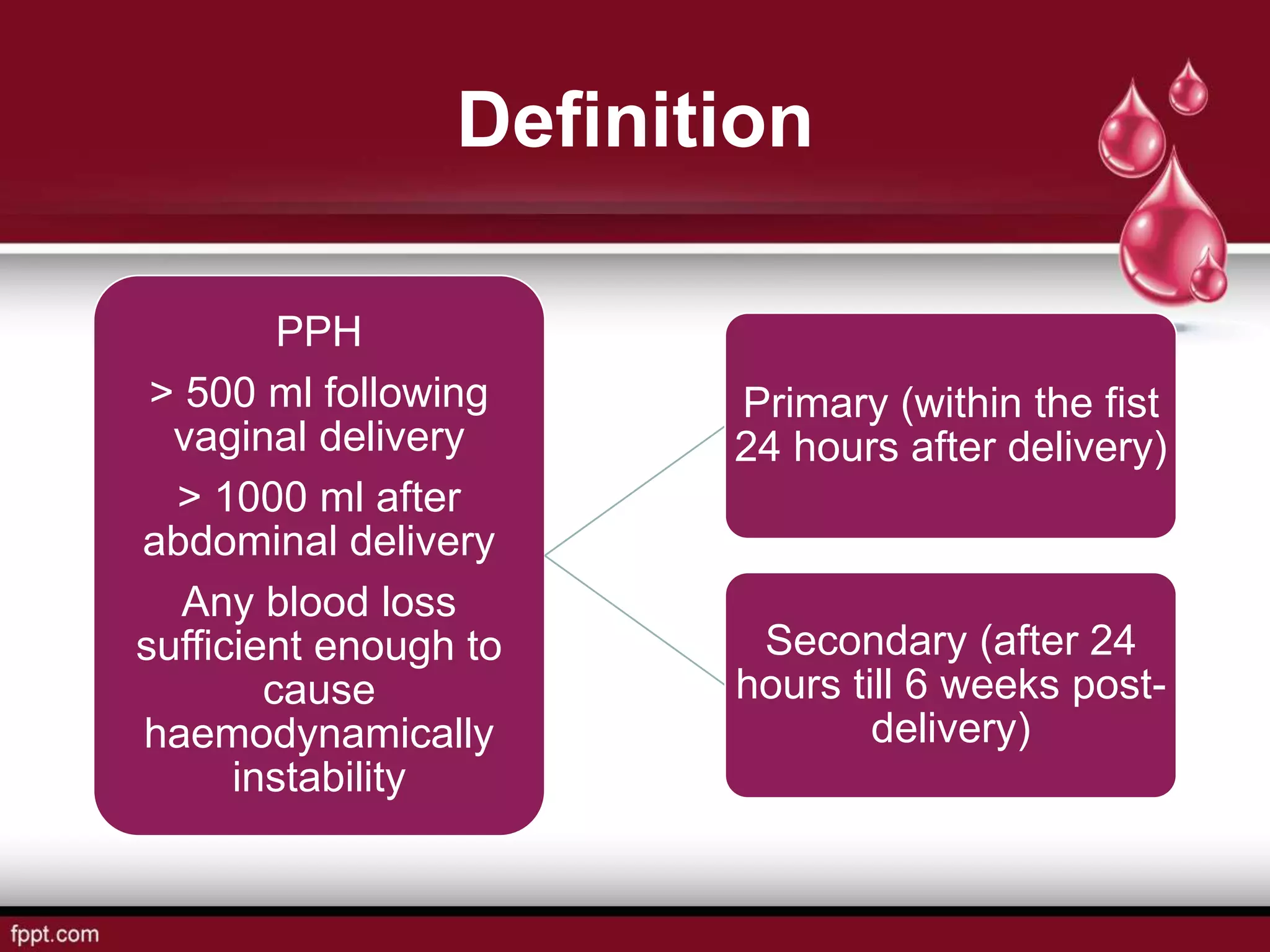
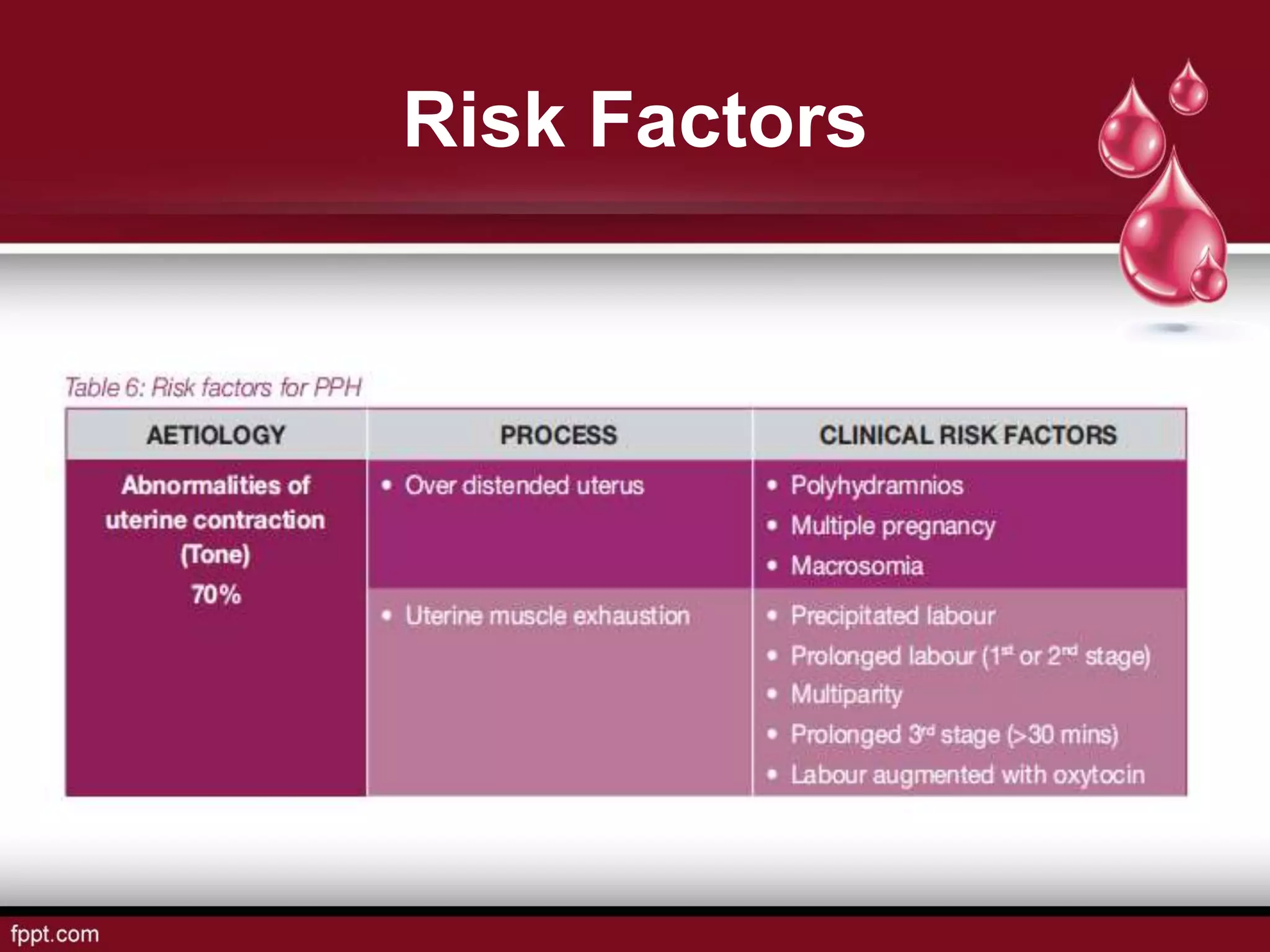
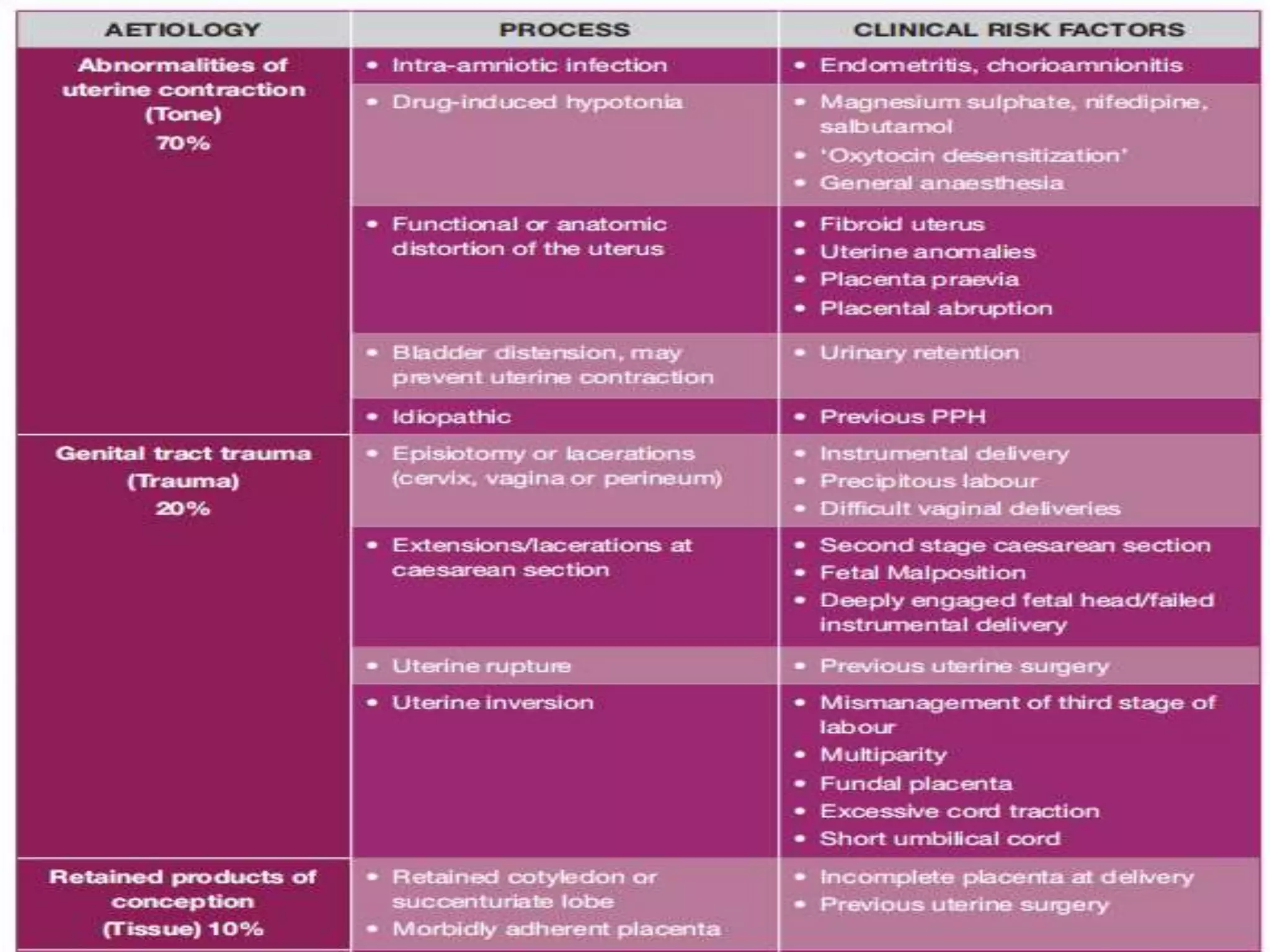
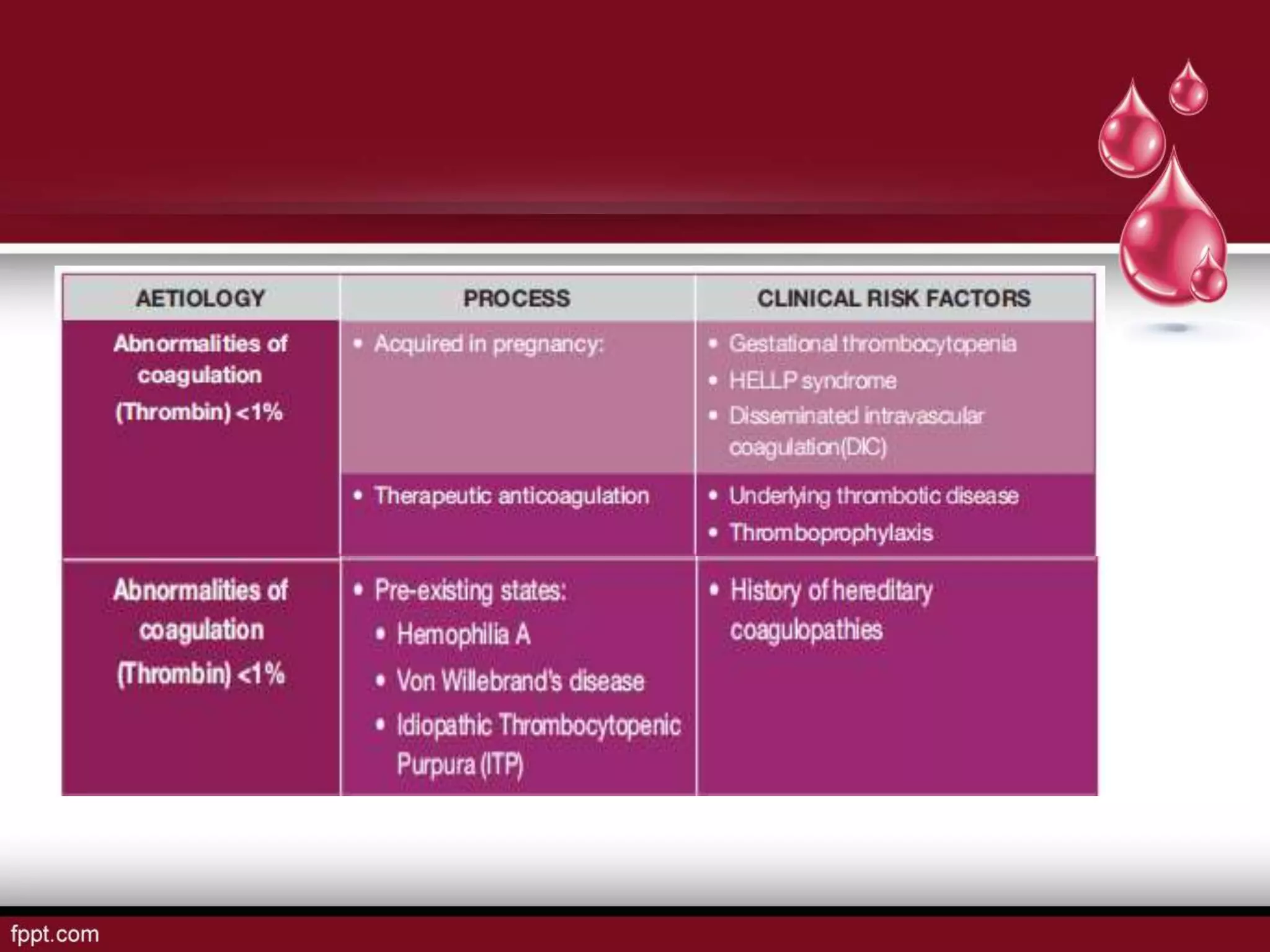
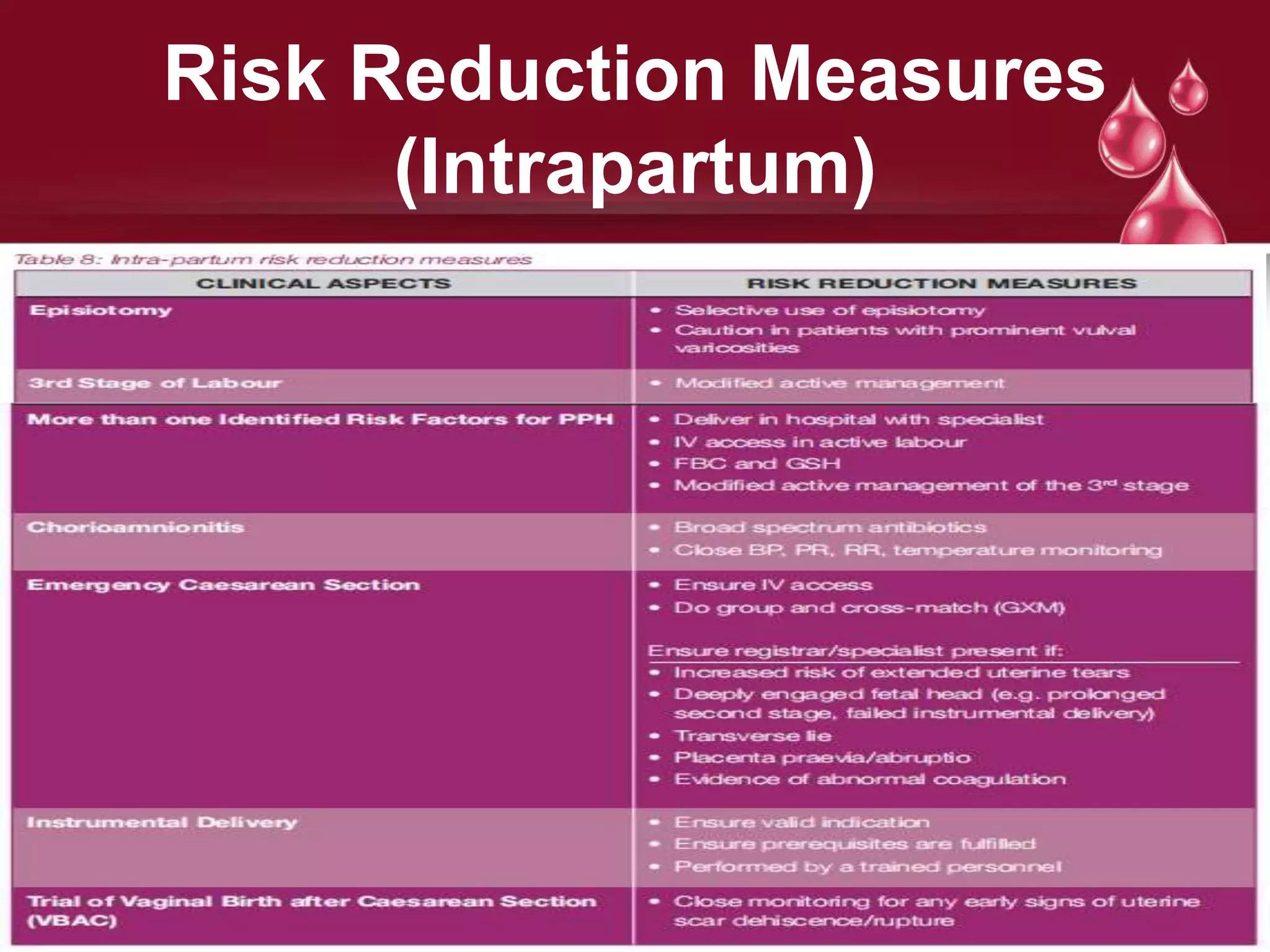
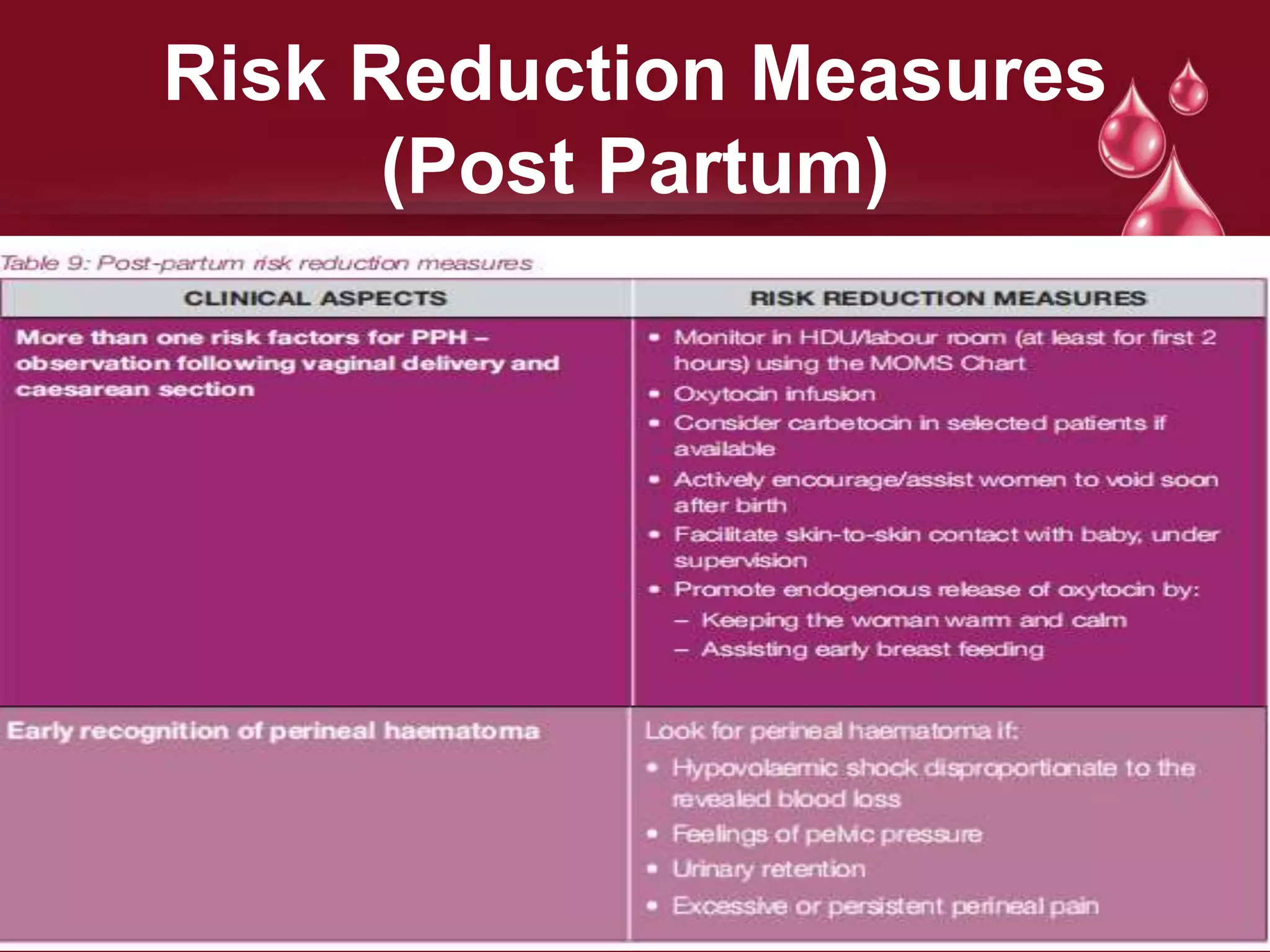
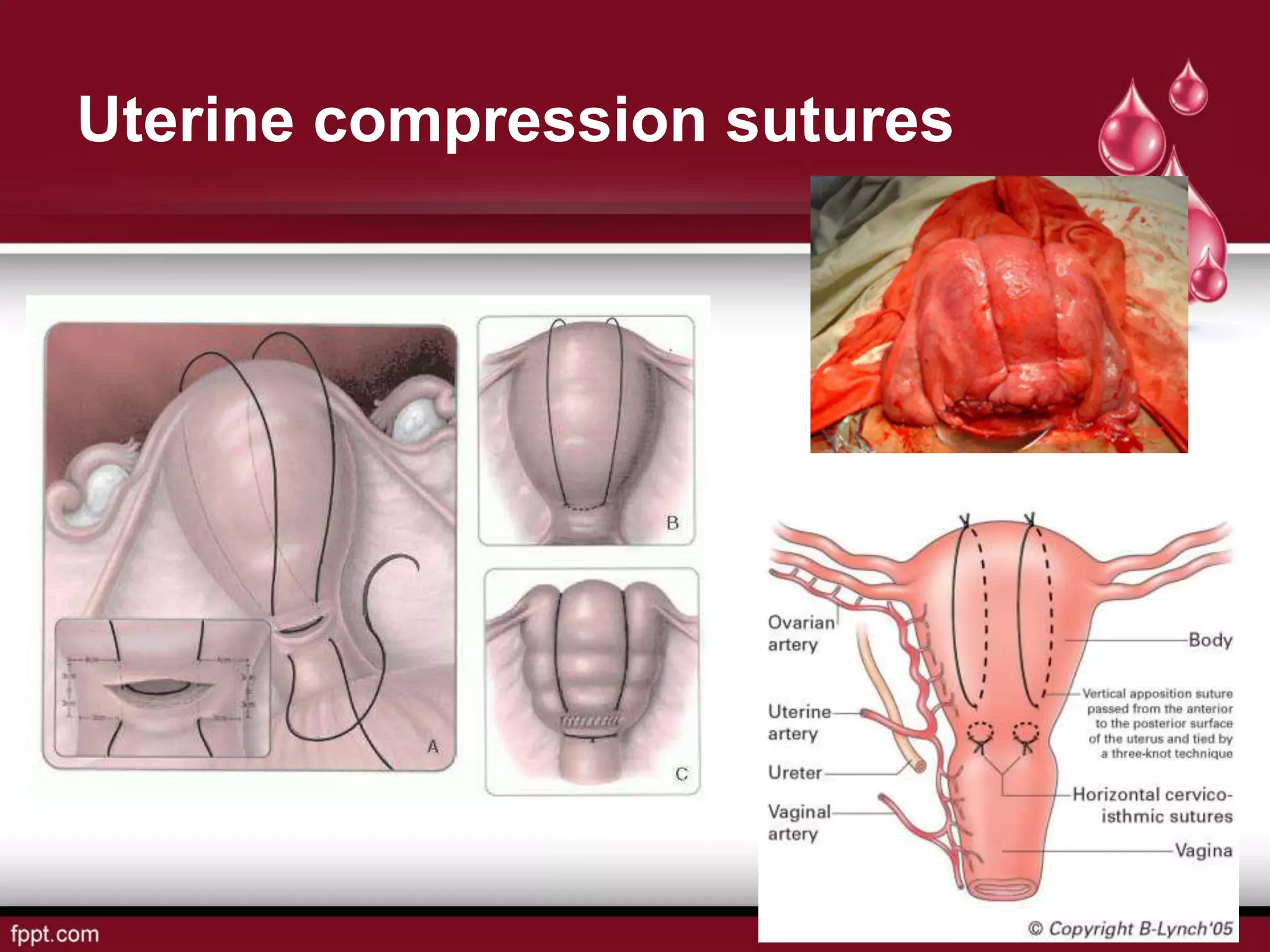
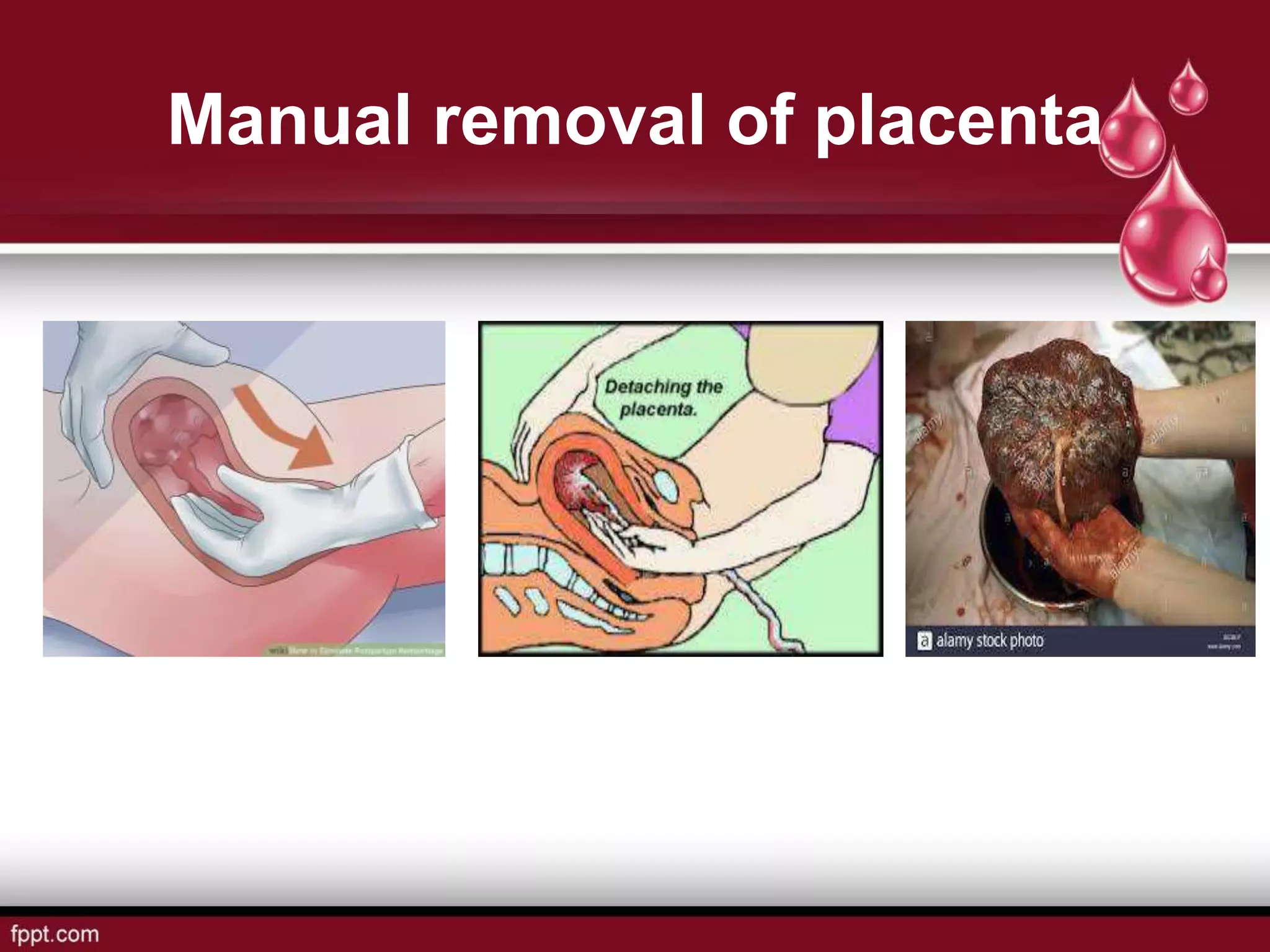
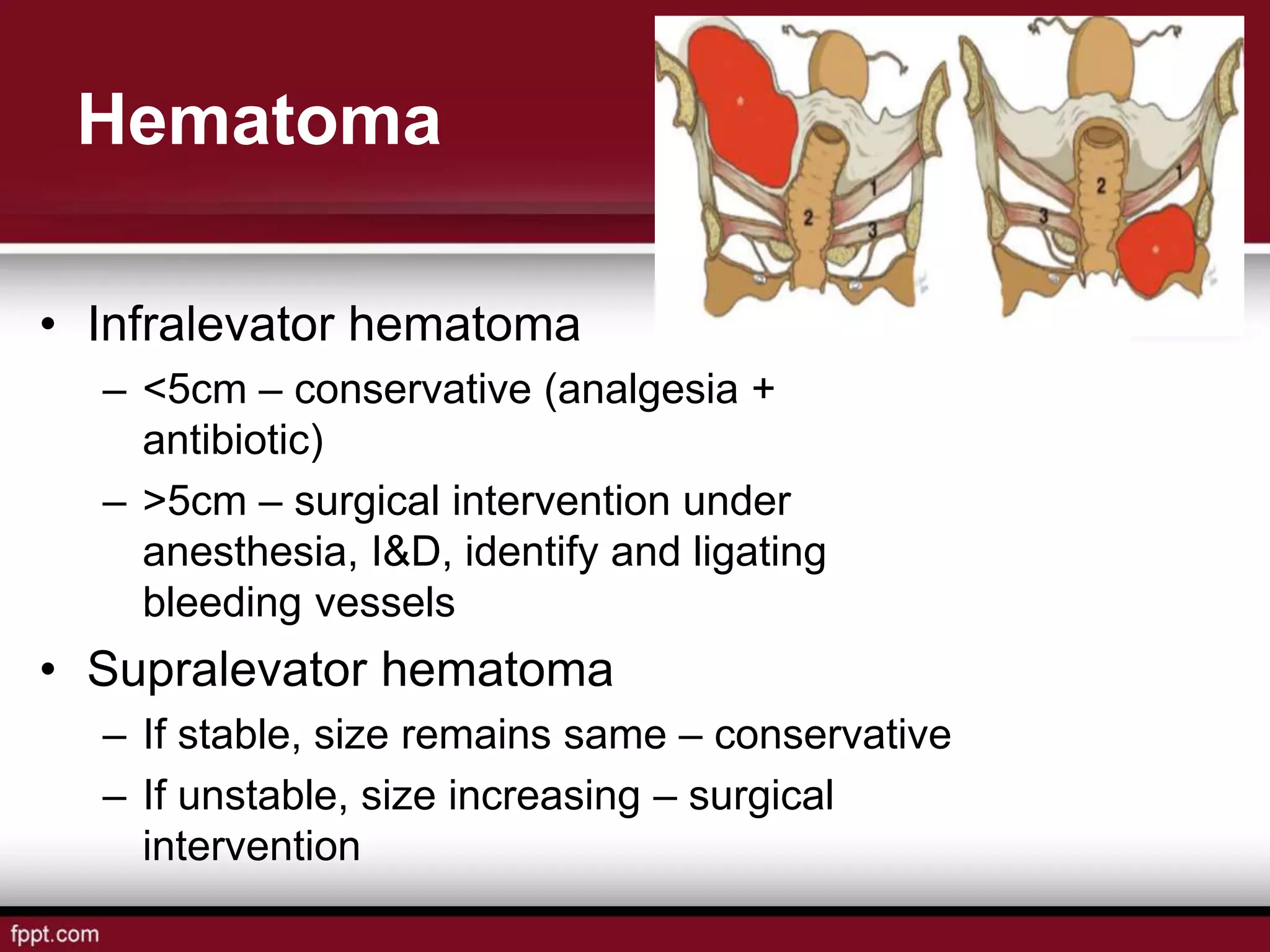
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is defined as blood loss greater than 500 ml following vaginal delivery or 1000 ml after cesarean delivery. Risk factors include prior history of PPH, anemia, uterine anomalies, and prolonged labor. Risk reduction measures include active management of the third stage of labor, use of uterotonics, and treatment of anemia. Management of PPH involves resuscitation, monitoring for vital signs and investigations, and arresting the bleeding through uterine massage, administration of uterotonics, repairing lacerations, and treating underlying causes such as atony, retained placenta, or inversion. Surgical interventions like compression sutures or hysterectomy may be needed in severe