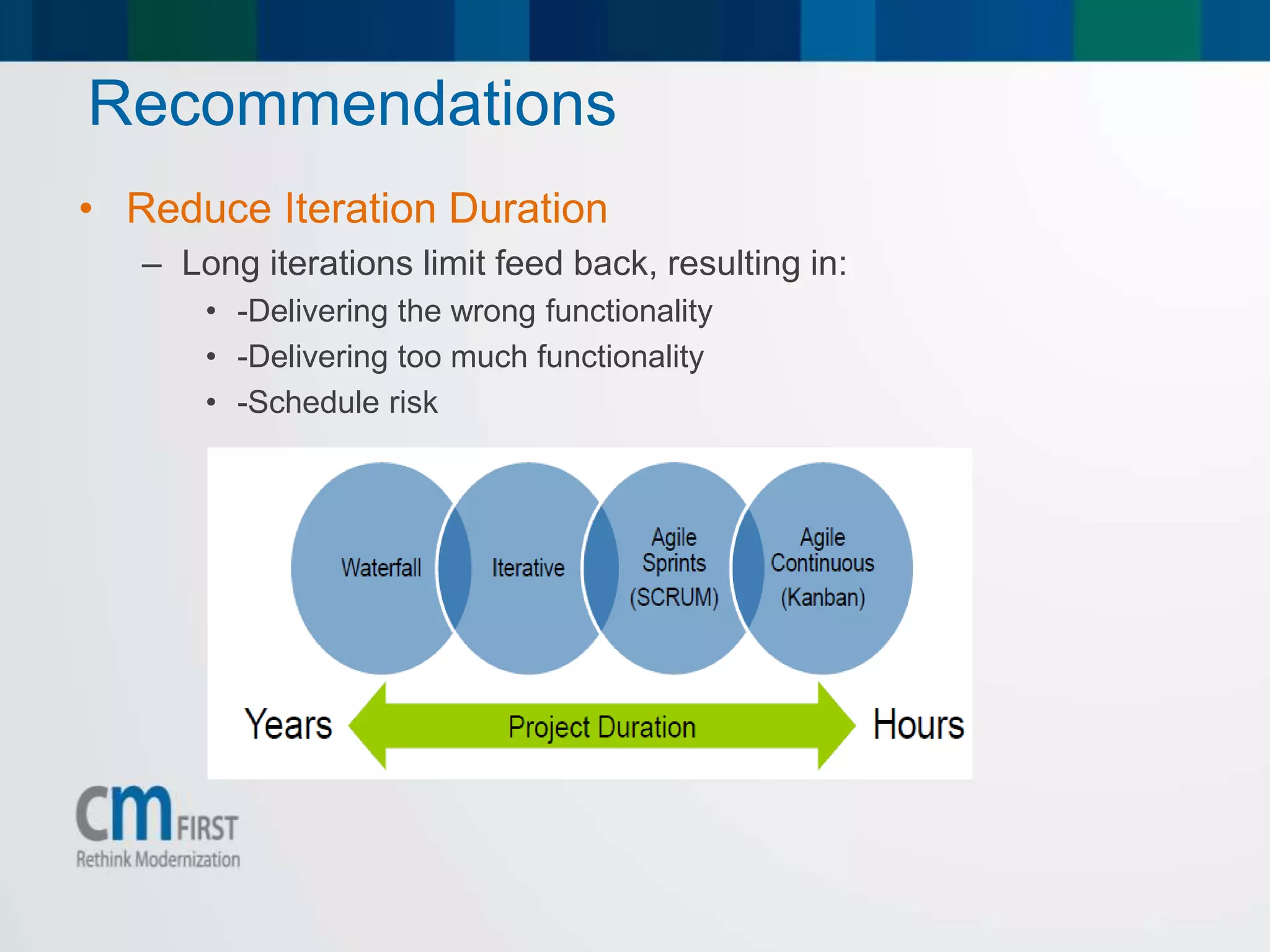
This document discusses how to use CM MatchPoint for managing agile projects using frameworks like SCRUM. It provides an overview of CM MatchPoint, explaining that it can cover the complete agile process including managing backlogs, planning sprints, monitoring progress, and automating deployments. The presentation also reviews agile concepts like SCRUM and its artifacts, roles, and events. It recommends adopting agile practices like reducing iteration duration and automating deployment and testing when using CM MatchPoint for agile software development.