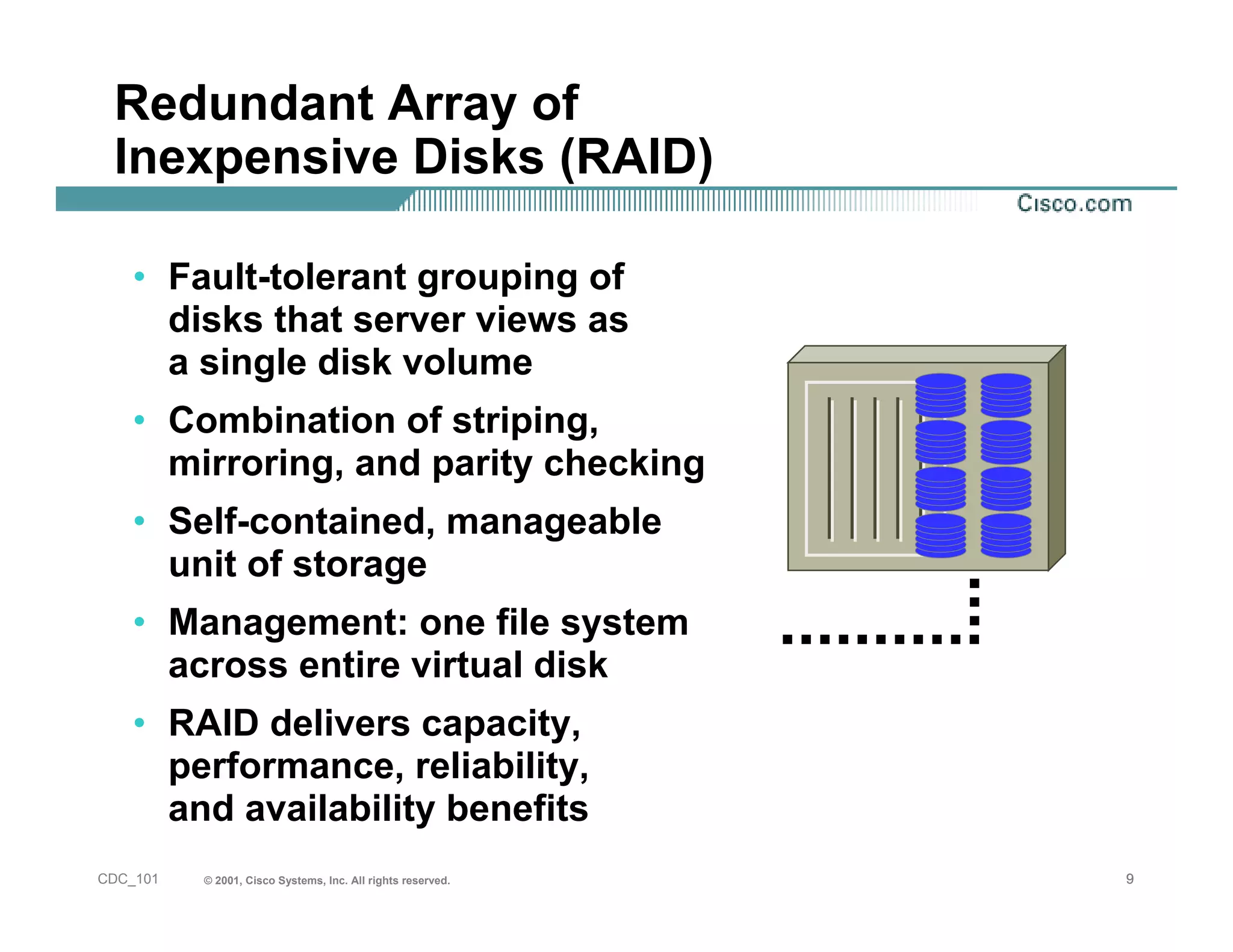
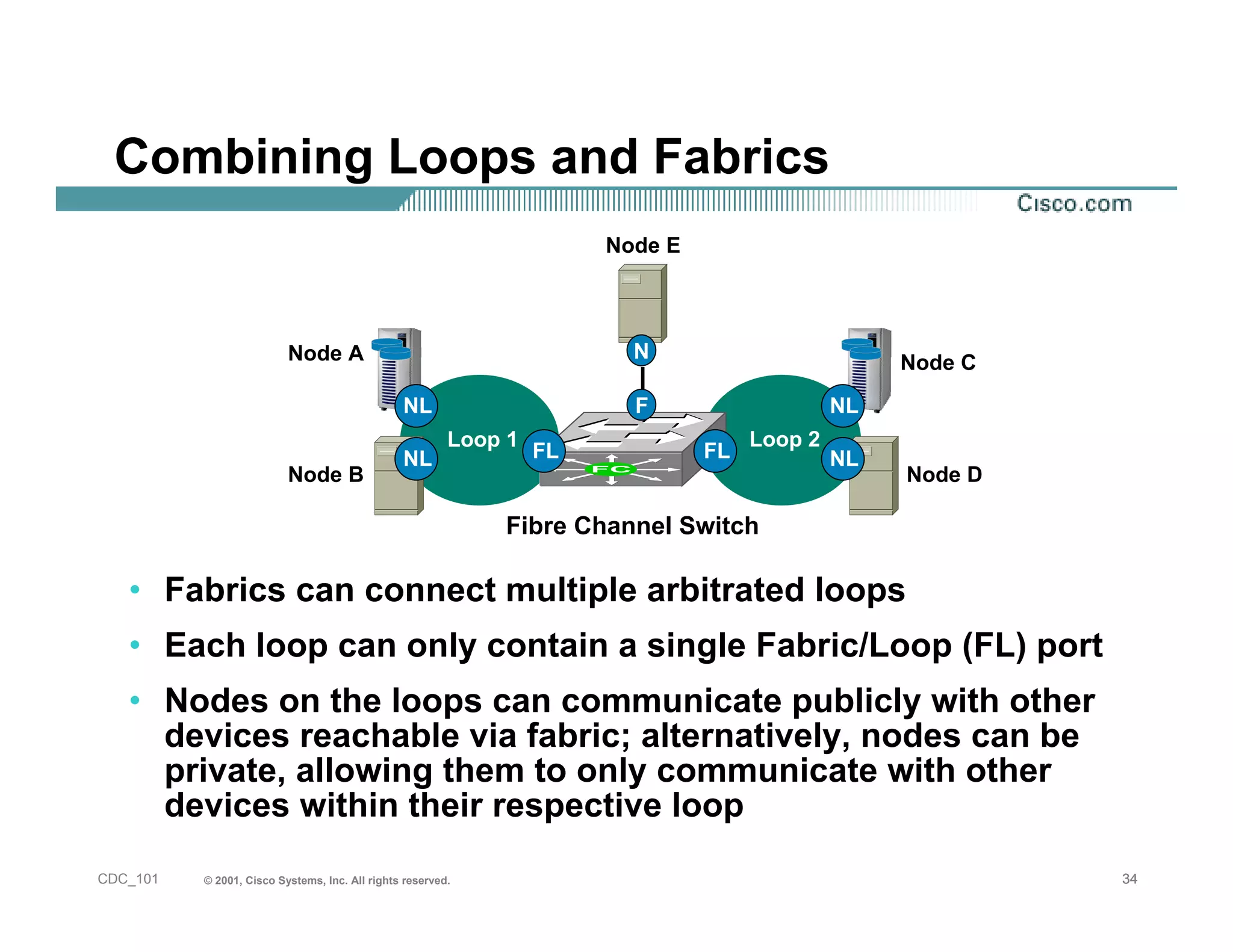
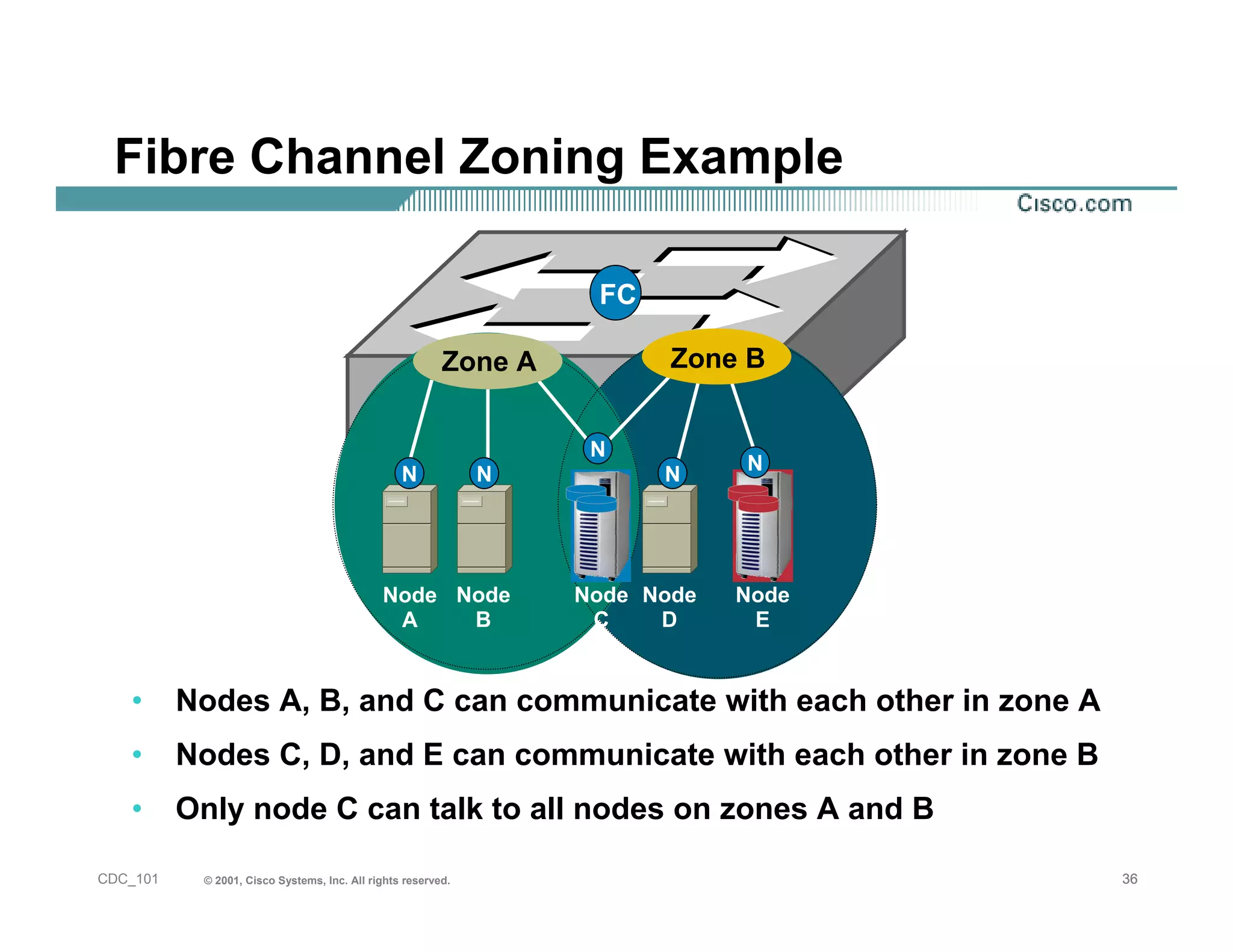
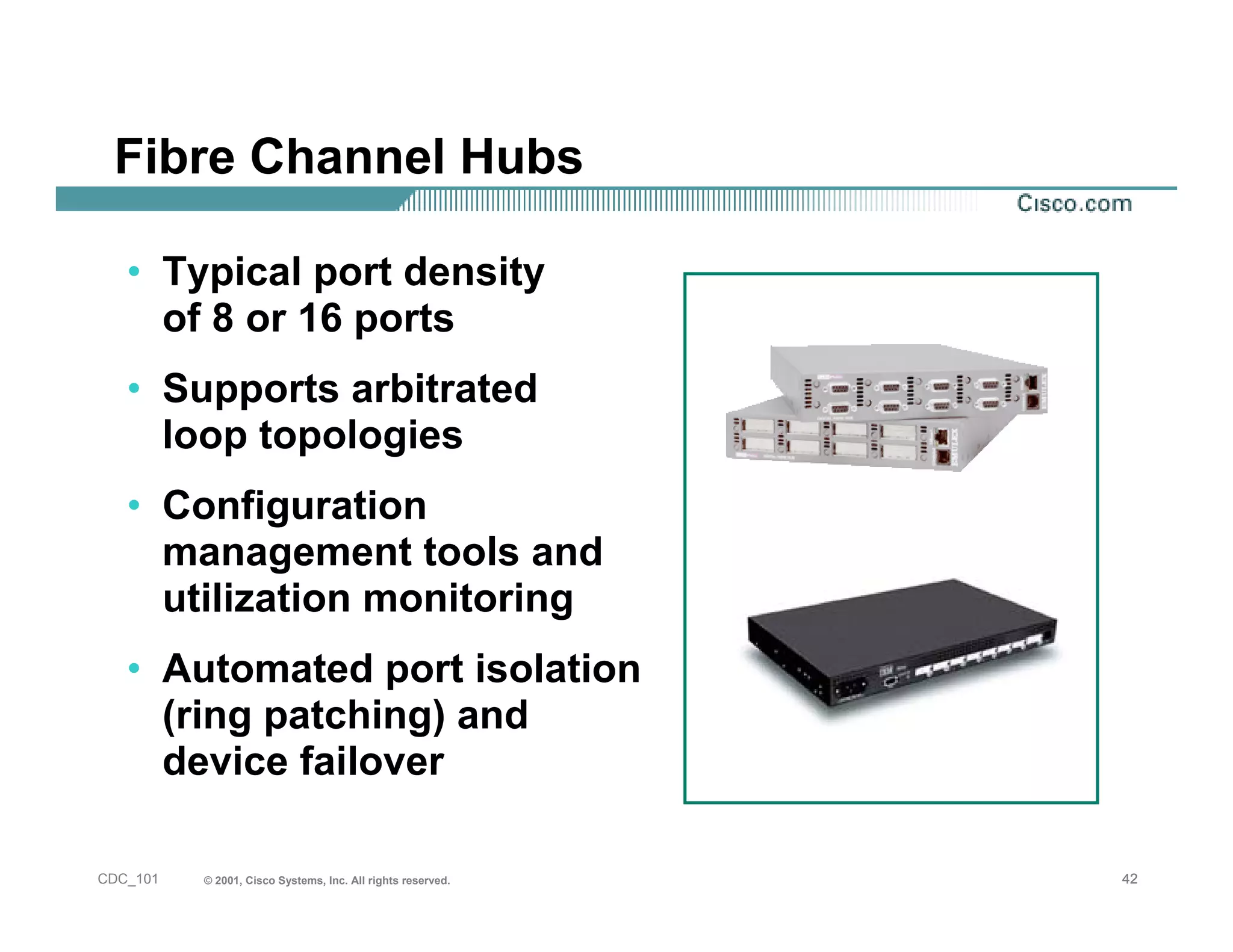
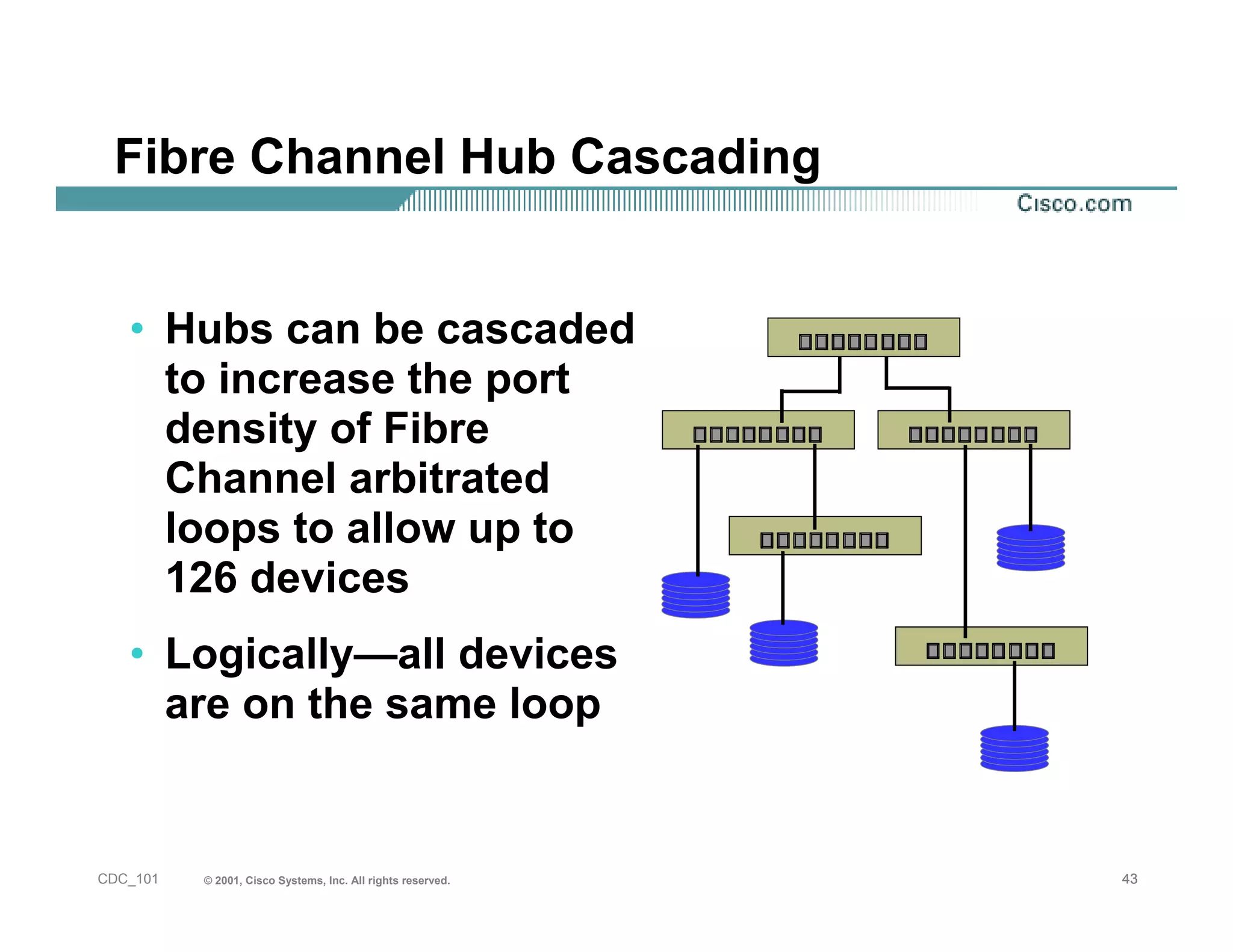
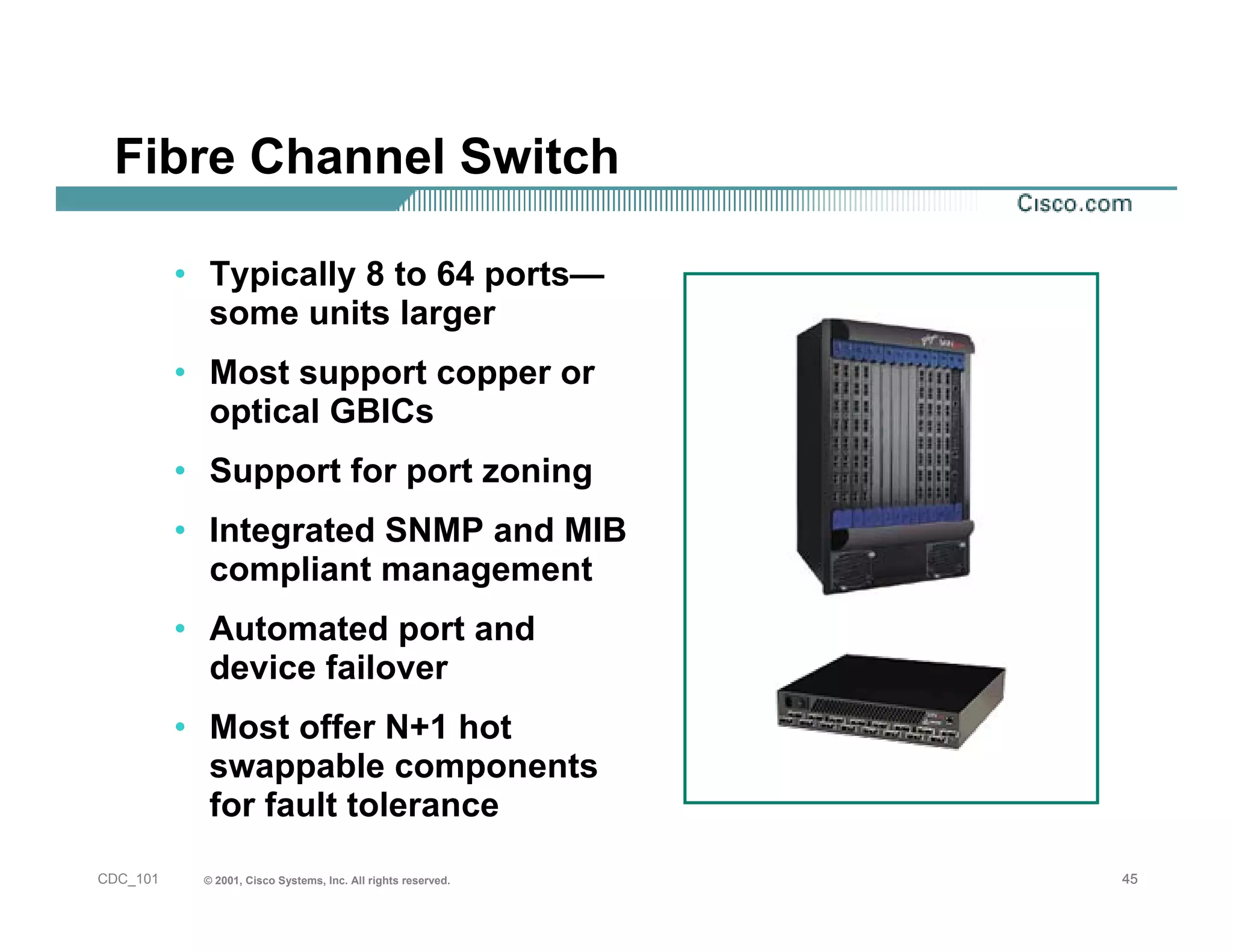
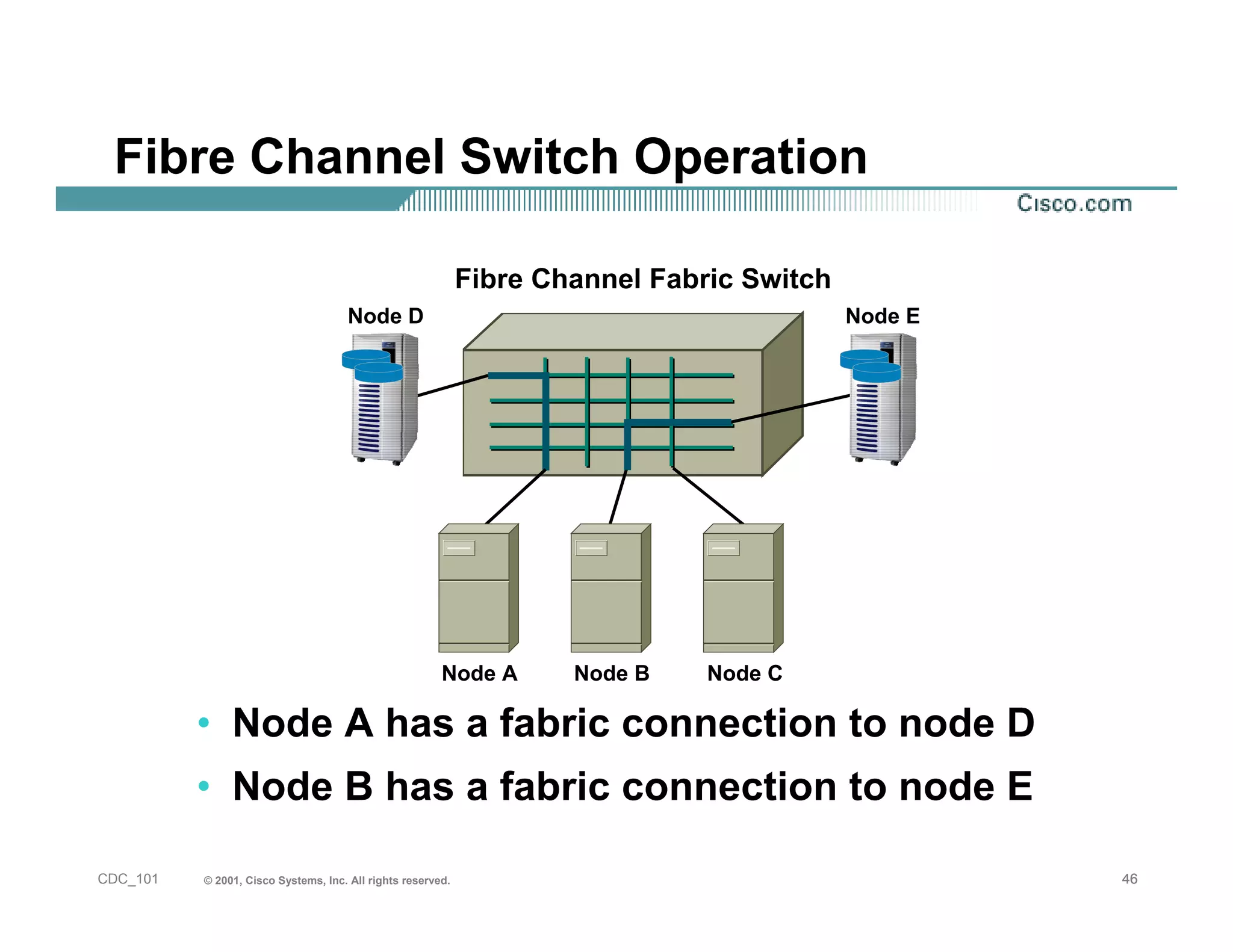
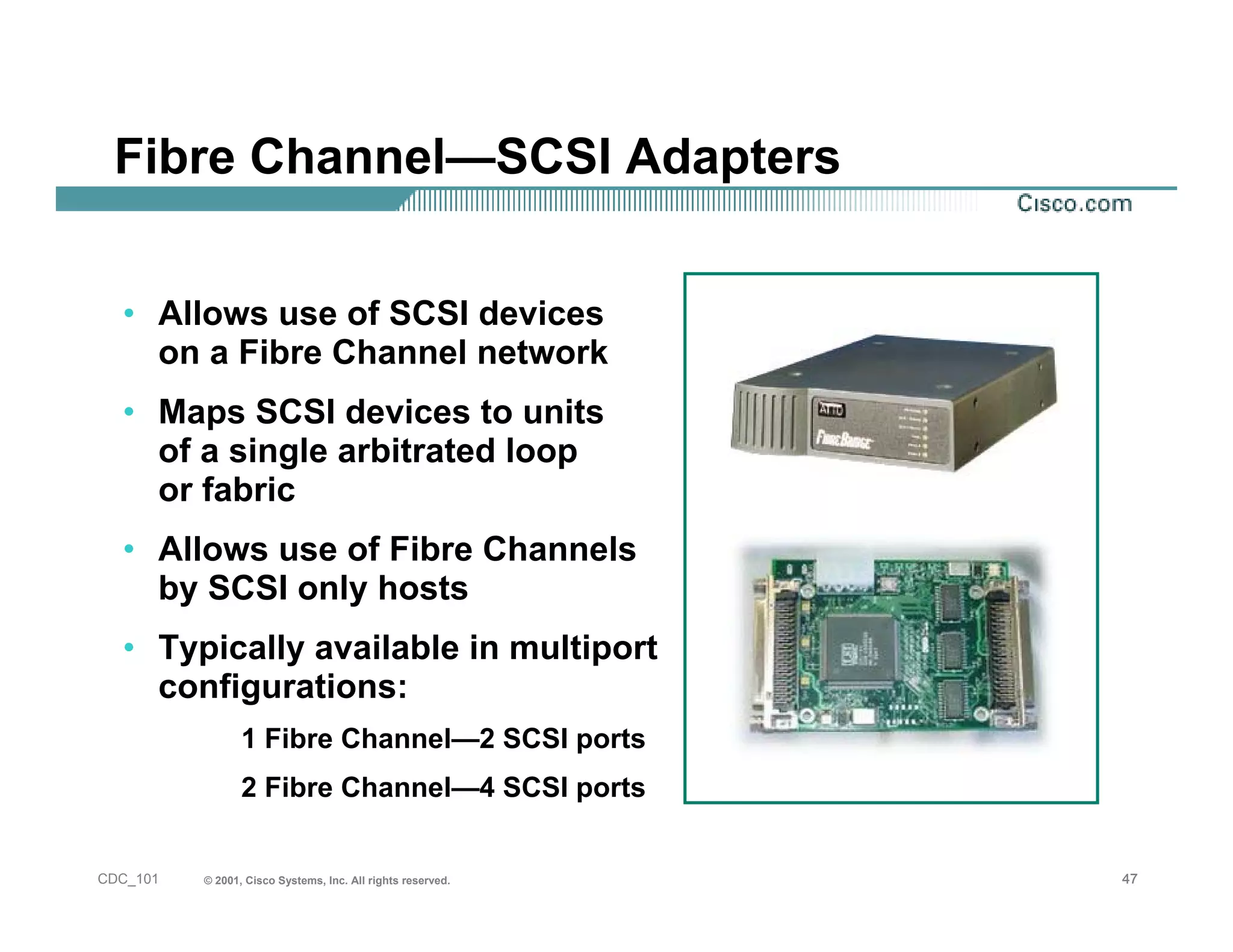
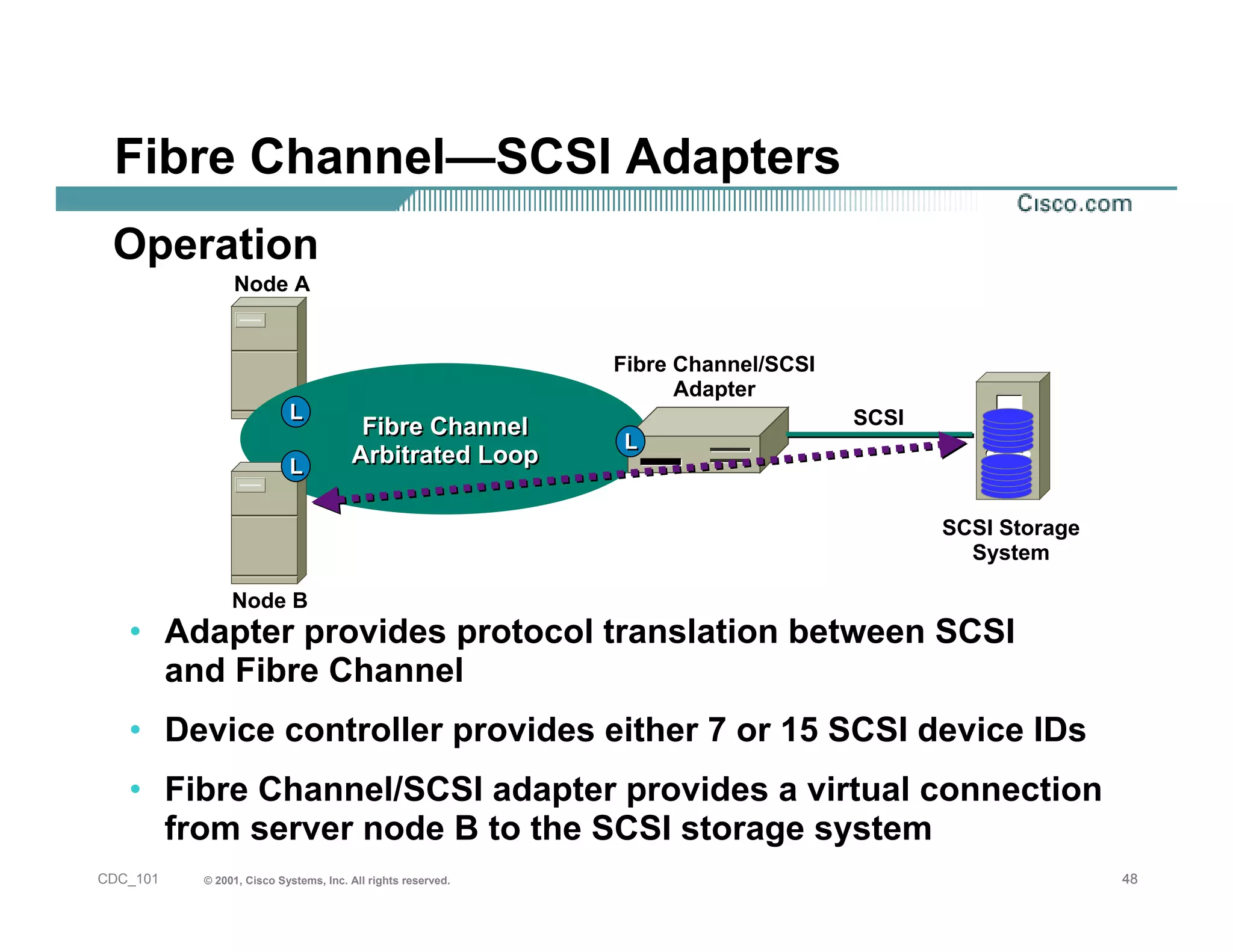
The document provides an in-depth overview of storage networking, highlighting the basics of storage technologies, as well as the distinctions between Storage Area Networks (SAN) and Network Attached Storage (NAS). It covers key components of SAN, including fibre channel connectivity and its applications, along with the advantages of scalability, reliability, and centralized management. Additionally, it discusses the implications of various architectures, protocols, and the current developments in the storage networking landscape.