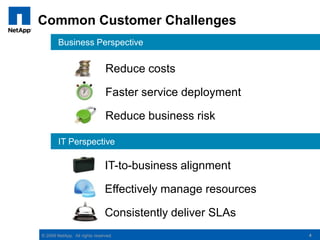
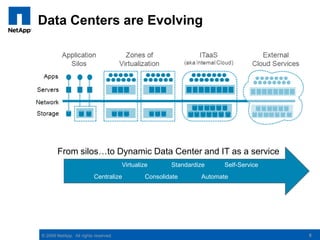
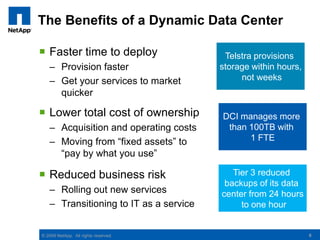
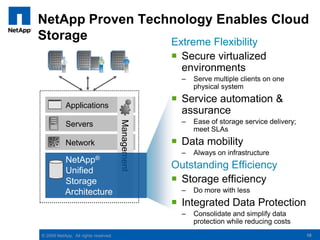
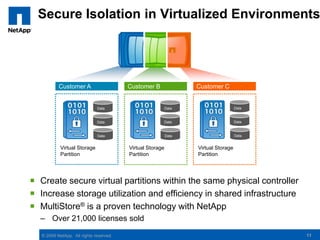
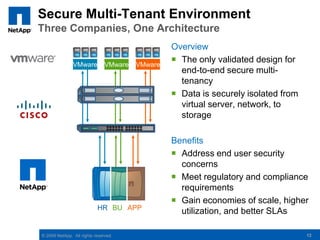
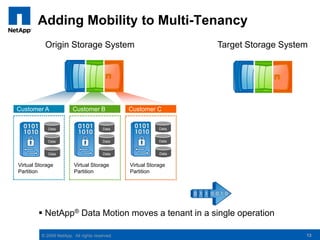
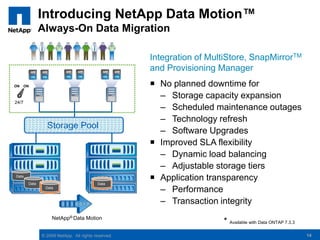
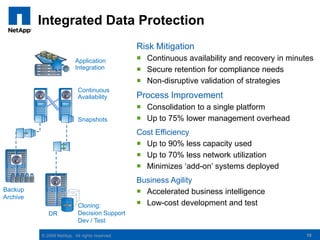
The document discusses the transformation of traditional data centers into dynamic data centers utilizing NetApp's cloud storage solutions. It highlights the benefits such as faster service deployment, reduced costs, and improved resource management while addressing common client challenges. Additionally, it provides examples of successful implementations and the technological capabilities that support multi-tenancy, data protection, and service automation.