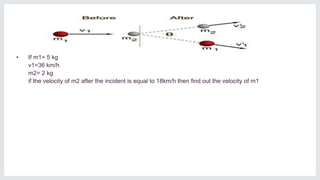
The document discusses fundamental concepts in Newtonian physics, specifically focusing on kinematics and dynamics. It covers Newton's laws of motion, the concept of inertia, momentum conservation, and impulse related to force application. Several examples and calculations related to motion and forces are also provided to illustrate these principles.