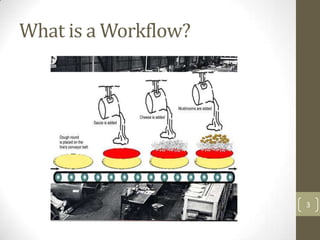
This document discusses scientific workflows systems for use in drug discovery informatics. It defines a scientific workflow as an automated "data analysis pipeline" that can process large volumes of data faster than scientists can manually. The document outlines challenges in designing scientific workflows, including mastering programming languages, visualizing workflows, sharing workflows, and locating datasets and services. It provides examples of scientific workflow software like Pipeline Pilot, KNIME, and Taverna Workbench, showing how they can perform routine data tasks without manual interference. Advantages of workflow systems include result reproducibility, reduced data loss and time savings.