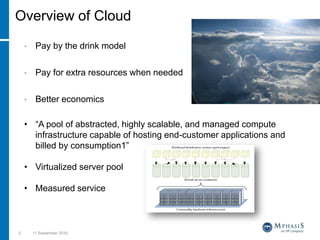
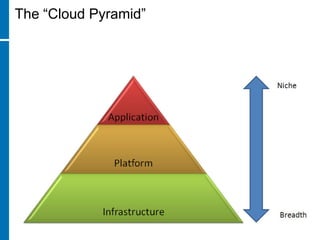
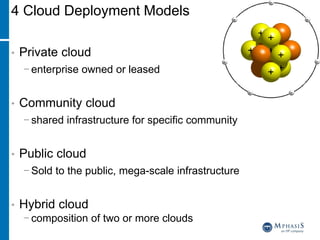
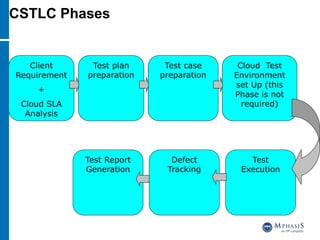
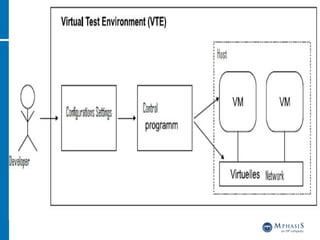
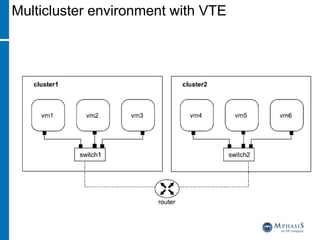
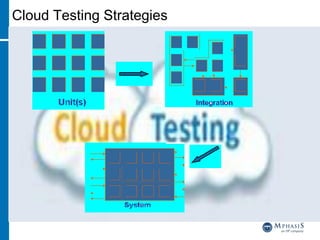
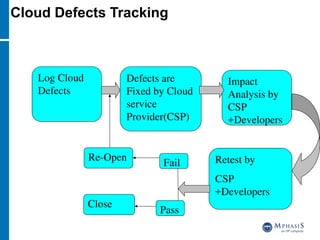
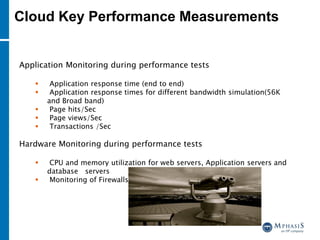
This document provides an overview of cloud computing and testing in the cloud. It discusses key aspects of cloud computing including pay-per-use models, virtual server pools, and various cloud deployment models. It then covers cloud service level agreements and their technical and commercial terms. The document outlines different strategies for testing in the cloud including automation, functional testing, and monitoring. It also discusses challenges like security and reliability and how defects are tracked. Overall the document is providing guidance on testing applications and infrastructure deployed in cloud environments.