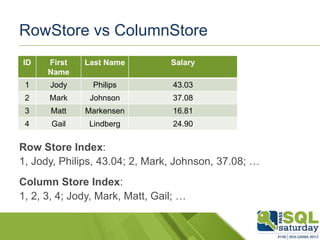
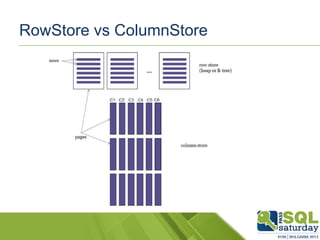
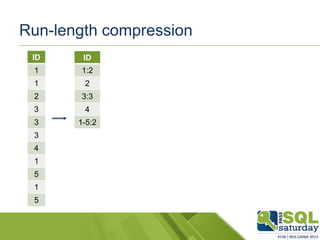
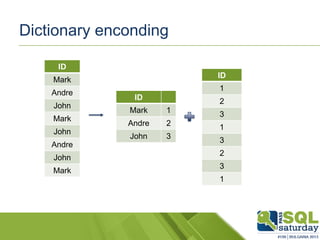
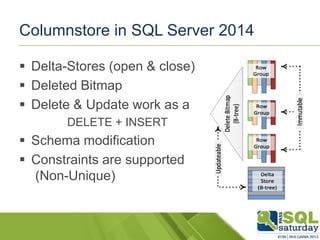
The document provides an introduction to clustered columnstore indexes, their principles, history, and development in SQL Server from 2012 to 2014. It highlights the differences between rowstore and columnstore, the benefits of batch mode processing, and the limitations of these technologies. It also mentions significant improvements in SQL Server 2014, such as the introduction of clustered columnstores, enhanced batch mode capabilities, and better data management features.