1) A cleanroom is defined as a room with controlled airborne particle concentration constructed and operated to minimize particle introduction, generation, and retention. Other parameters like temperature, humidity, and pressure can also be controlled.
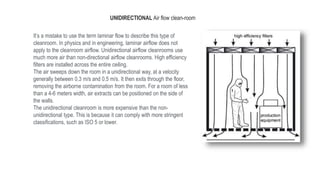
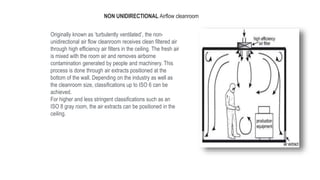
2) Particle introduction, generation and retention in a cleanroom are minimized by supplying filtered air, using materials that don't generate contaminants, and protective clothing for operators.
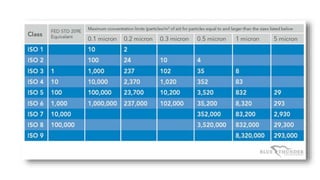
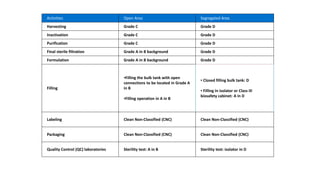
3) Cleanrooms are used in industries like electronics, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology to maximize yield, ensure quality control and product safety. Different cleanroom classes control different variables like temperature, humidity and particles.