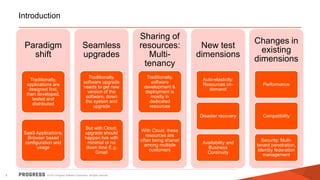
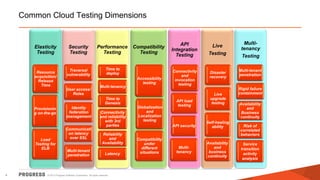
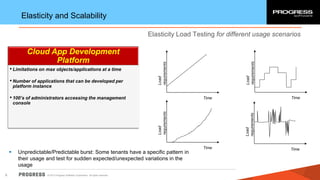
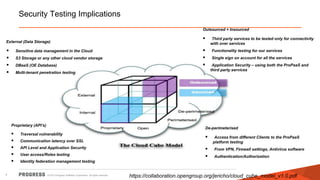
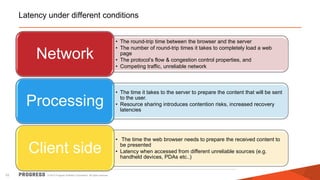
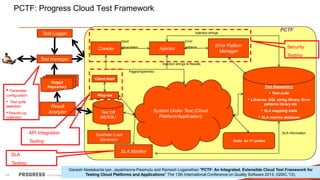
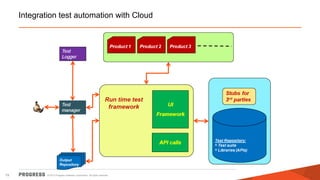
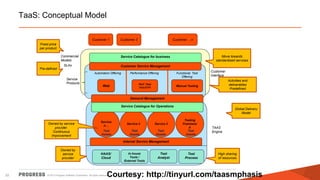
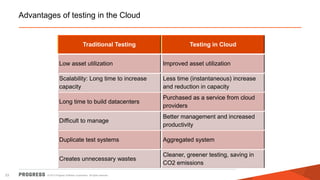
The document discusses test challenges and methodologies for cloud computing. It outlines various dimensions that need to be tested for cloud platforms and applications, including elasticity, security, performance, multi-tenancy, and integration. Testing in the cloud provides advantages over traditional testing such as improved scalability, asset utilization, and reduced costs and environmental impact. Testing as a service (TaaS) is also discussed as a shared services delivery model for software testing on demand.