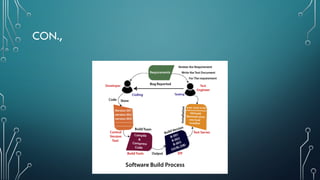
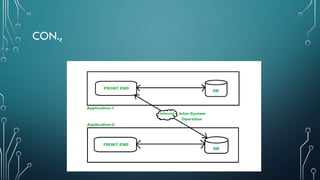
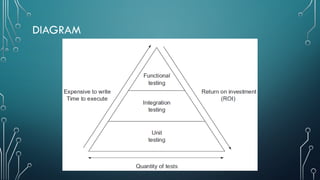
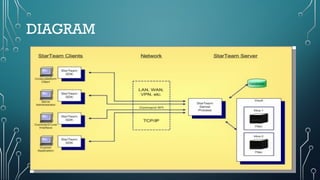
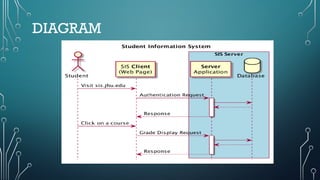
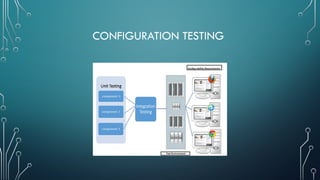
The document outlines client-server computing, detailing server management tasks, advantages, and types of server-management including client/server application functionalities. It discusses comprehensive software testing techniques such as GUI testing, manual testing, configuration testing, and interoperability testing essential for ensuring optimal application performance across various systems. Additionally, it highlights the importance of testing in identifying defects and ensuring smooth application functionality in client-server environments.



















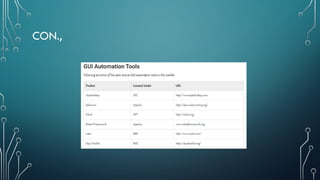
![USER INTERFACE TESTING
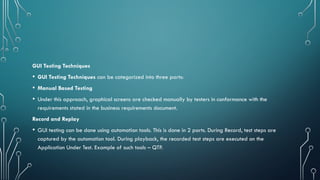
• User interface testing, a testing technique used to identify the presence of defects
is a product/software under test by using Graphical user interface [GUI].
Approaches:
• Manual Based - Based on the domain and application knowledge of the tester.
• Capture and Replay - Based on capture and replay of user actions.
• Model-based testing - Based on the execution of user sessions based on a GUI
model. Various GUI models are briefly discussed below.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clientservercomputingunit5-241226154301-a8948d8f/85/CLIENT-SERVER-COMPUTING-FINAL-UNIT-5-pptx-26-320.jpg)