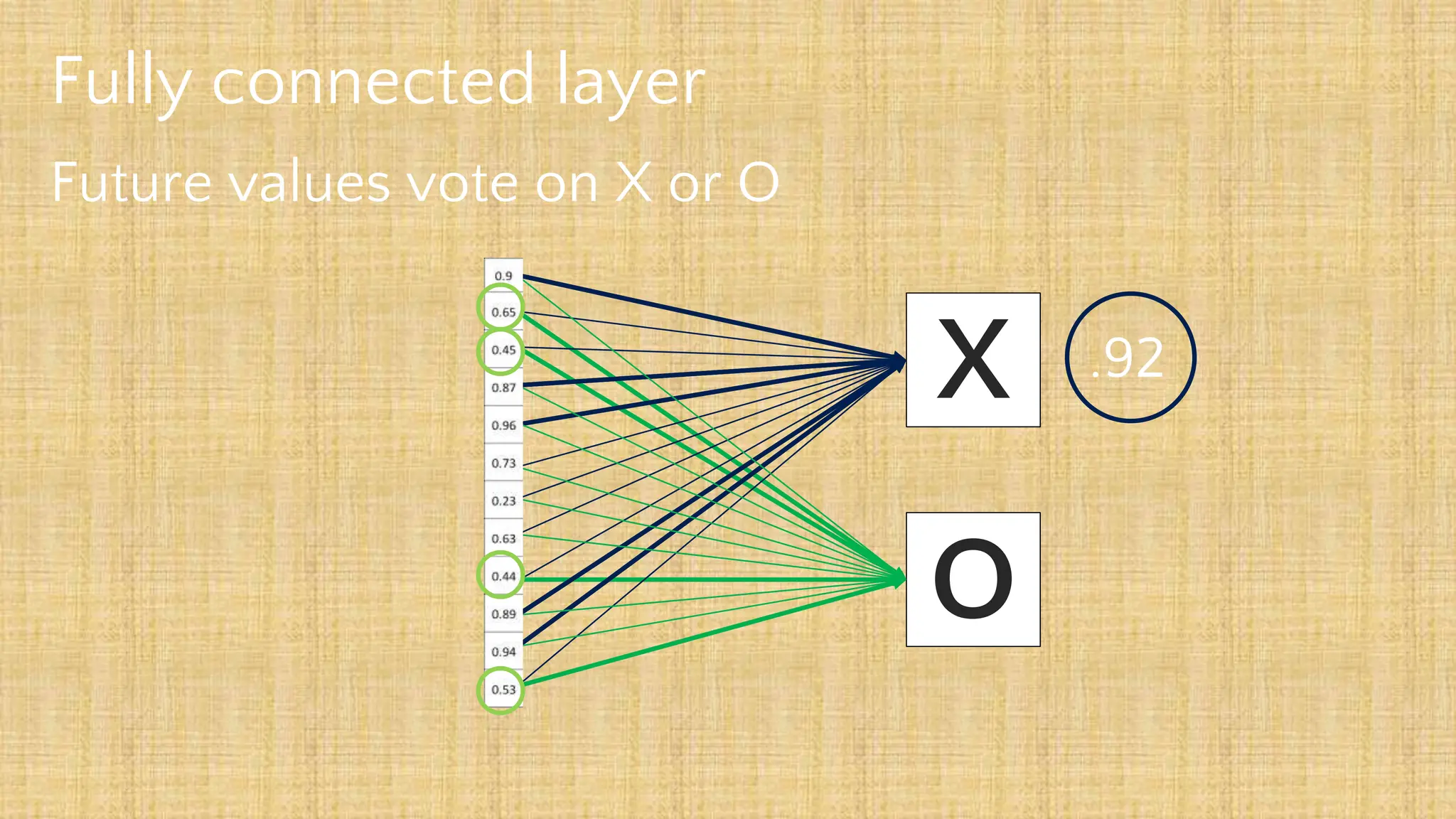
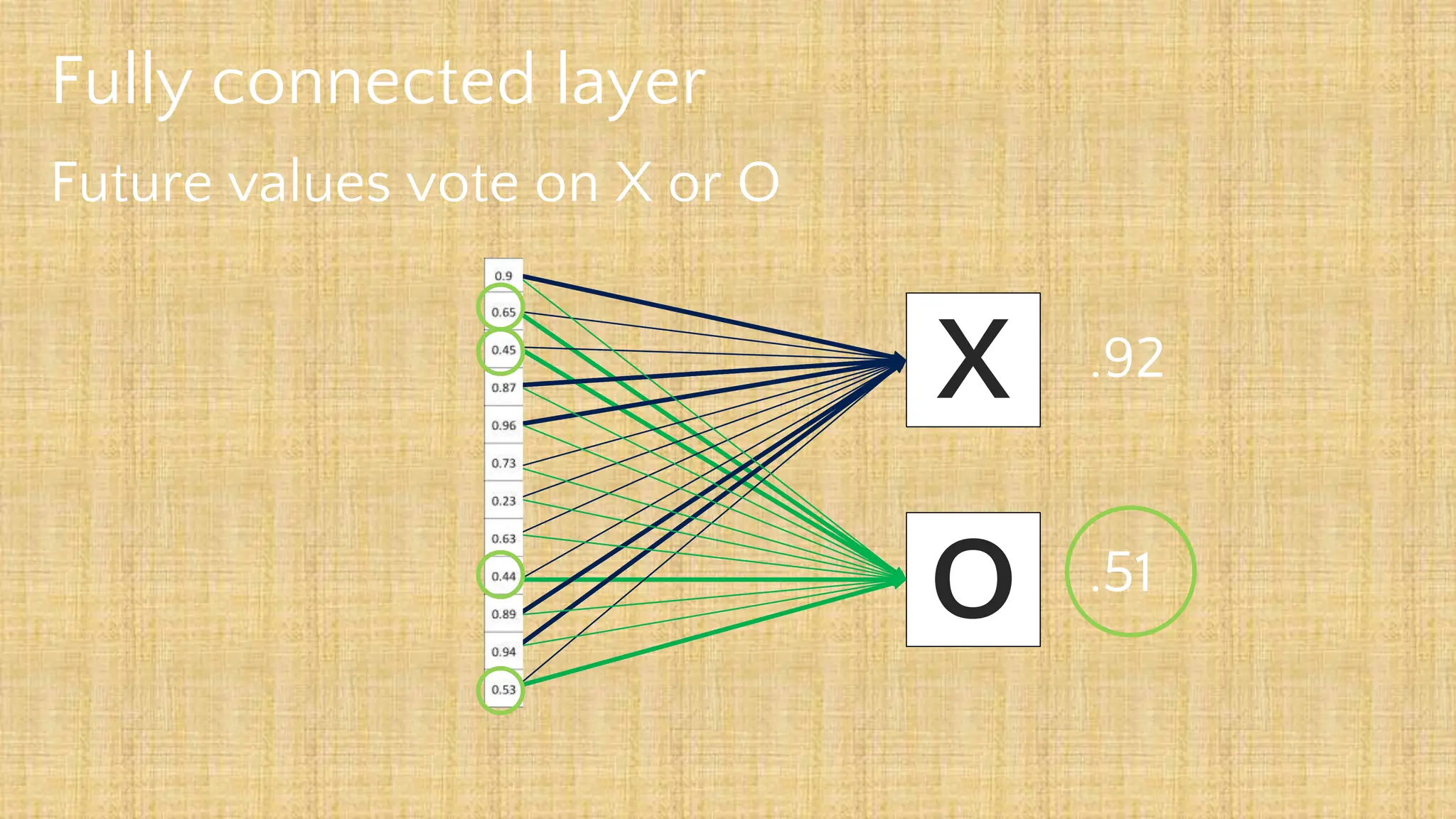
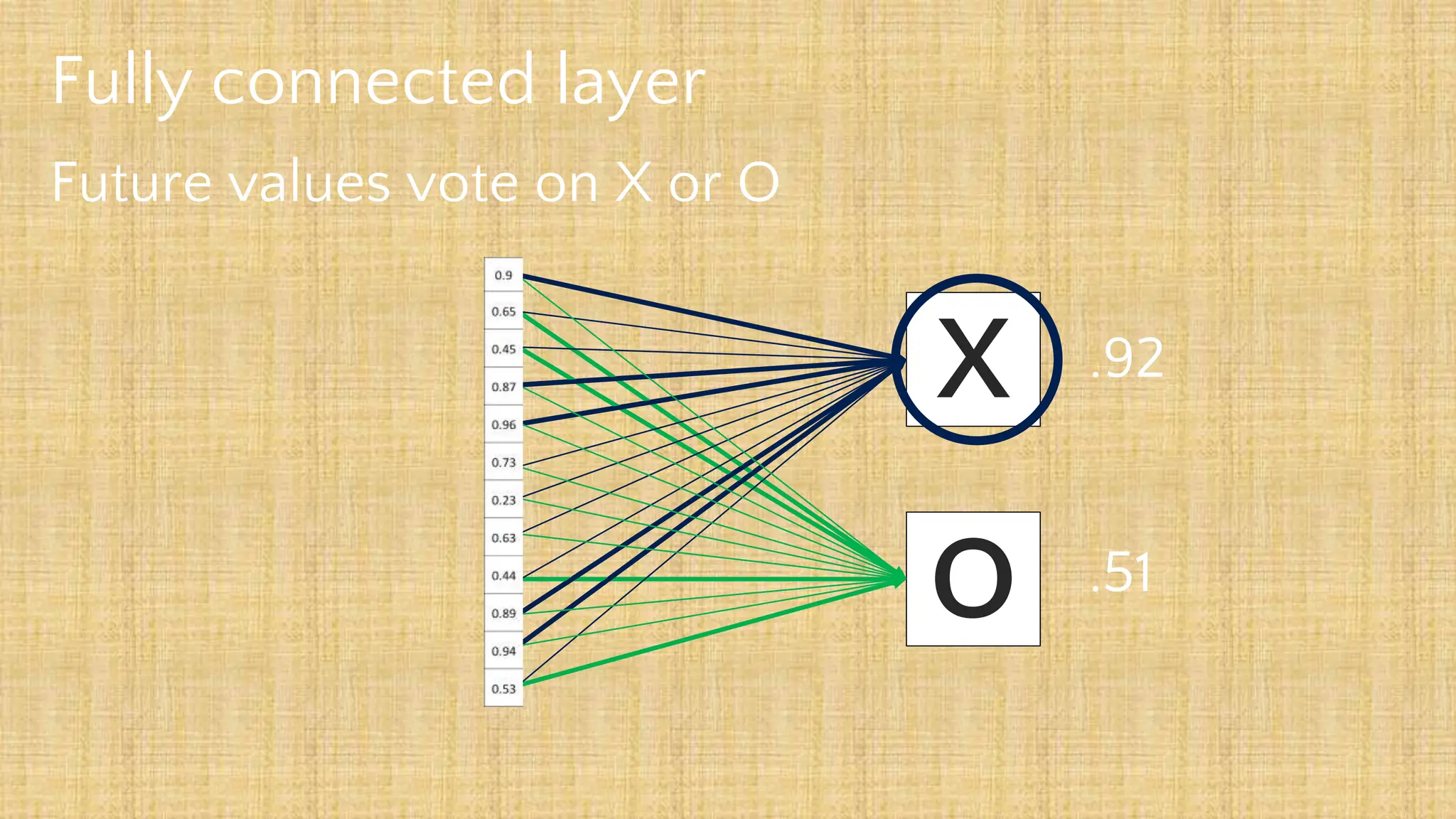
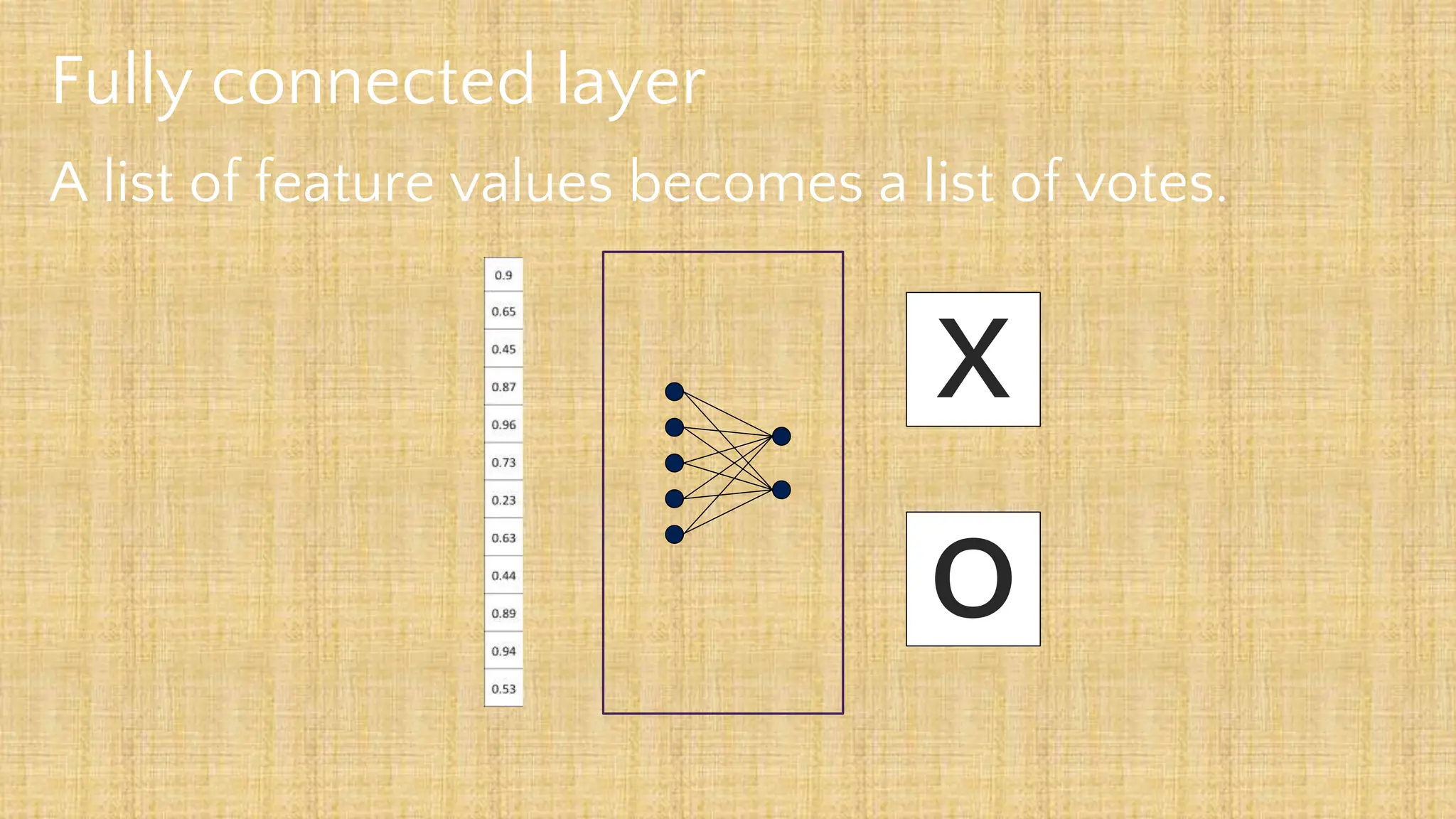
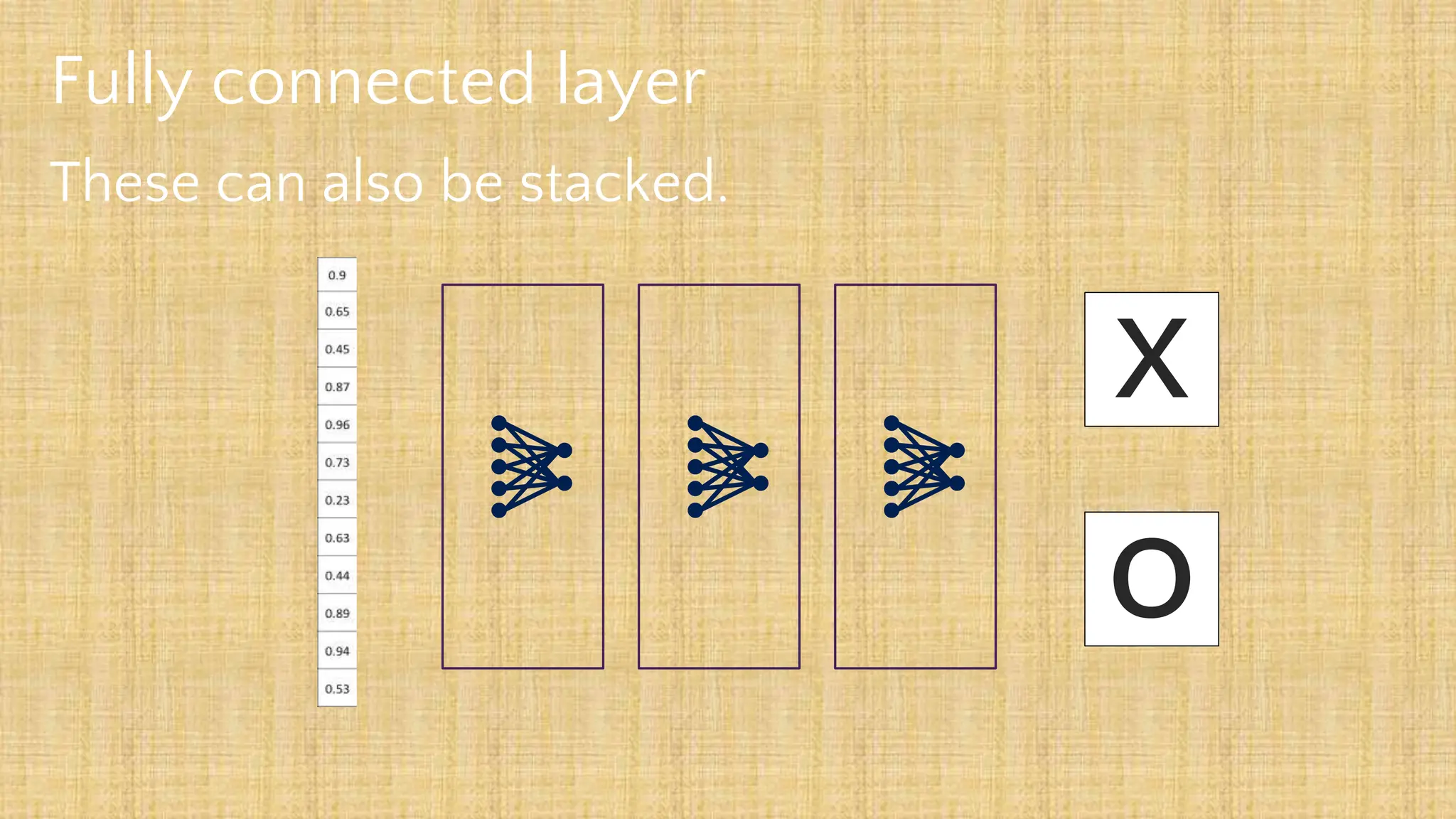
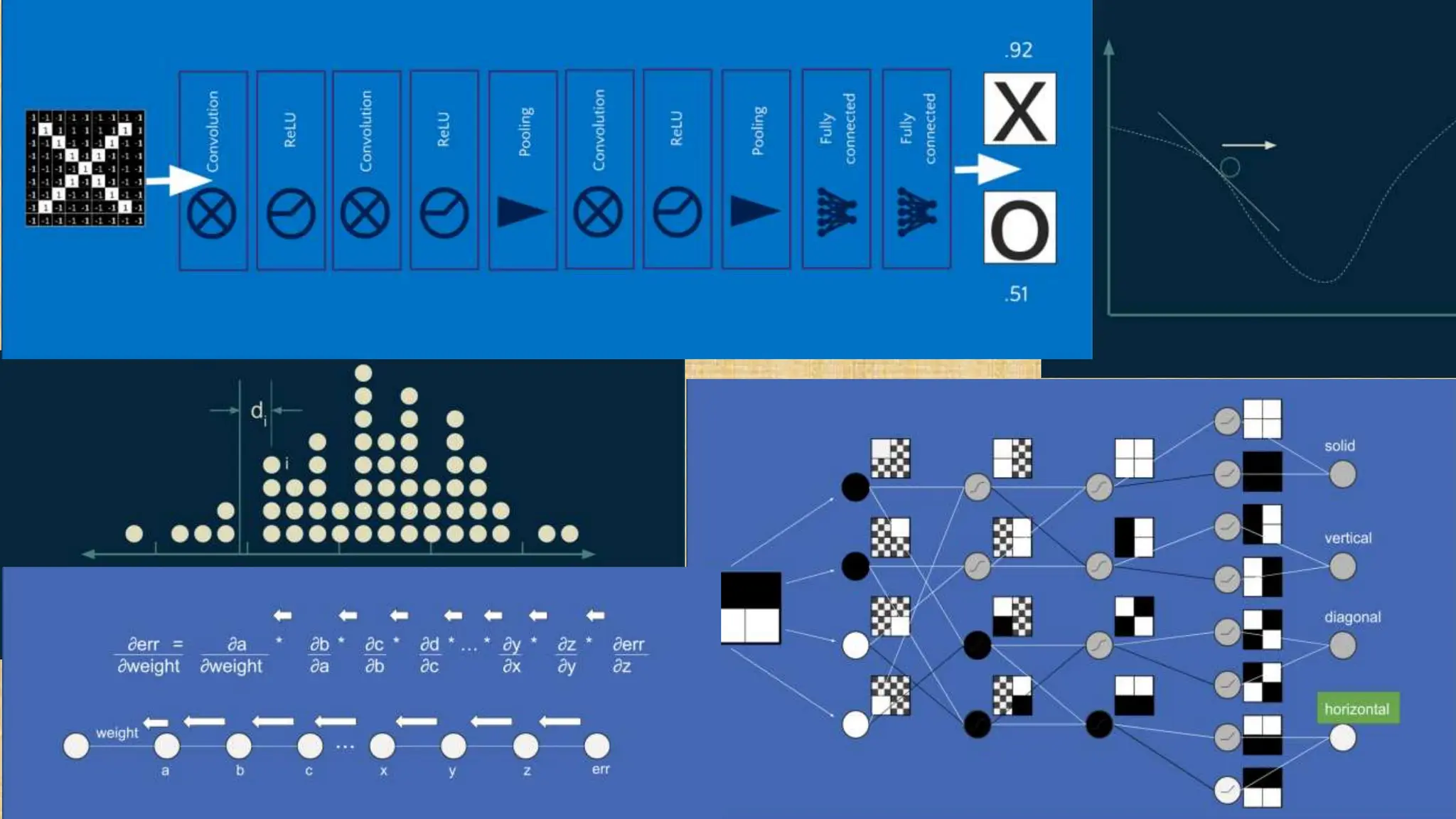
The document outlines the structure and functionality of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), detailing the layers involved such as convolution, activation using ReLU, pooling, and fully connected layers. It explains how images are processed through these layers to classify objects with applications in image recognition, classification, and object detection. The document also emphasizes the importance of techniques like zero-padding, stride, and various pooling methods in enhancing CNN performance.