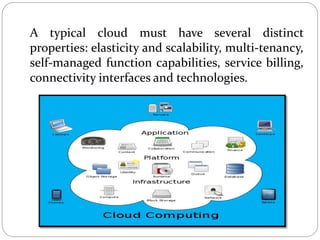
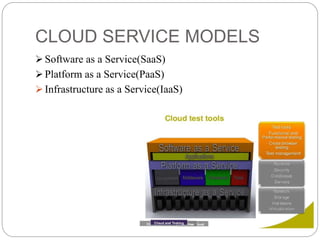
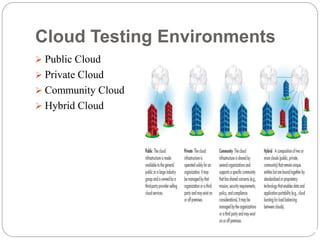
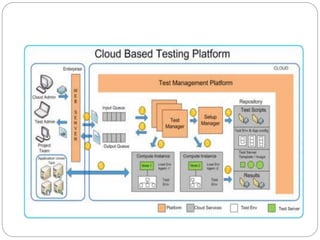
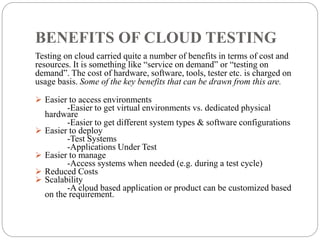
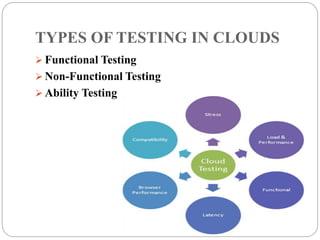
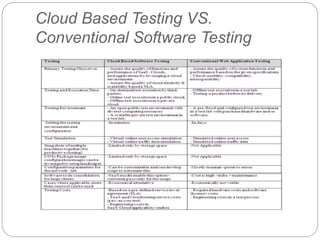
This document discusses cloud-based testing. It defines cloud computing and the different cloud service models: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Cloud-based testing uses cloud technologies and infrastructure to simulate real-world user traffic. Benefits of cloud testing include easier access to testing environments, easier deployment of test systems and applications, easier management, reduced costs, and scalability. Types of testing in the cloud include functional, non-functional, and load testing. Cloud testing provides increased availability, security, performance, and disaster recovery compared to conventional software testing. Most organizations are adopting cloud testing due to its flexibility, scalability, and reduced costs.