This document discusses the classification of medicinal and aromatic plants (MAPs) in Nepal based on different criteria. It provides an overview of:
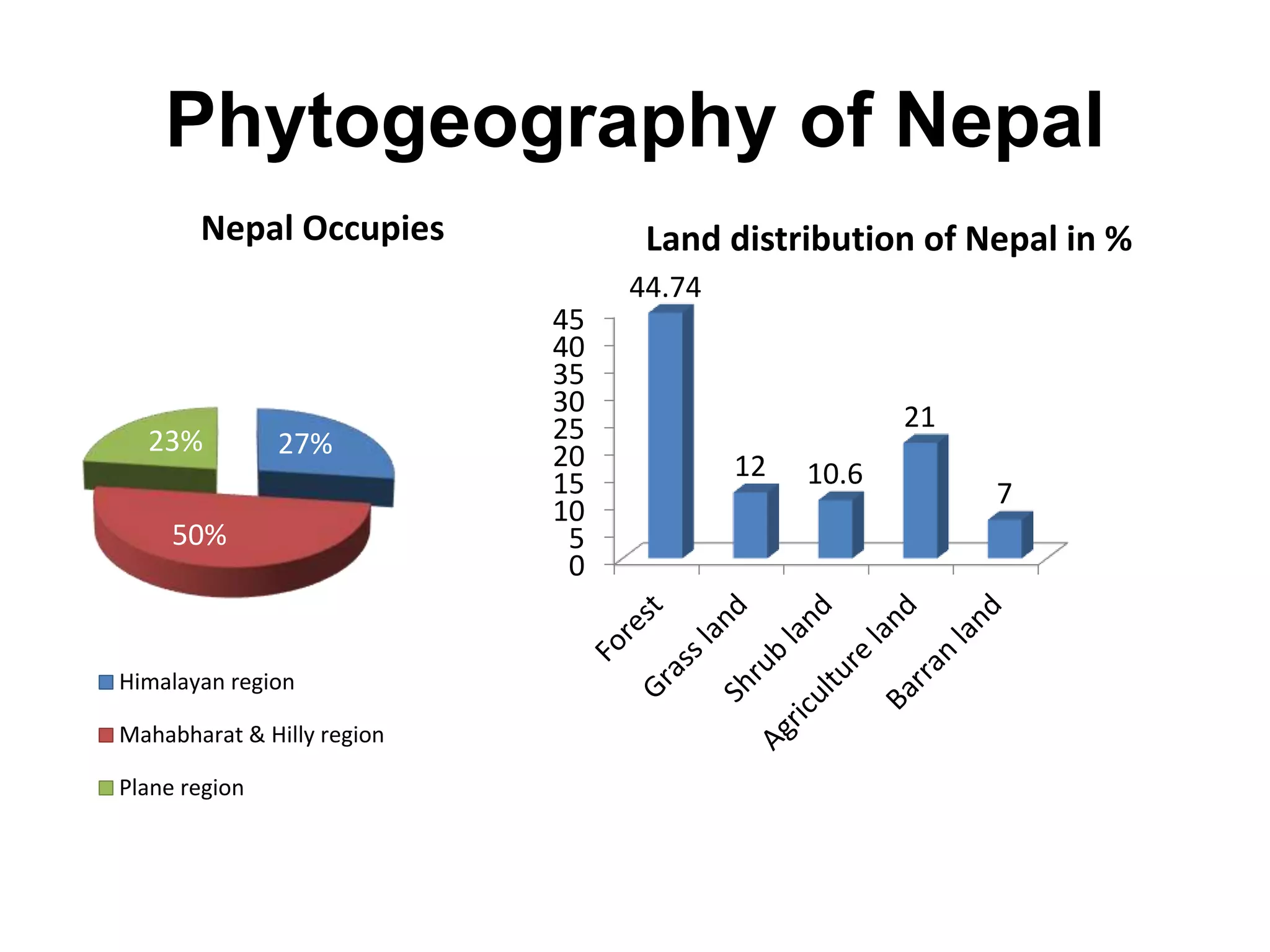
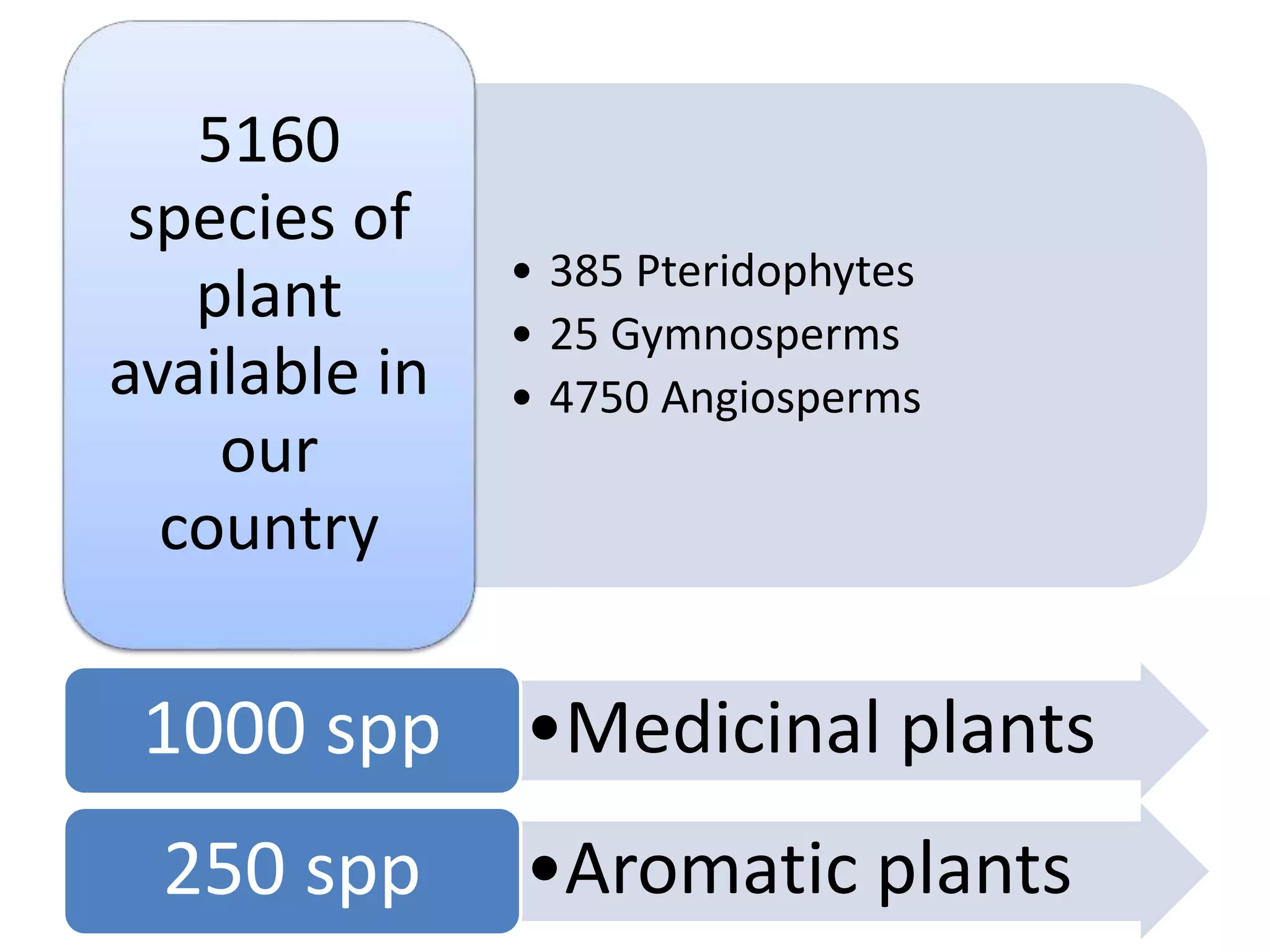
- The distribution of land types in Nepal and the number of plant species found in the country.
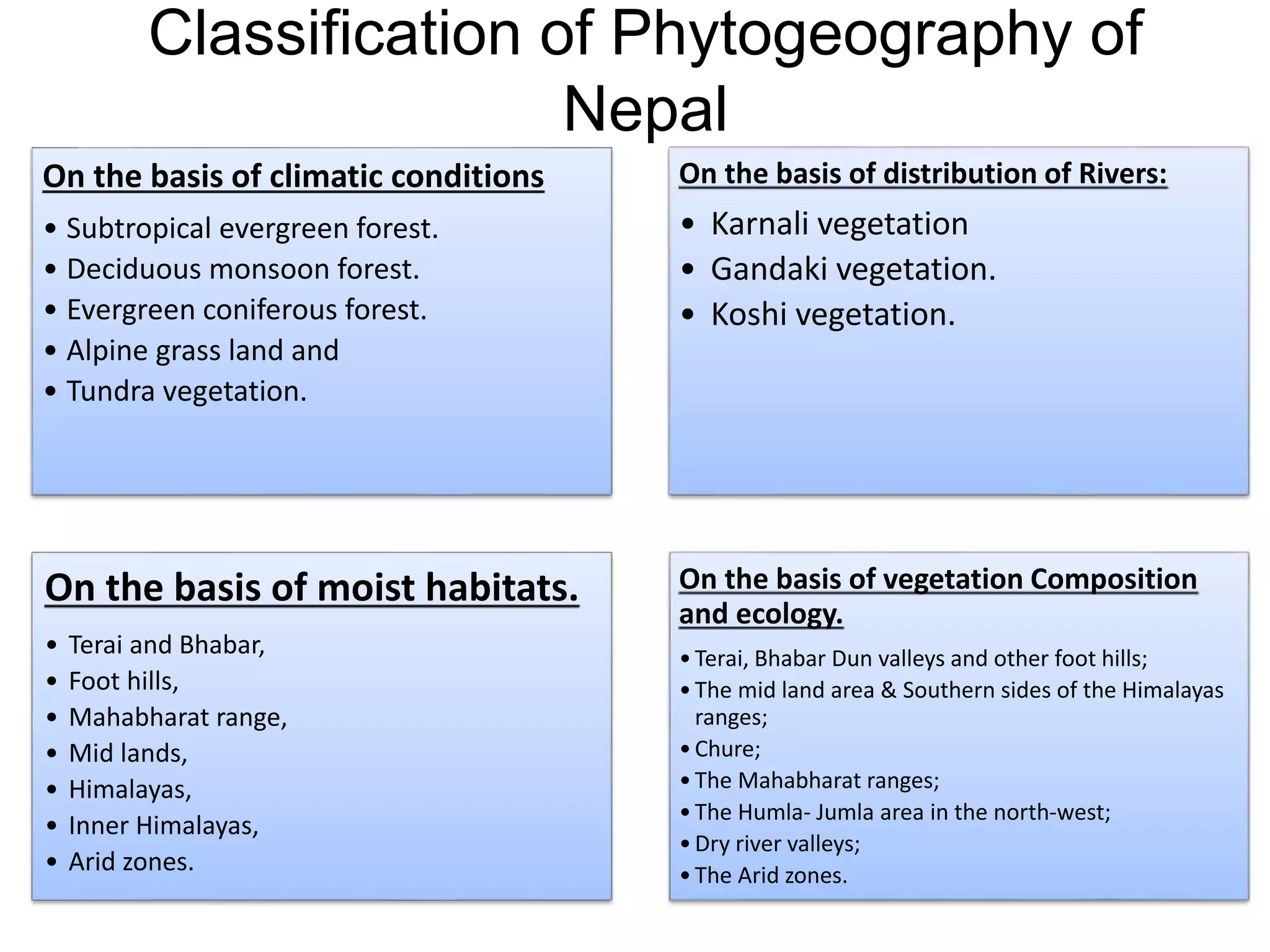
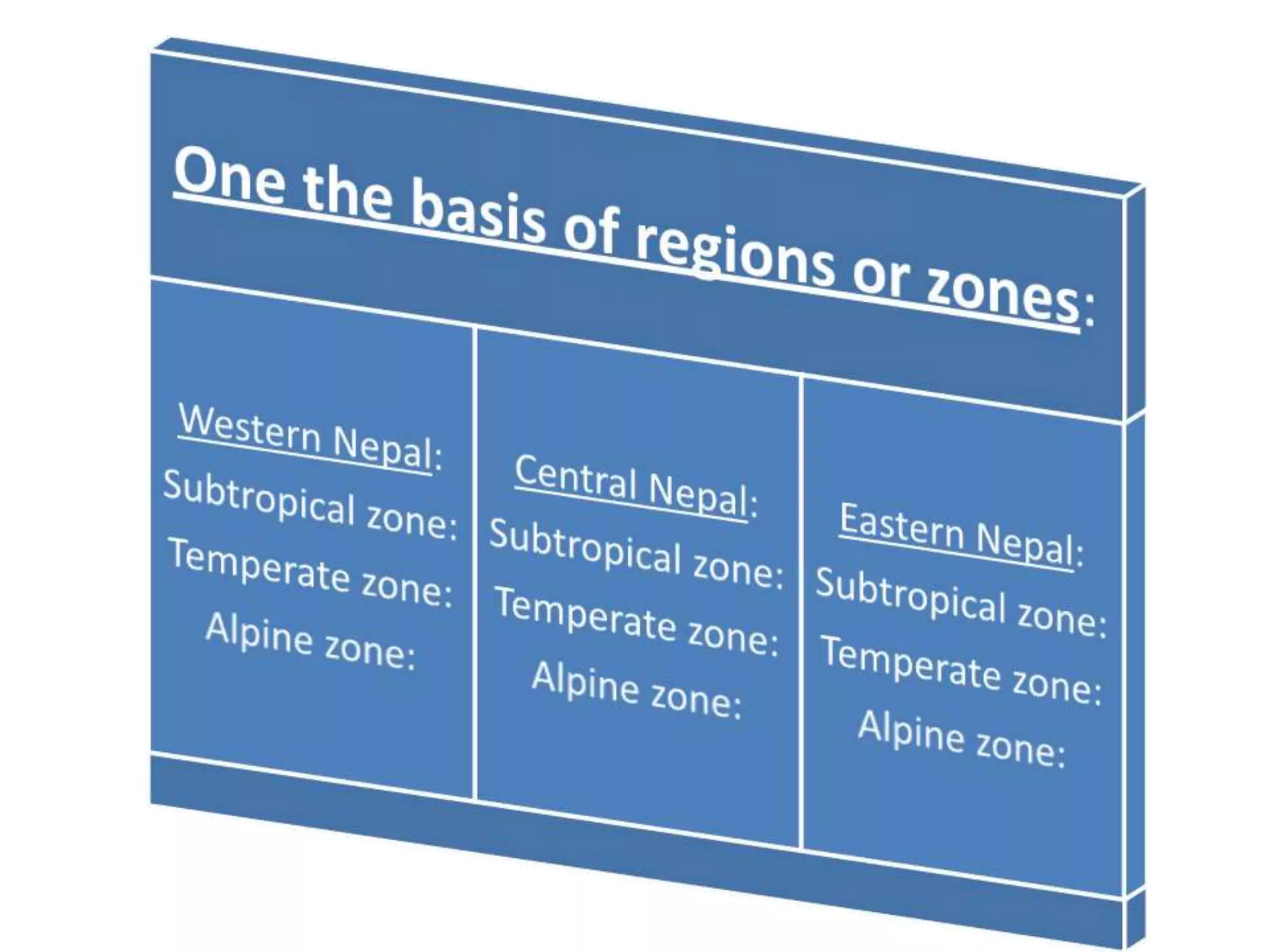
- Classification approaches including by climate/vegetation zones, river distributions, moisture levels, plant composition/ecology.
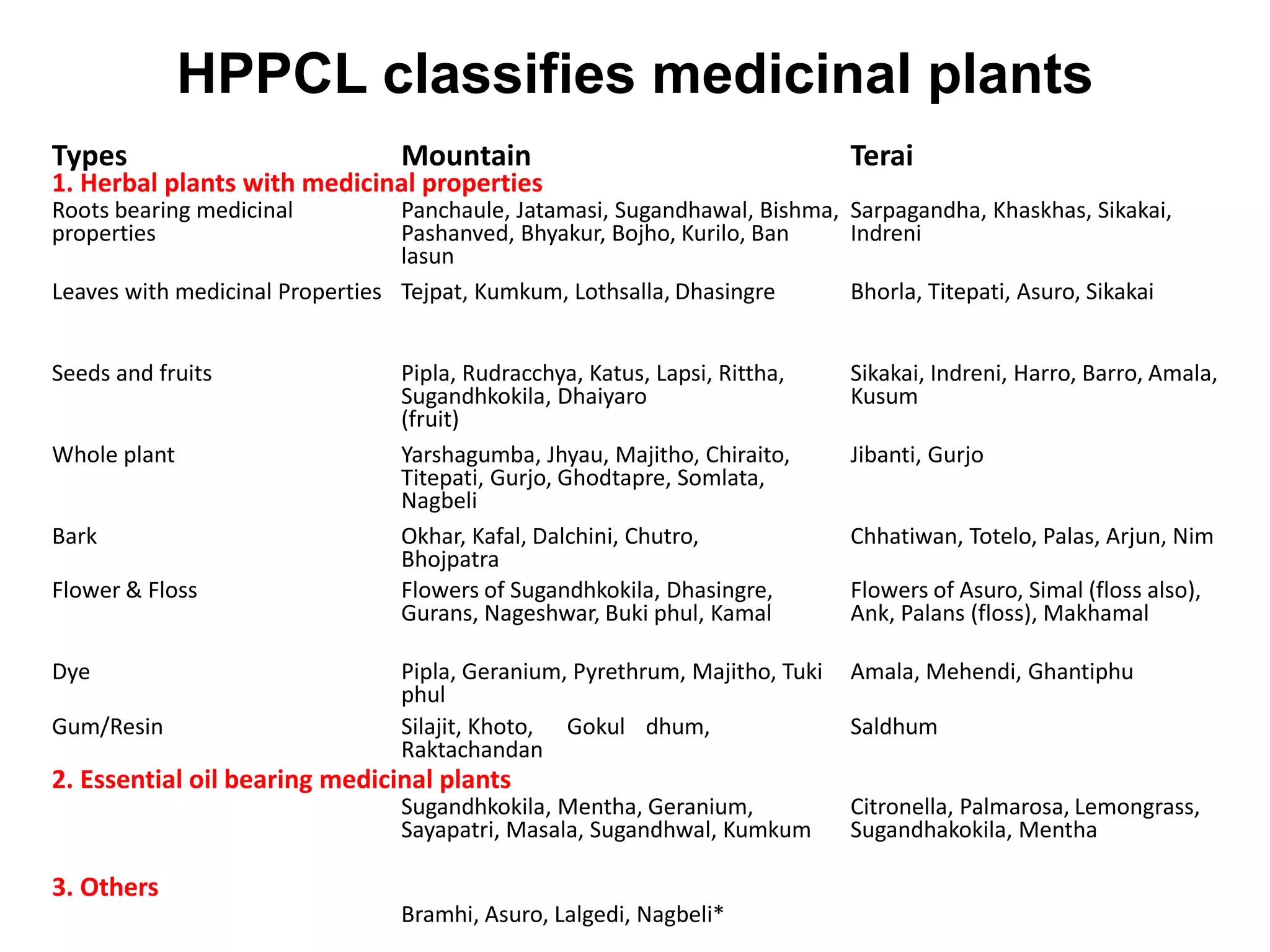
- The types of MAPs classified by the mountain versus Terai regions and parts of plants with medicinal properties.
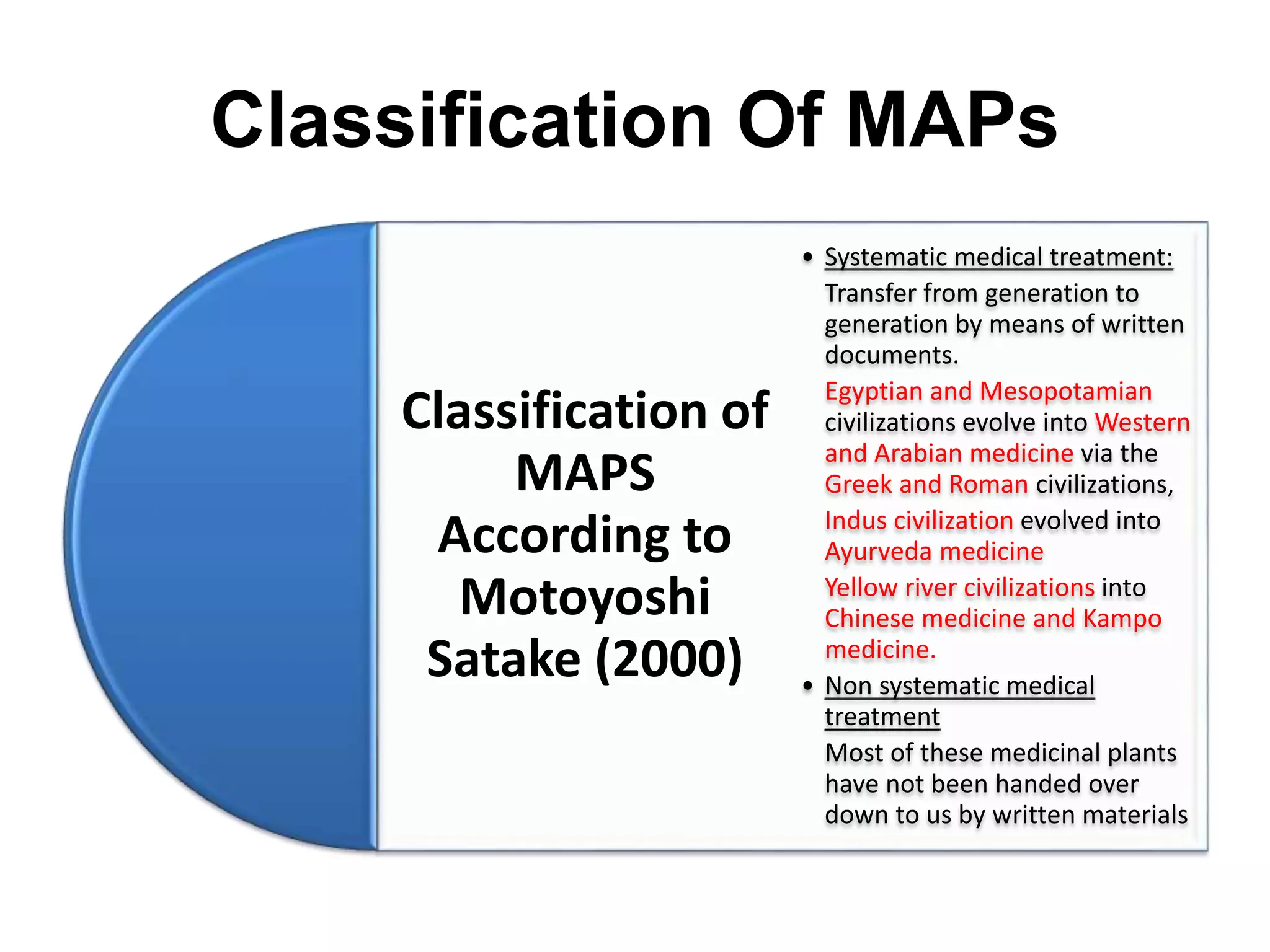
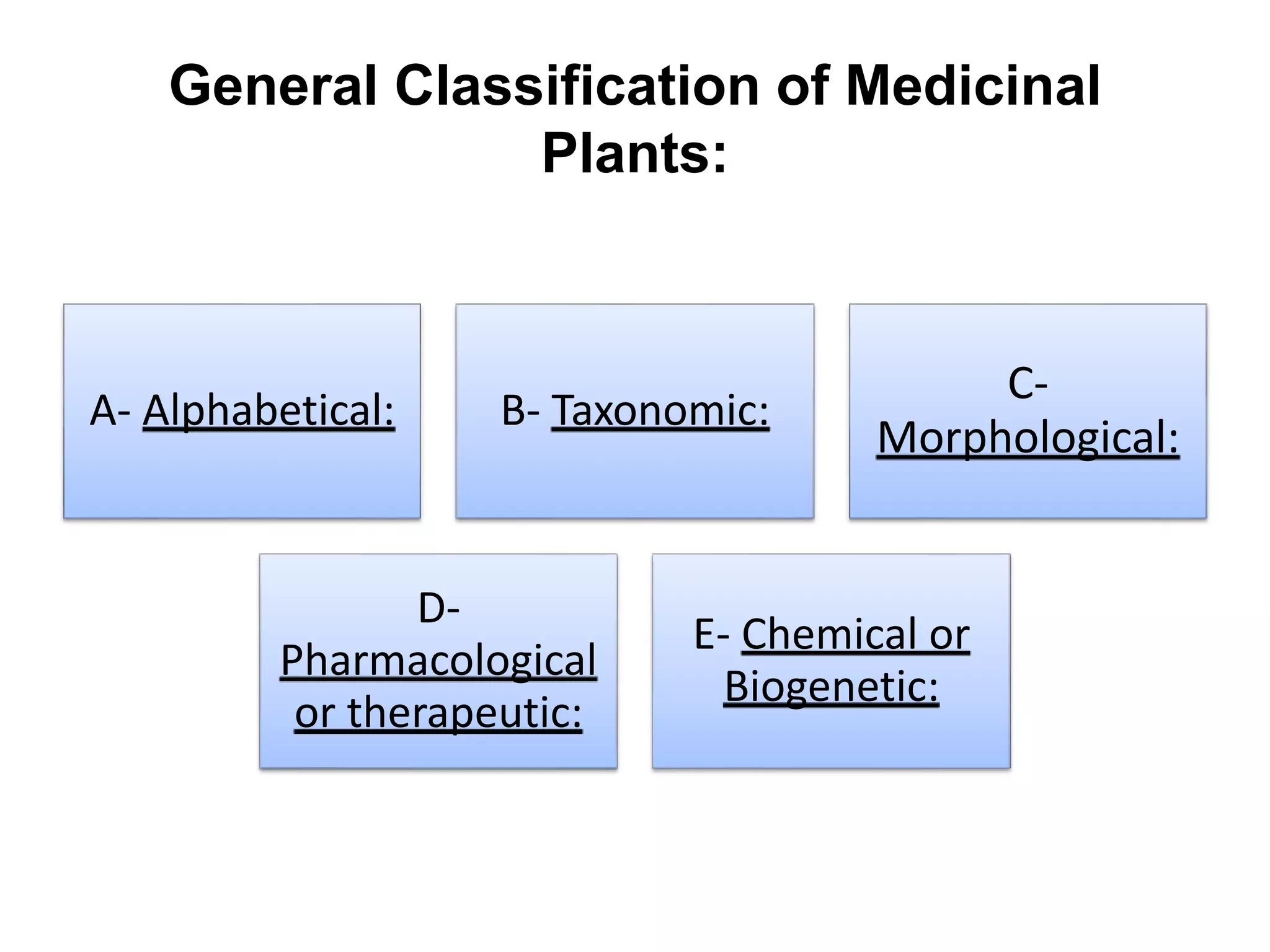
- Additional classification methods like systematic vs. non-systematic treatment, alphabetical, taxonomic, morphological, pharmacological, chemical, and by families.
- Categorization of aromatic plants based on scented parts like