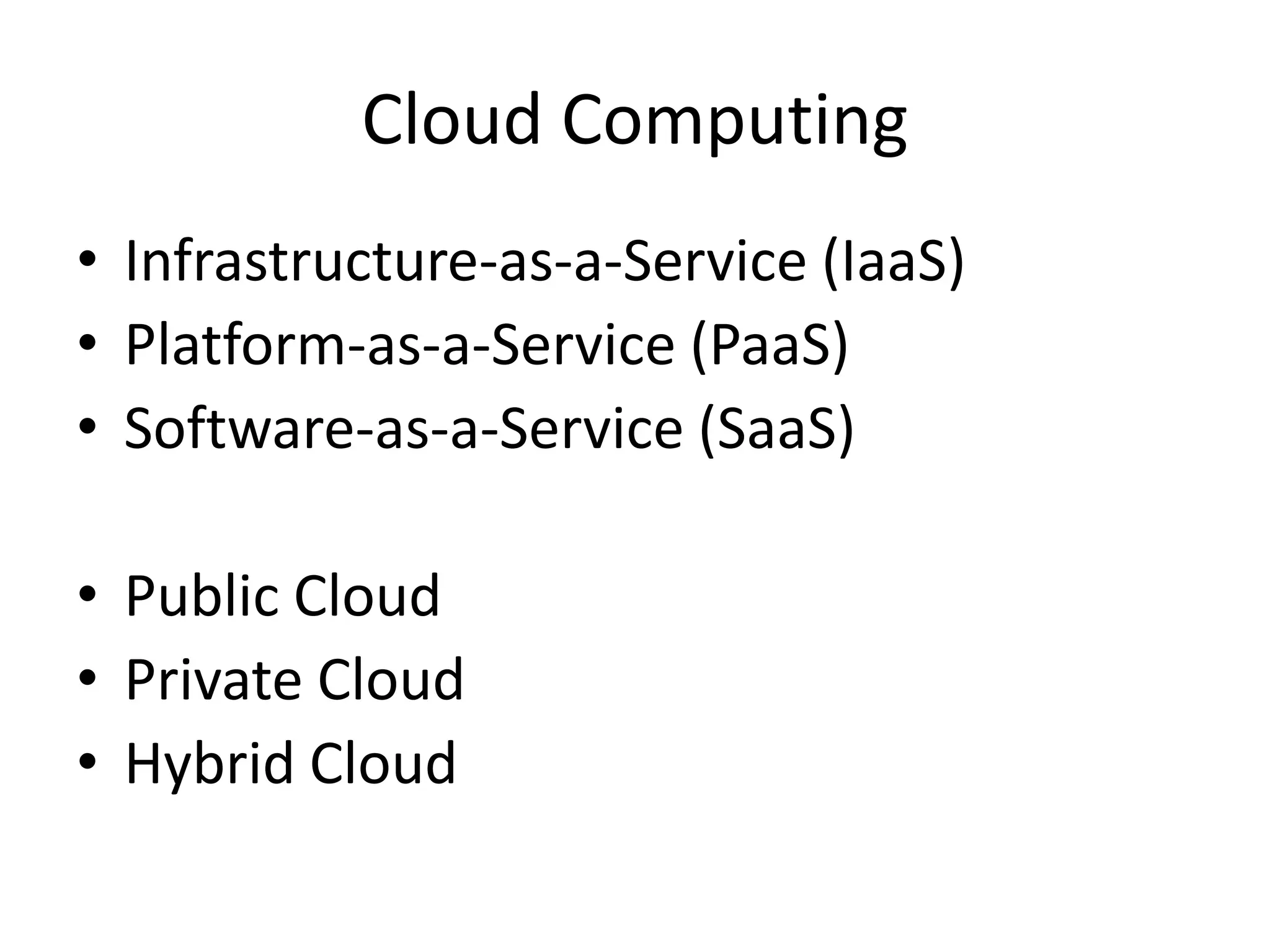
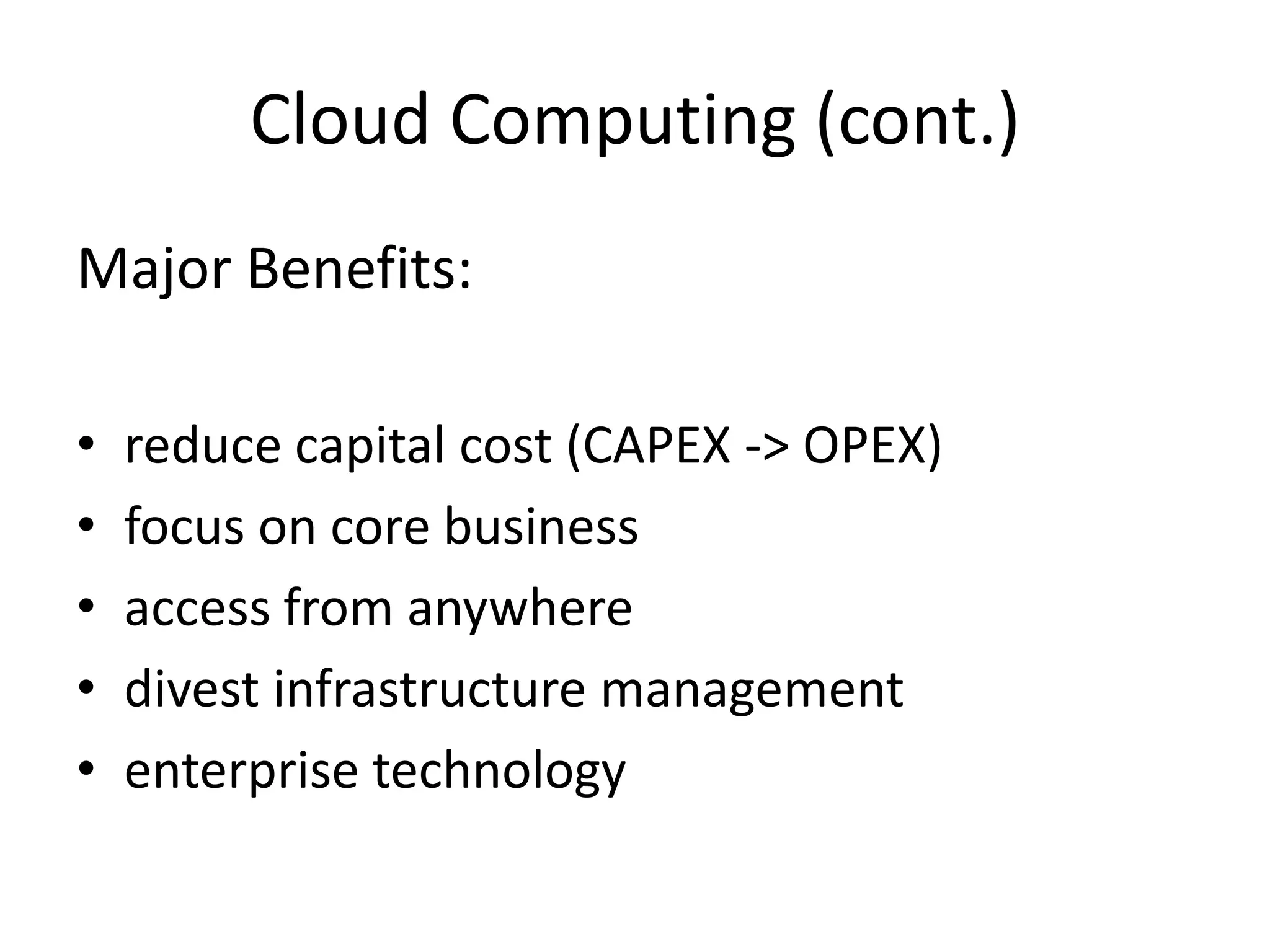
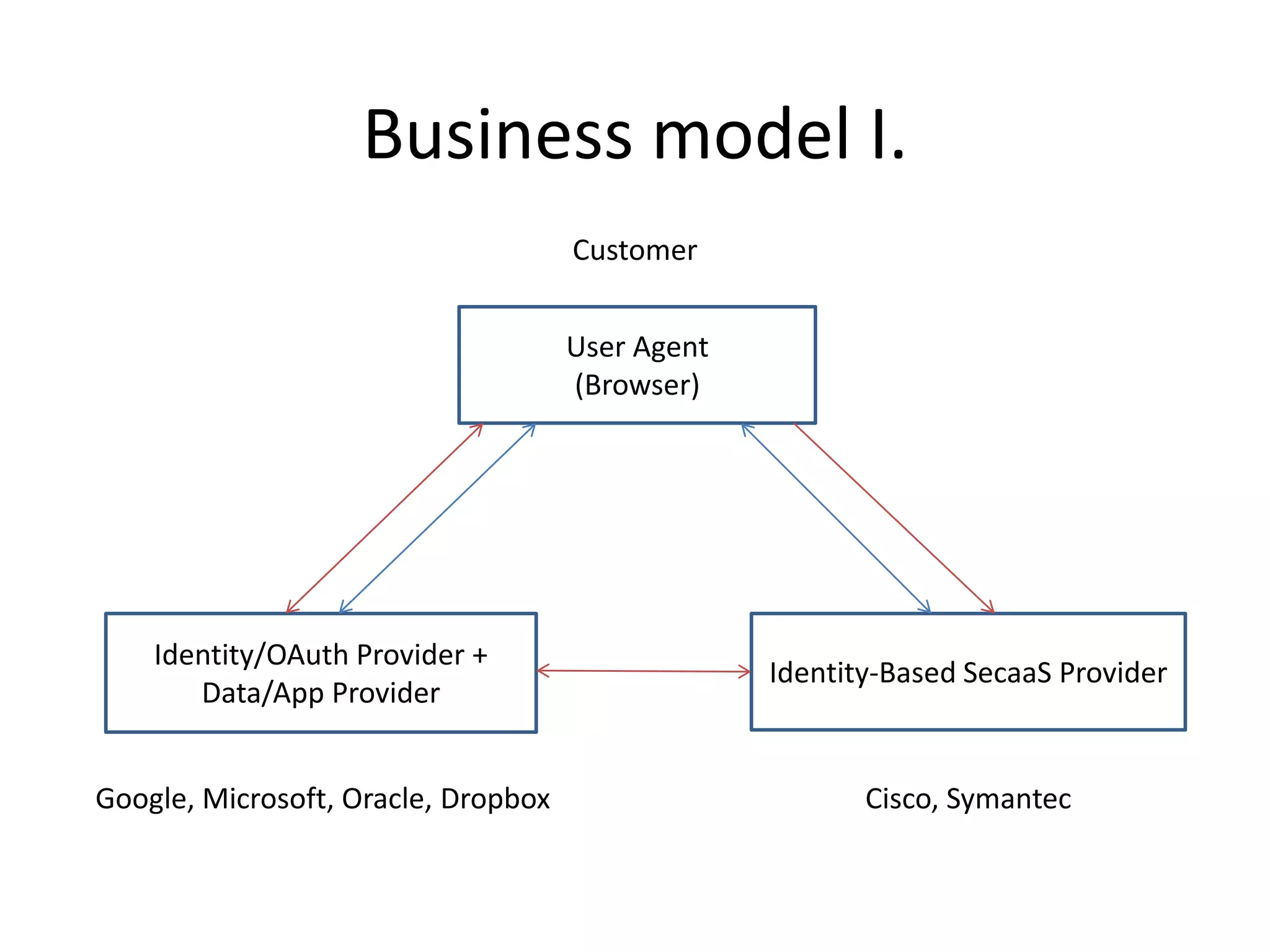
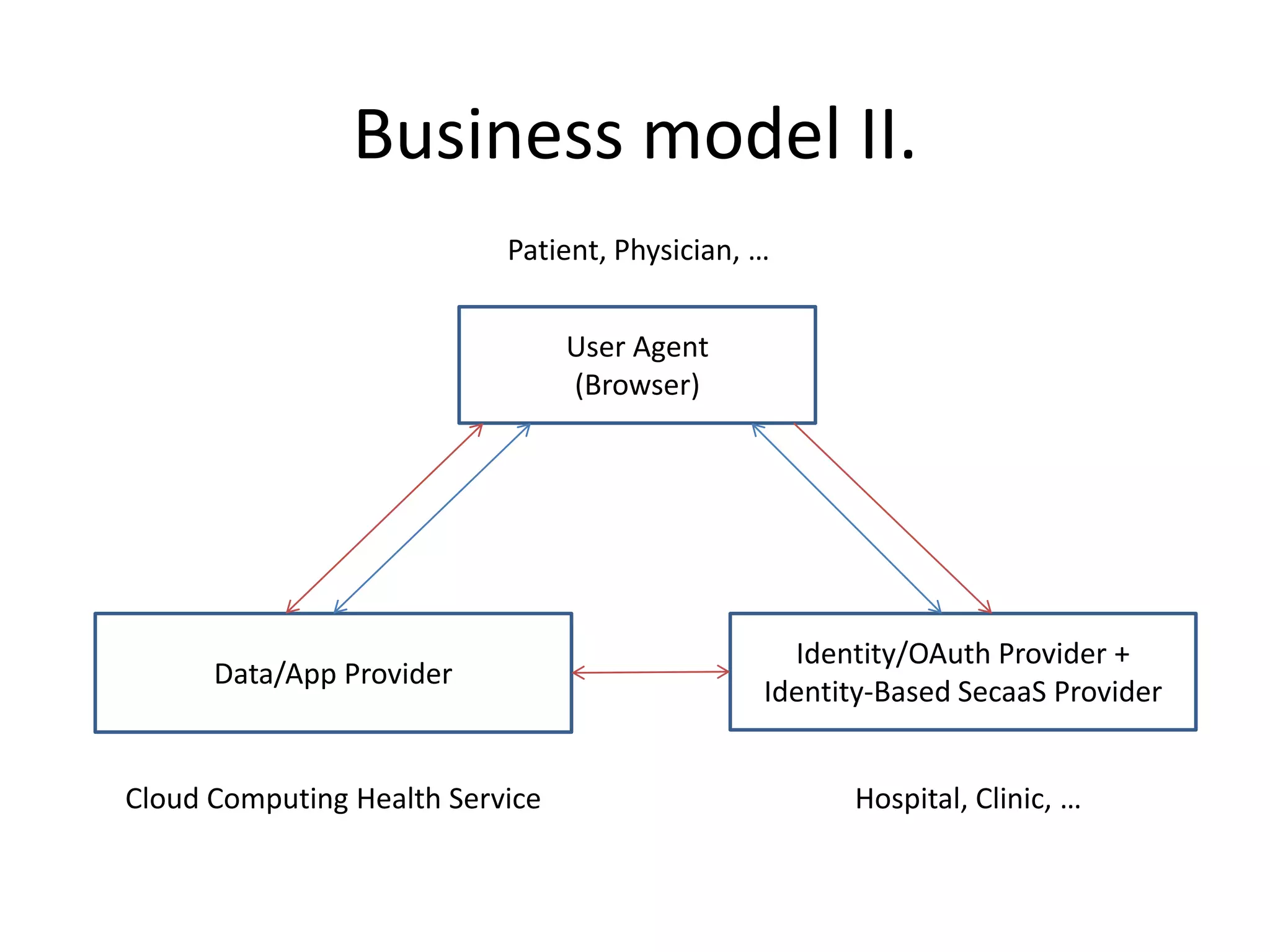
This document discusses cloud computing and privacy protection. It describes various cloud computing models including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. While cloud computing provides benefits like reduced costs, it also raises issues around security and privacy. The document proposes an identity-based encryption and identity management model using technologies like OAuth2 and OpenID Connect to help address privacy concerns when using cloud computing.