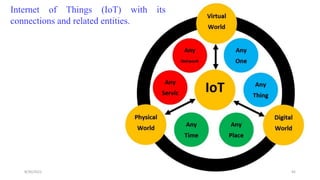
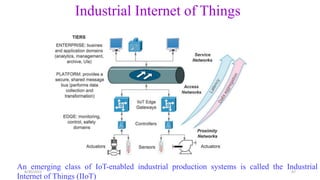
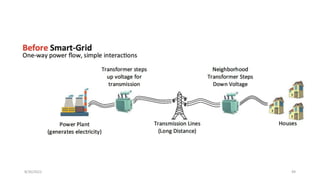
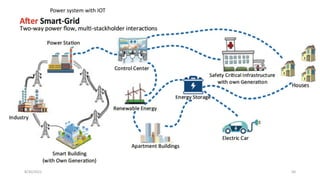
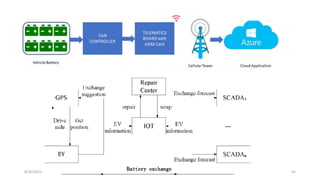
The document discusses cloud controlled electric vehicle charging stations. It covers several key points:
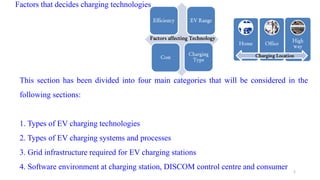
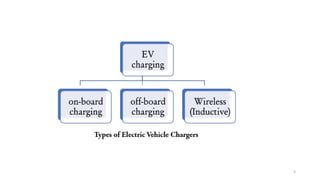
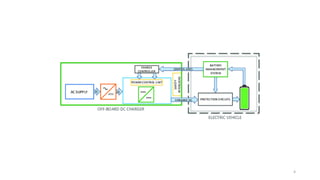
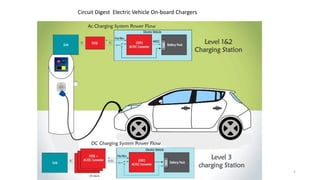
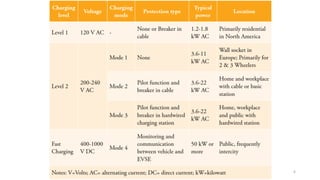
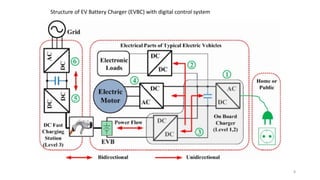
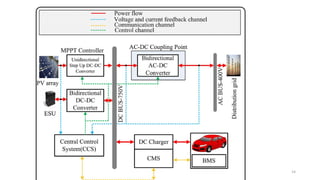
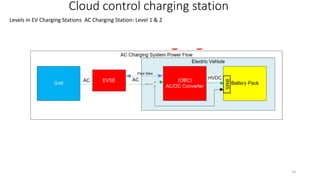
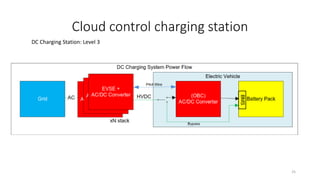
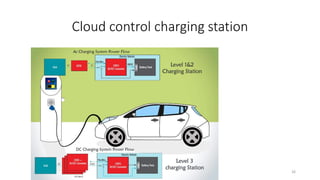
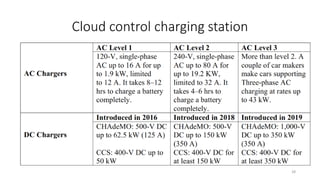
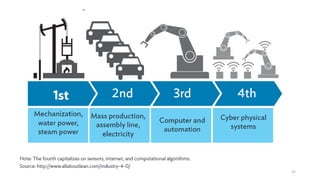
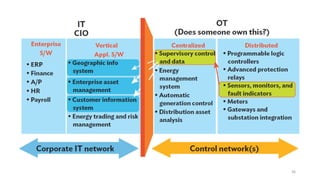
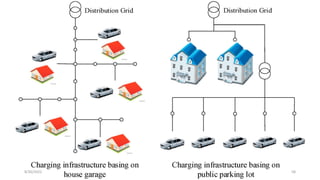
1. Types of EV charging technologies, systems, required grid infrastructure, and software environments must be considered when deciding on charging technologies.
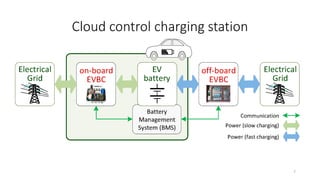
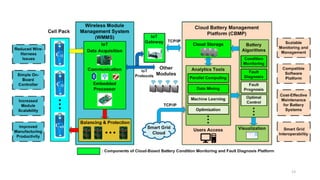
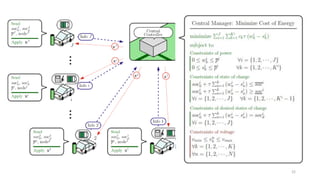
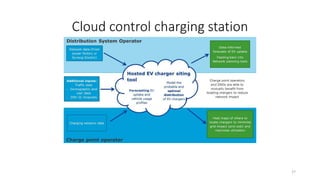
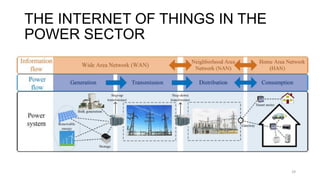
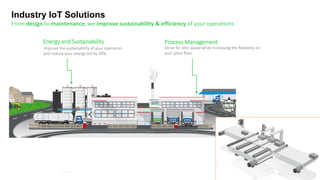
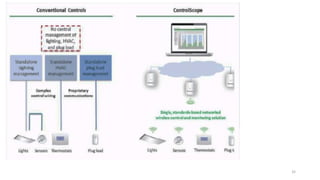
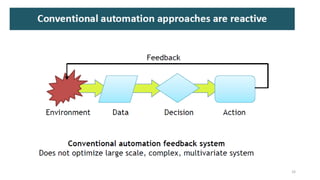
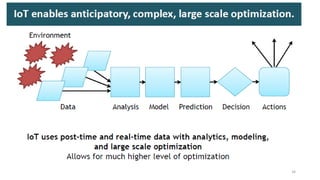
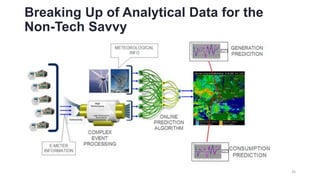
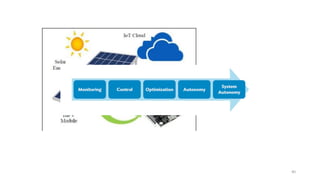
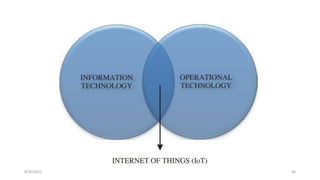
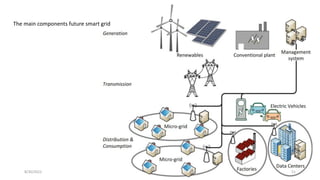
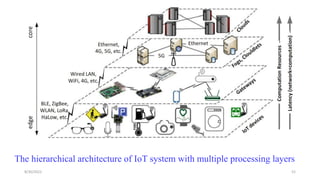
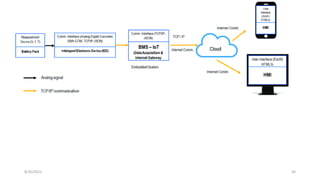
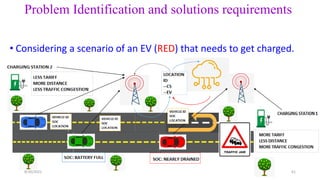
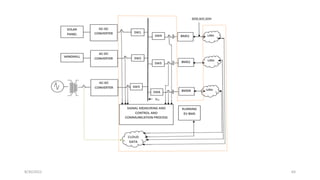
2. Cloud control is important for continuously monitoring battery charge levels, optimizing charging station locations, enabling communication between vehicles and the grid, and developing power quality monitoring systems.
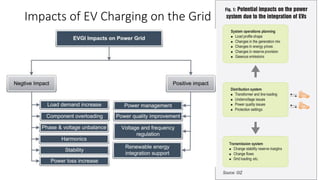
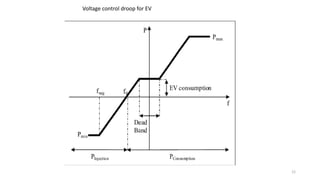
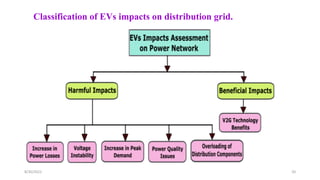
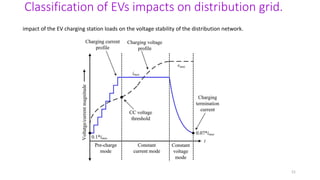
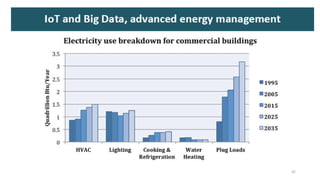
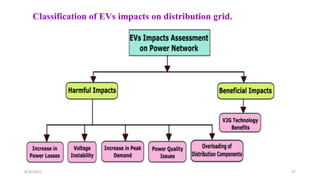
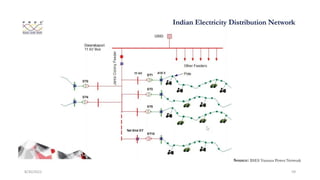
3. The impacts of EV charging on the power grid include effects on transformers, power cables, switchgear, capacitors, voltage fluctuations, and system imbalances.