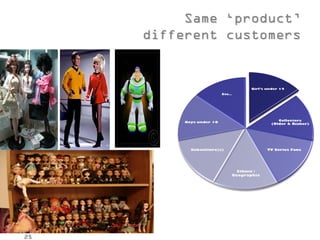
This document provides an introduction to marketing concepts for web 2.0 projects. It discusses what marketing is, how it has evolved beyond just selling, and how the goal is to understand customers and align offerings to create value for both customers and businesses. Good marketing decreases the need for promotion by creating advocates. The document also covers segmentation, targeting, and positioning of customers, and stresses the importance of using market information to make better decisions and justify strategies.