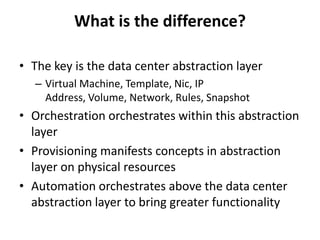
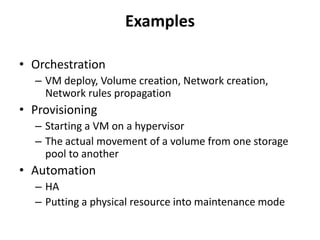
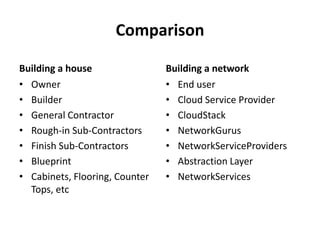
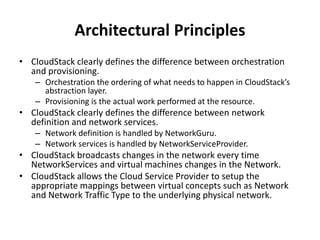
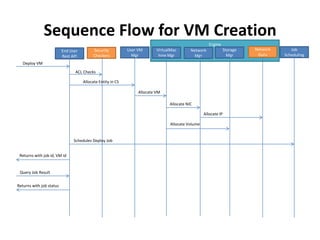
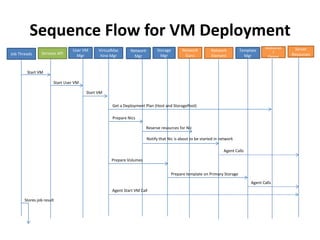
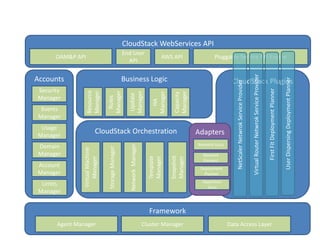
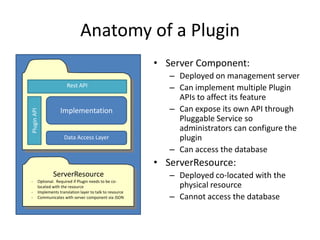
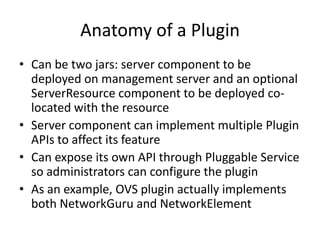
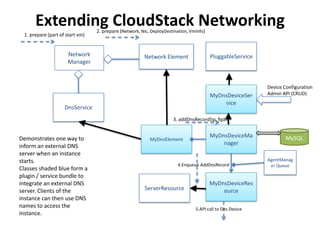
CloudStack provides an orchestration platform that abstracts physical network resources and allows third party plugins to integrate their networking services. It separates orchestration from actual provisioning, with CloudStack only handling orchestration events and notifications, while provisioning is handled by plugins. This allows services to scale independently of CloudStack. CloudStack defines common concepts like Networks, but plugins determine how these map to physical networks through interfaces like NetworkGuru. This architecture enables innovation from partners through well-defined plugin APIs and abstraction layers.