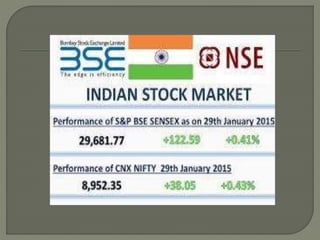
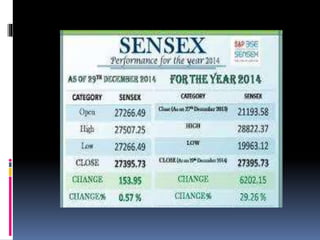
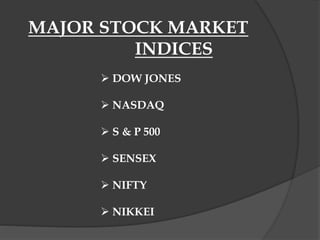
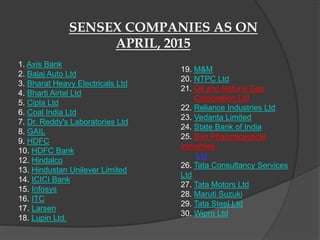
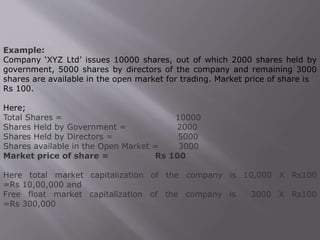
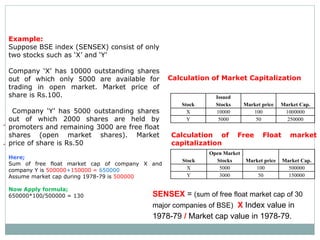
Stock market indices measure the price movements of baskets of stocks selected to represent the overall market. The SENSEX and NIFTY 50 are the major Indian stock market indices, tracking the performance of 30 and 50 largest companies listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange and National Stock Exchange, respectively. Both indices are free-float market capitalization weighted and calculated based on the base value and year. They provide investors a way to track broad market trends and compare company performance.