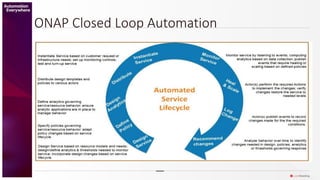
This document discusses closed loop automation for network functions virtualization (NFV). It begins by outlining the goal of achieving fully closed loop automation through techniques like machine learning, where the network can detect and fix issues without human intervention. It then discusses the current state of play, including tools that allow operators to confirm automated changes. The document outlines the key aspects of closed loop systems, including continuous monitoring, anomaly detection, corrective action recommendation by a policy engine, and status monitoring after repair. It discusses approaches to closed loop automation by projects like ONAP and ETSI OSM. Finally, it explores how machine learning can help make closed loop systems more predictive, intelligent, and dynamic over time as more data is collected.