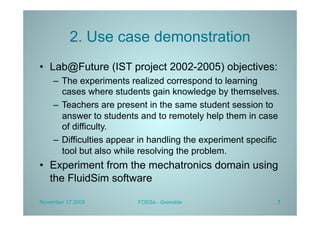
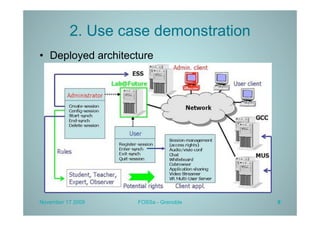
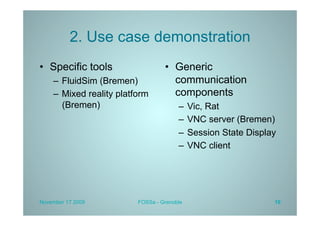
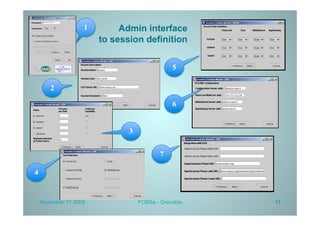
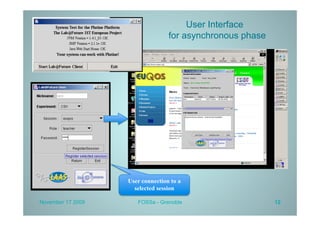
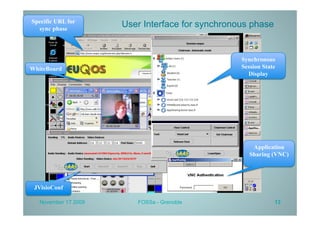
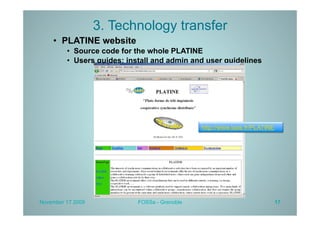
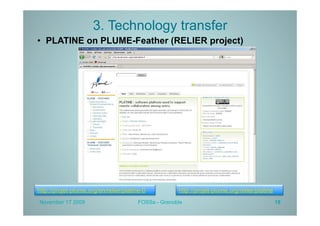
PLATINE is a synchronous and distributed cooperative platform for remote collaboration. It was developed since 1998 and has been used in European and French projects. PLATINE offers mechanisms for asynchronous and synchronous collaboration and includes components for session preparation, chat, videoconferencing, application sharing, and a shared whiteboard. The presentation demonstrates its use for an e-learning use case, discusses transferring its technology under an open source license, and describes lessons learned from the project including a lack of resources for completion but useful applications in research projects.