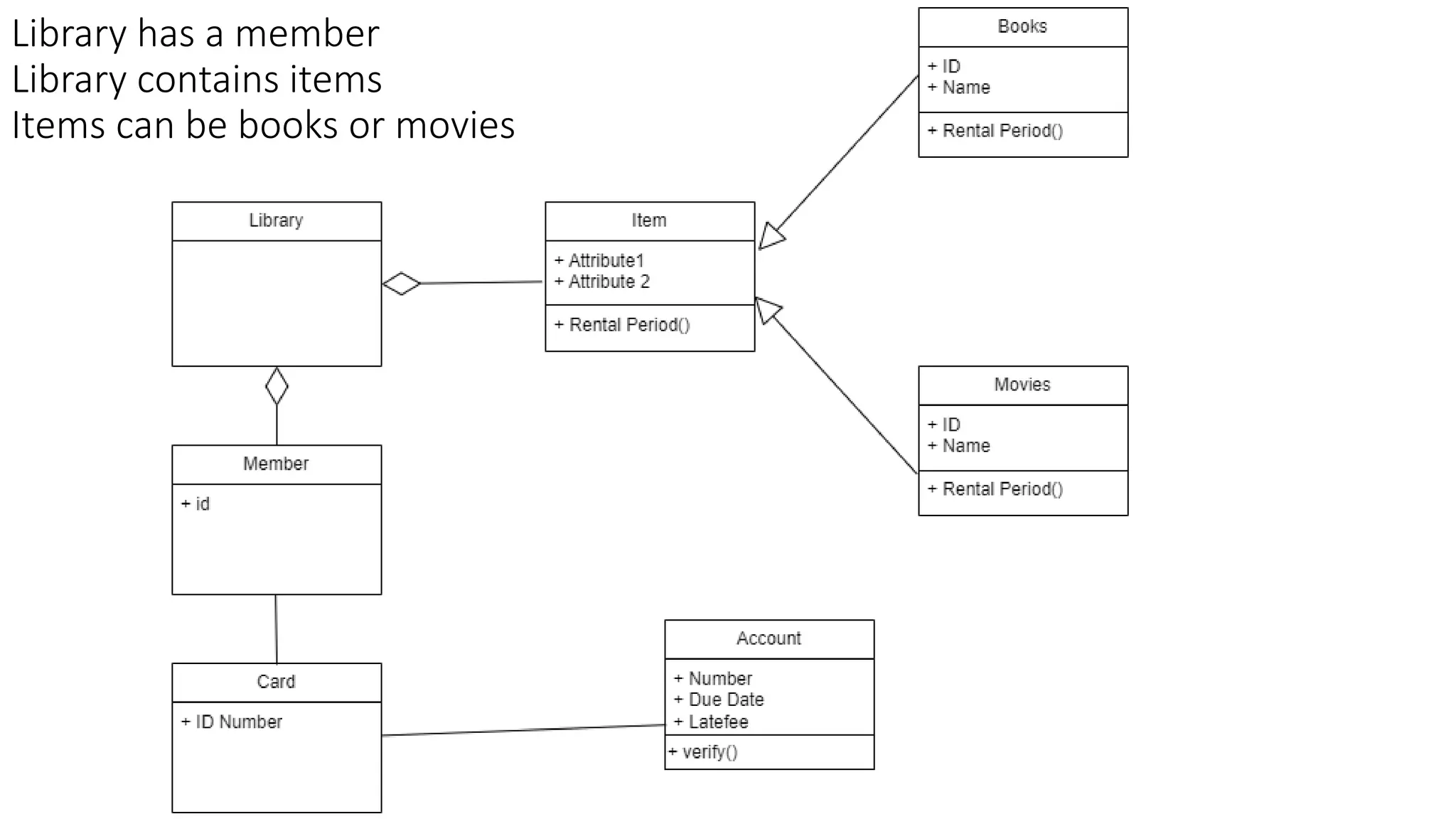
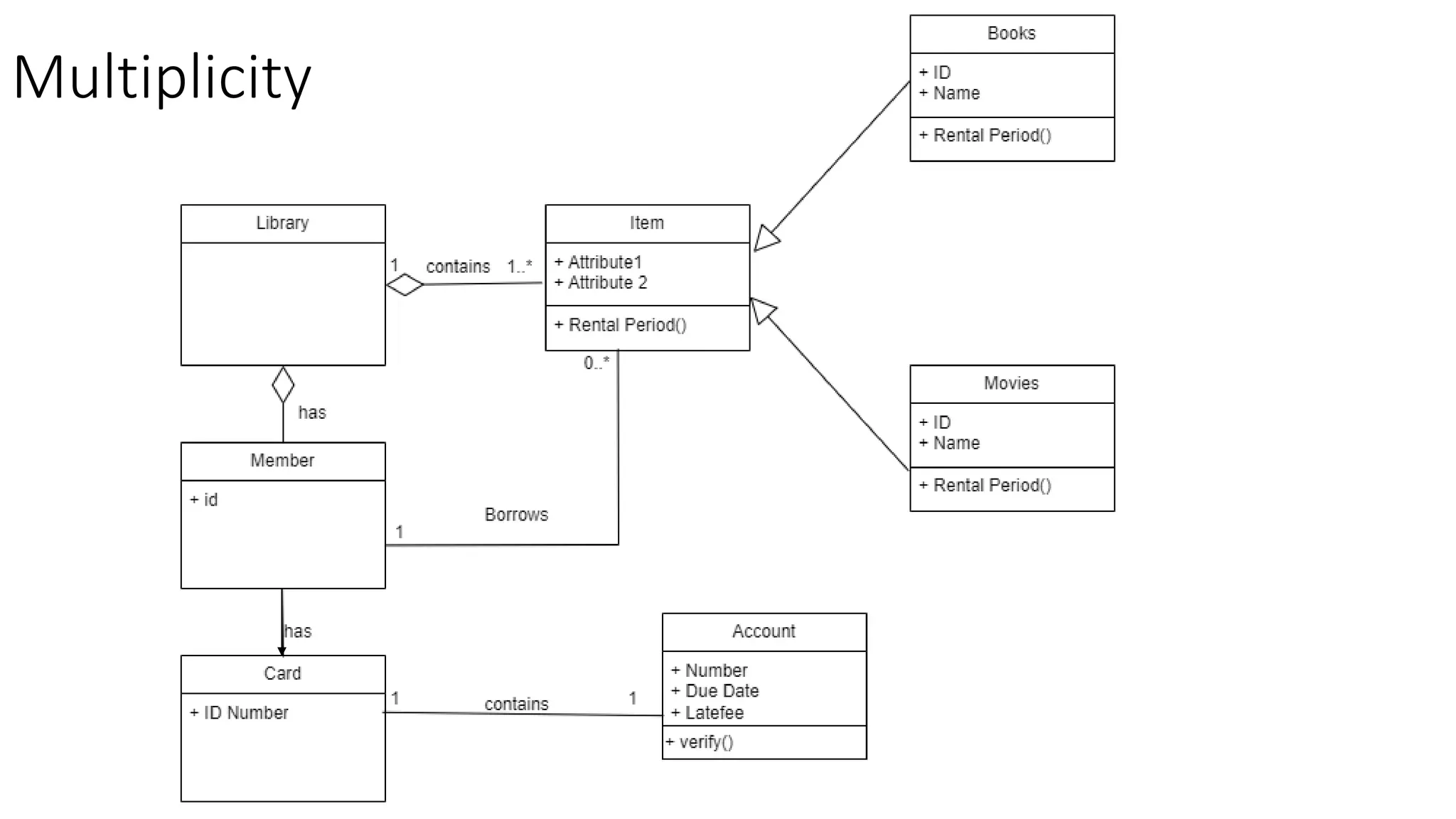
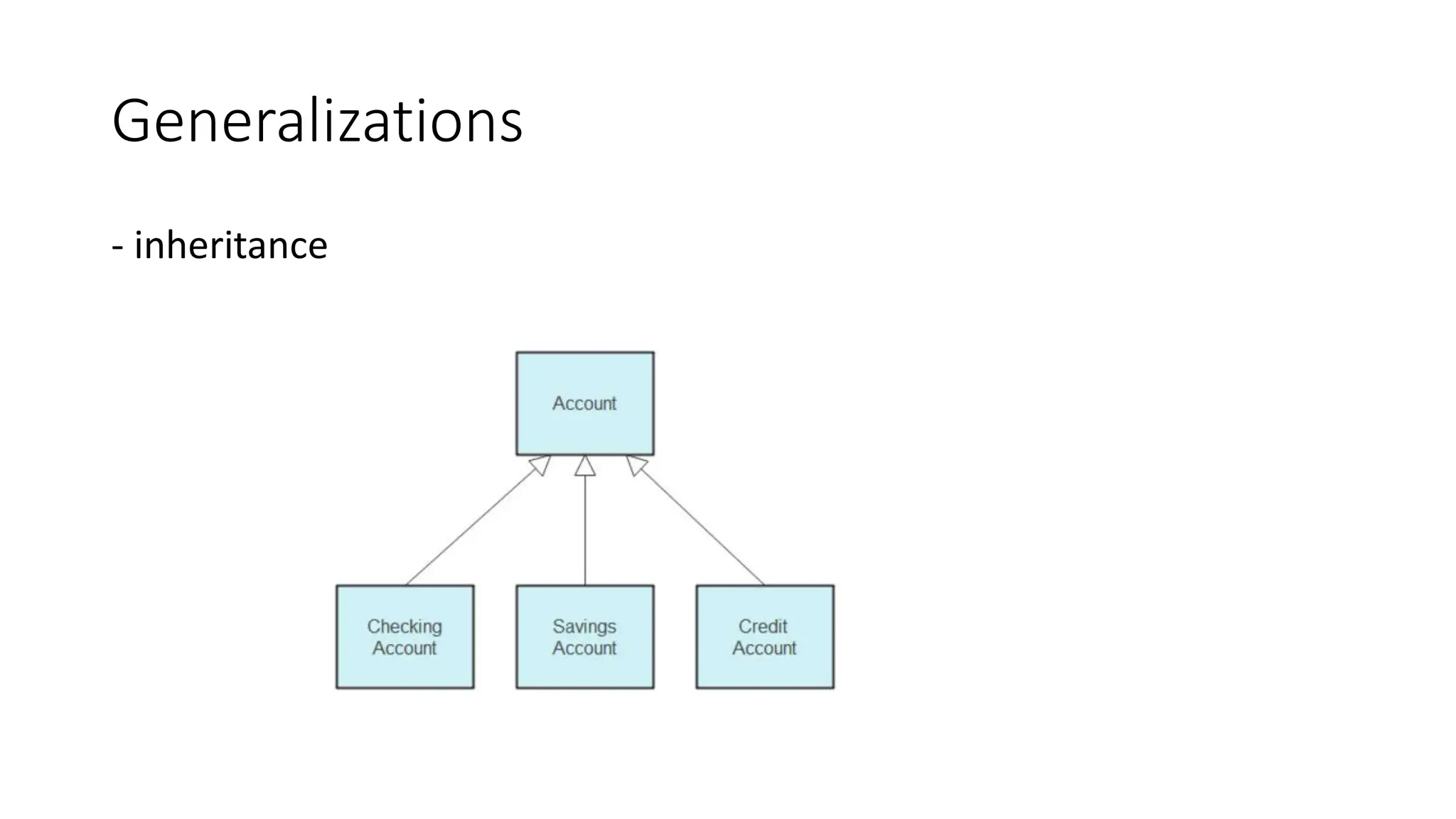
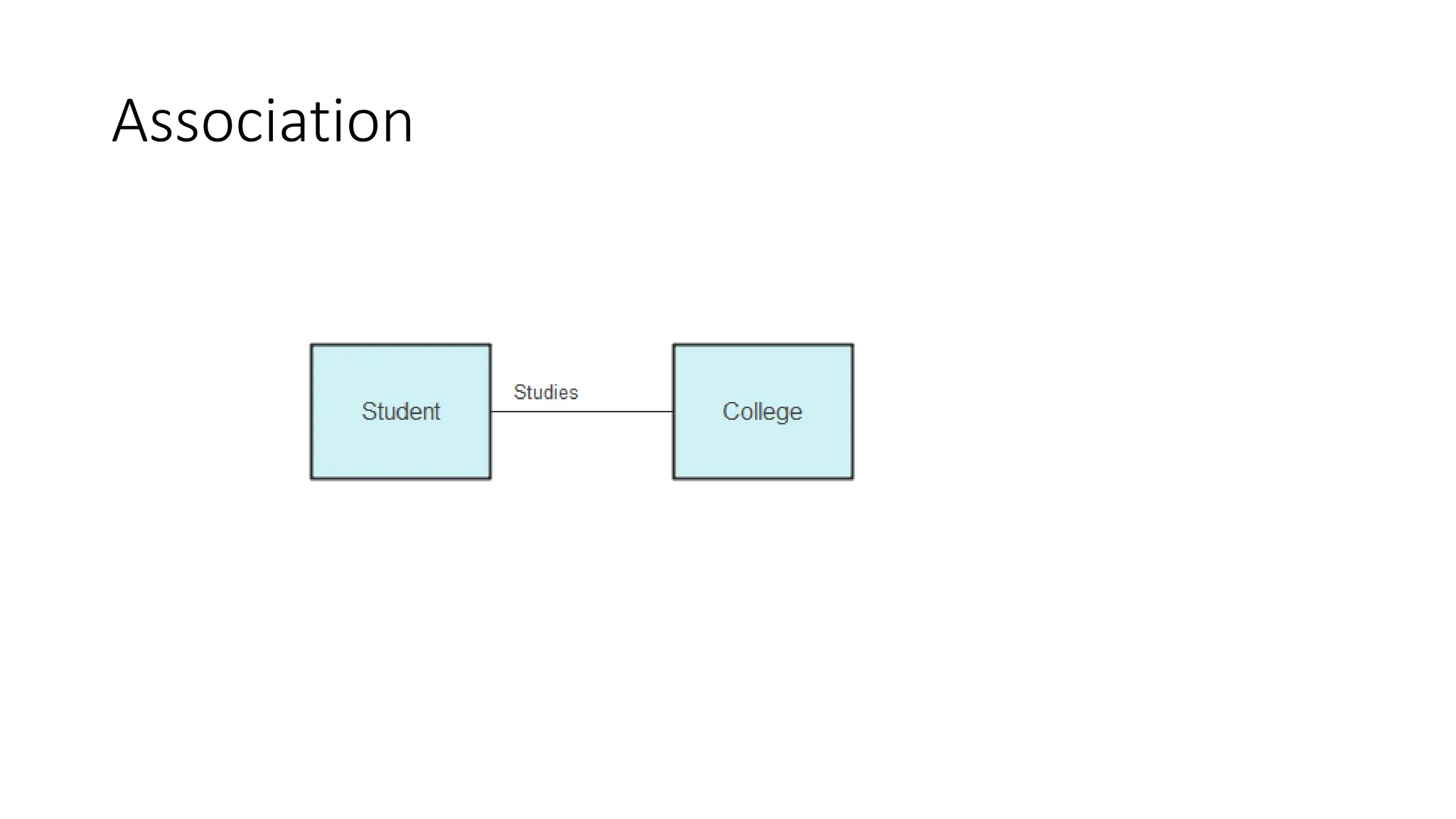
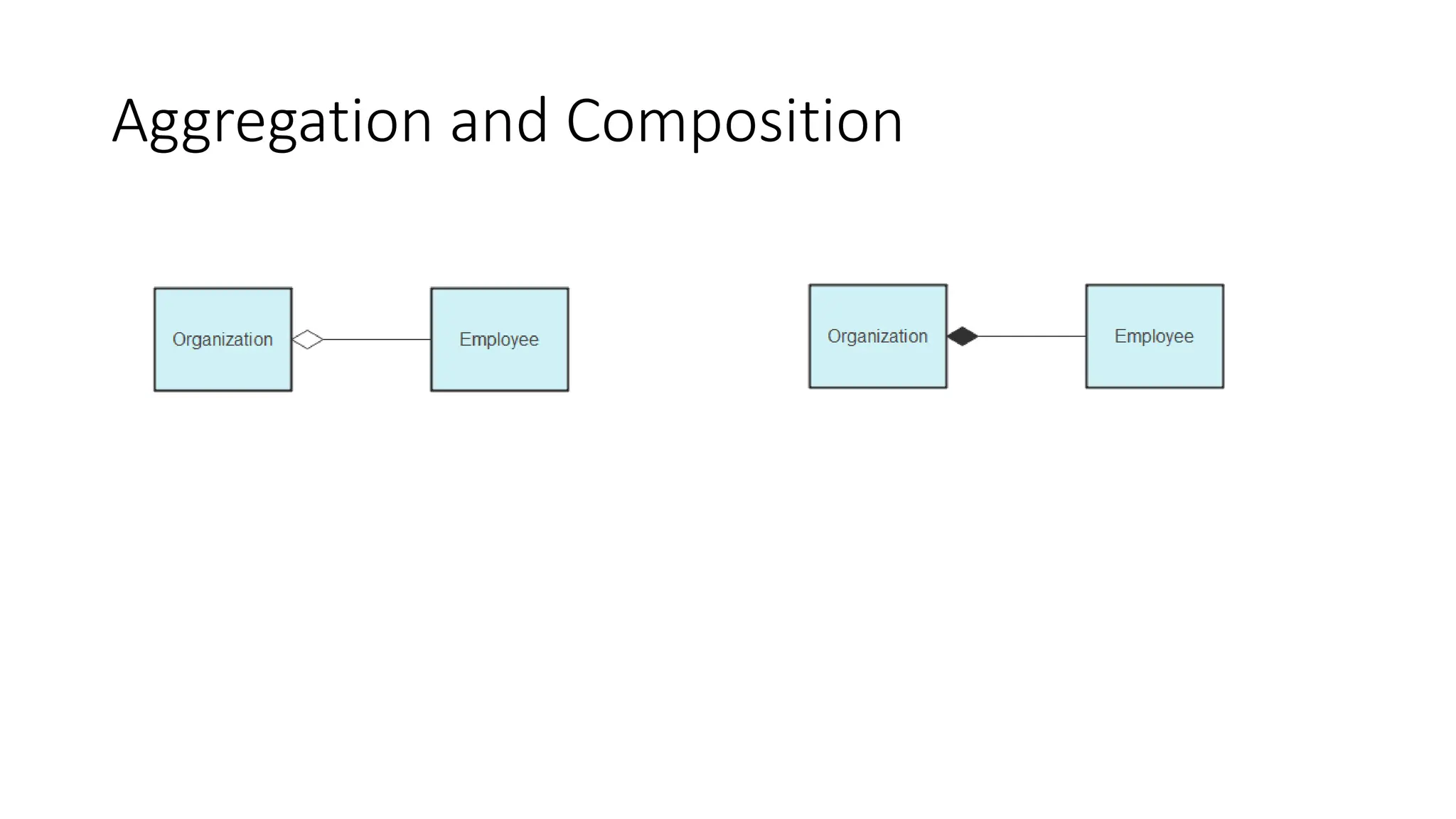
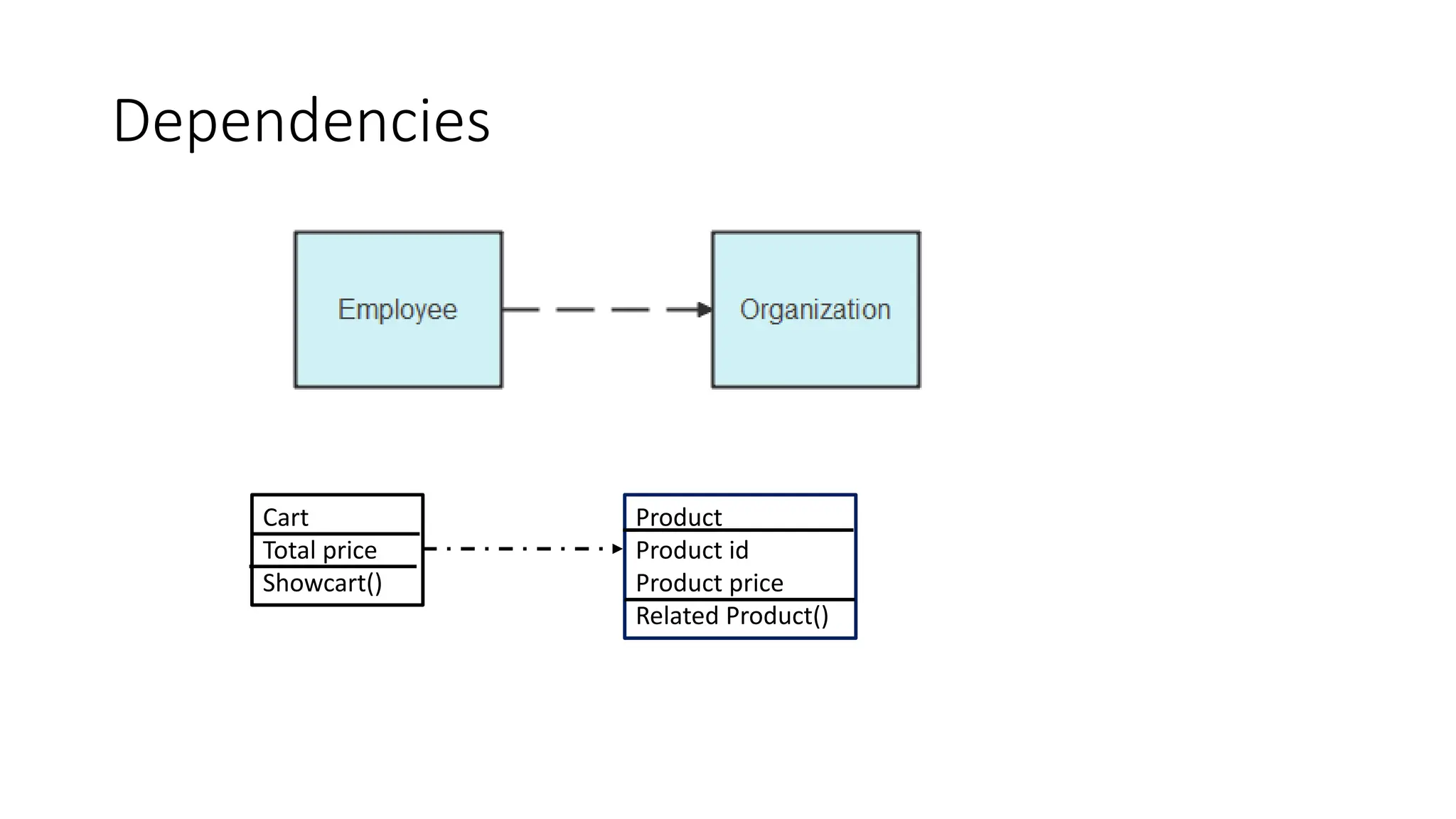
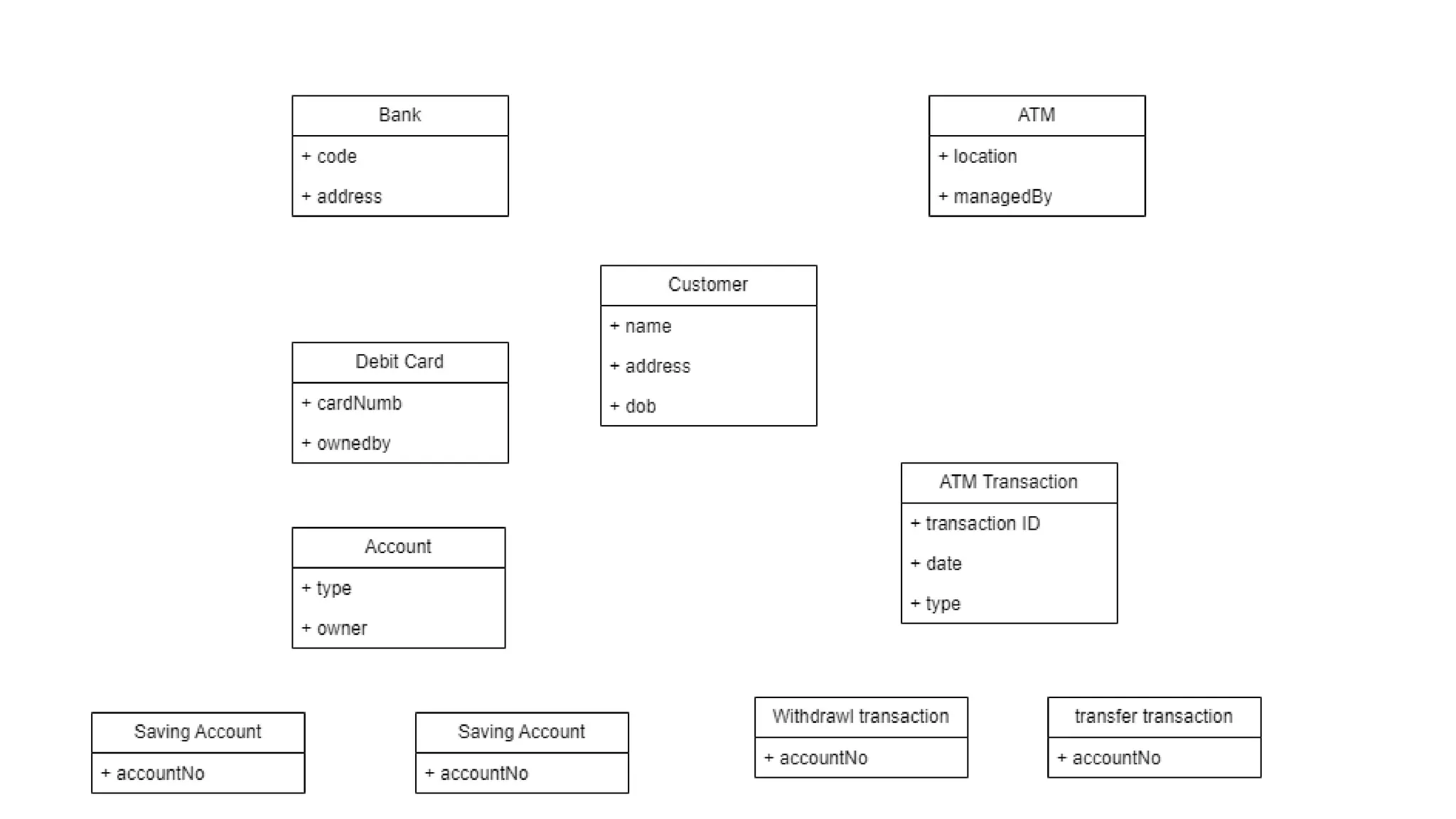
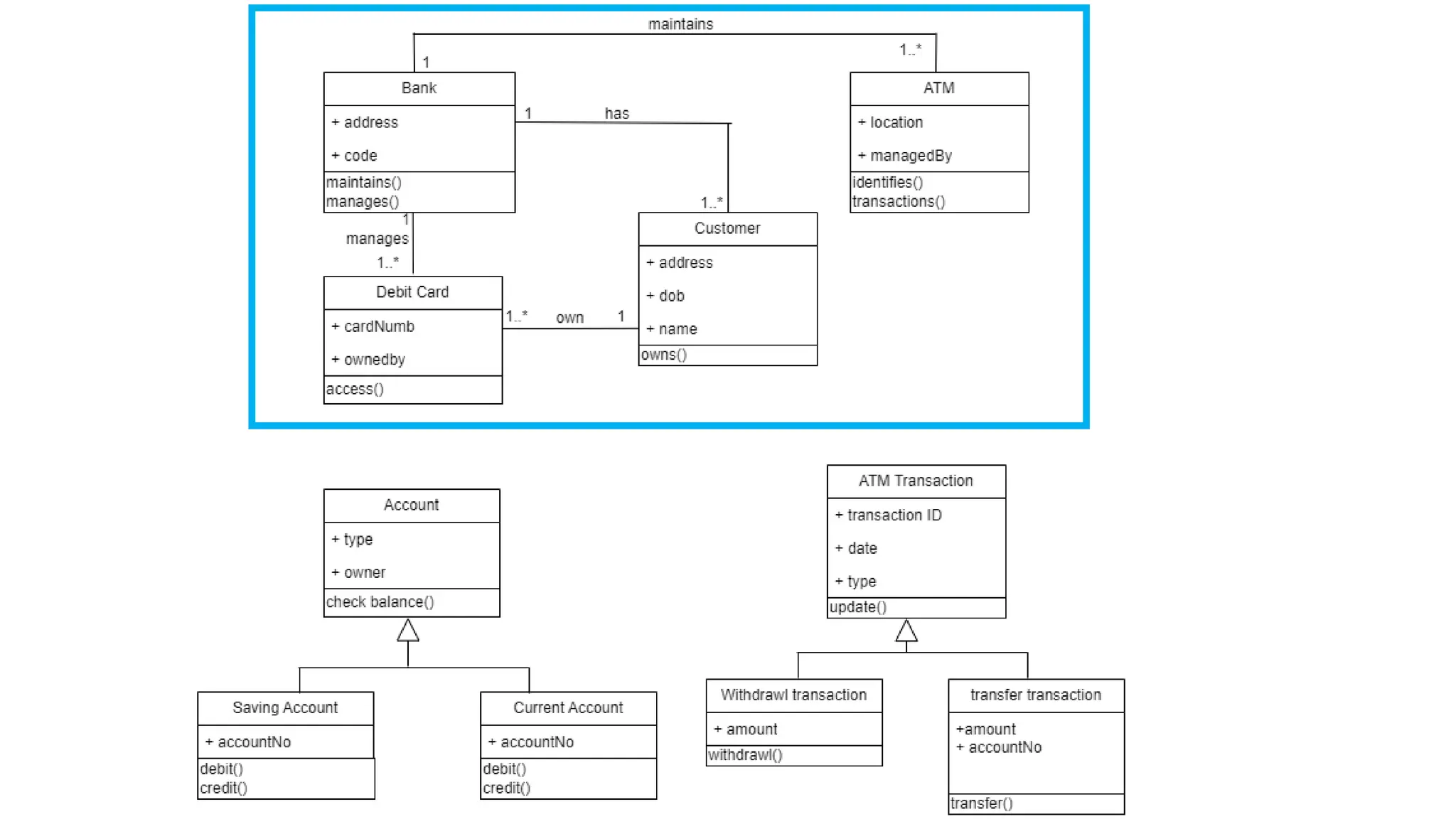
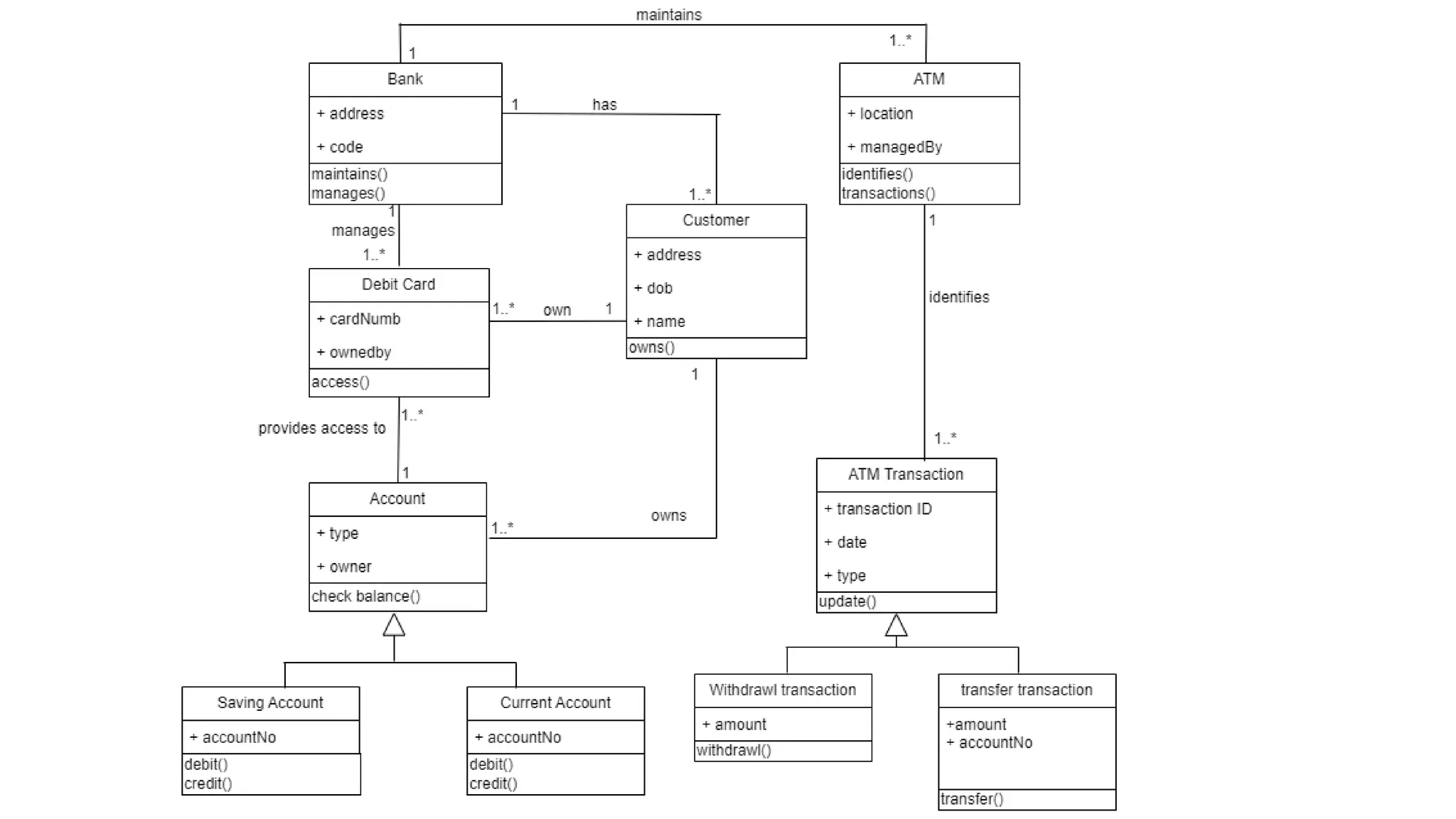
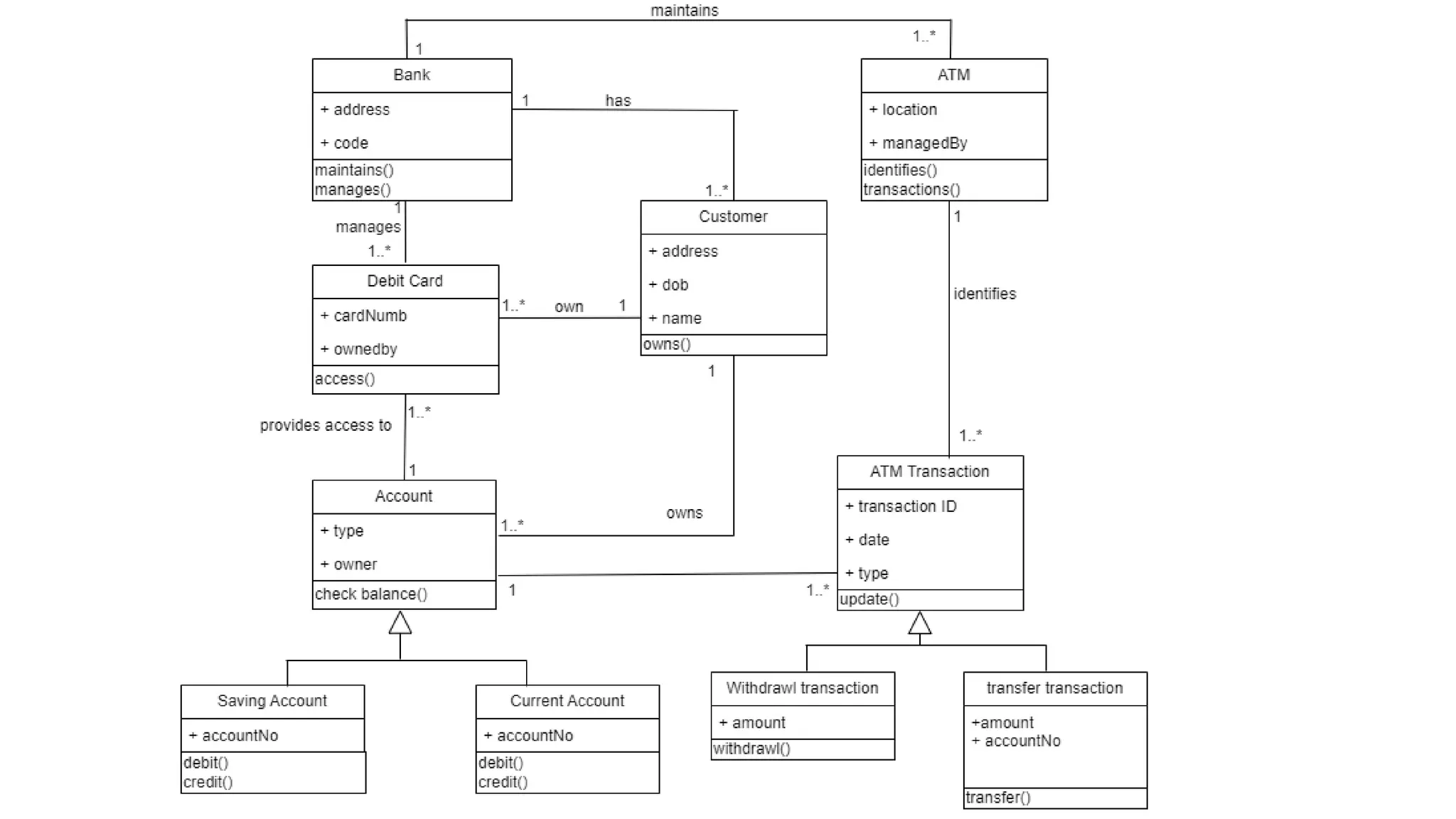
- A class diagram shows the classes, attributes, operations, and relationships between classes in a system.
- It identifies the key classes in a public library system including Library, Member, Item, Book, and Movie.
- The classes have attributes like member ID and account details for Member, rental periods for Items, and relationships like Library containing Items and Member borrowing Items.