Circuitos ELECTRICOS EJEMPLOS TAREA ELECTRICIDAD Y MAGNETISMO
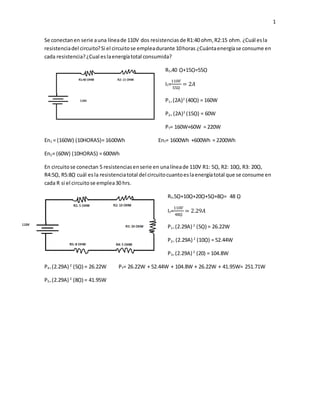
- 1. 1 Se conectanen serie auna líneade 110V dos resistenciasde R1:40 ohm, R2:15 ohm. ¿Cuál esla resistenciadel circuito?Si el circuitose empleadurante 10horas ¿Cuántaenergíase consume en cada resistencia?¿Cual eslaenergíatotal consumida? RT=40 ῼ+15ῼ=55ῼ IT= 110𝑉 55ῼ = 2𝐴 P1= (2A)2 (40ῼ) = 160W P2= (2A)2 (15ῼ) = 60W PT= 160W+60W = 220W En1 = (160W) (10HORAS)= 1600Wh EnT= 1600Wh +600Wh = 2200Wh En2= (60W) (10HORAS) = 600Wh En circuitose conectan 5 resistenciasenserie en unalíneade 110V R1: 5ῼ, R2: 10ῼ, R3: 20ῼ, R4:5ῼ, R5:8ῼ cuál esla resistenciatotal del circuitocuantoeslaenergíatotal que se consume en cada R si el circuitose emplea30 hrs. RT=5ῼ+10ῼ+20ῼ+5ῼ+8ῼ= 48 ῼ IT= 110𝑉 48ῼ = 2.29𝐴 P1= (2.29A) 2 (5ῼ) = 26.22W P2= (2.29A) 2 (10ῼ) = 52.44W P3= (2.29A) 2 (20) = 104.8W P4= (2.29A) 2 (5ῼ) = 26.22W PT= 26.22W + 52.44W + 104.8W + 26.22W + 41.95W= 251.71W P5= (2.29A) 2 (8ῼ) = 41.95W
- 2. 2 CALCULAR RT ,IT , PT , RT= 10ῼ + 20ῼ + 5ῼ + 7ῼ= 42ῼ IT= 110𝑉 42ῼ = 2.61𝐴 PT= 110V ( 2.69A)= 295.9W CALCULAR RT ,IT , PT , Y LA POTENCIA DE CADA R RT=20ῼ+30ῼ+5ῼ= 55ῼ IT= 110𝑉 55ῼ = 2𝐴 P1= (2A) 2 (20ῼ) = 80W P2= (2A) 2 (30ῼ) = 120W P3= (2A) 2 (5ῼ) = 20W PT= 80W + 120W + 20W =220W CALCULAR RT ,IT , PT , Y LA ENERGIA SI SE USA 5HR RT=5 ῼ+35ῼ+80ῼ+20ῼ=140ῼ IT= 110𝑉 140ῼ = 0.0857𝐴 P1= (0.0857A)2 (5ῼ) = 0.036W P2= (0.0857A)2 (35ῼ) = 0.257W P3= (0.0857A)2 (80ῼ) = 0.587W P4= (0.0857A)2 (20ῼ) = 0.146W En4 = (0.146W) (5HORAS)=0.73Wh PT= 0.036W+0.257W+0.587W+0.146W = 1.028W En1 = (0.036W) (5HORAS)= 0.18Wh EnT= 0.18Wh +1.285Wh +2.93Wh+0.73Wh= 2200Wh En2 = (0.257W) (5HORAS)=1.285Wh En3 = (0.587W) (5HORAS)=2.93Wh
- 3. 3 Calcular RT IT P1 P2 P3 PT con una intensidad de 3A RT= 110𝑉 3𝐴 = 36.6ῼ R1= 35𝑉 3𝐴 = 11.66ῼ R2= 45𝑉 3𝐴 = 15ῼ R3= 30𝑉 3𝐴 = 10ῼ P1= (3A)2 (11.66ῼ) = 104.94W P2= (3A)2 (15ῼ) = 135W PT= 104.94W+135W+90W= 329.94W P3= (3A)2 (10ῼ) = 90W Calcular RT IT P1 P2 P3 PT con una intensidad de 8A RT= 110𝑉 8𝐴 = 13.75ῼ R1= 55𝑉 8𝐴 = 6.875ῼ R2= 55𝑉 8𝐴 = 6.875ῼ P1= (8A)2 (6.875ῼ) = 440W P2= (8A)2 (6.875ῼ) = 440W PT= 440W+440W=880W CalcularRT IT y voltaje de cada una de lasresistencias RT=60 ῼ+30ῼ=90ῼ IT= 4.5𝑉 90ῼ = 0.05𝐴 V1=0.05 A (60ῼ)=3V V2= 0.05 A (30ῼ)= 1.5V
- 4. 4 CALCULAR RT IT PT Y EN EN CADA RESISTENCIA SISE USA POR16.5 HR RT=50 ῼ+25ῼ+85ῼ=160 ῼ IT= 110𝑉 160ῼ = 0.6875𝐴 PT= 110 V( 0.6875 A )= 75.625W P1= (0.6875A)2 (50ῼ) = 23.63W P2= (0.6875A)2 (25ῼ) = 11.81W P3= (0.6875A)2 (85ῼ) = 40.17W En1 = (23.63W) (16.5HORAS)= 389.89Wh En2 = (11.81W) (16.5HORAS)= 194.865Wh En3 = (0.6875W) (16.5HORAS)=662.805Wh CalcularRT IT y voltaje de cada una de lasresistencias RT=30 ῼ+10ῼ+6ῼ=46 ῼ IT= 12𝑉 46ῼ = 0.260𝐴 V1=0.260 A (30ῼ)=7.82V V2= 0.260 A (10ῼ)= 2.60V V3= 0.260 A (6ῼ)= 1.56 V
- 5. 5 CIRCUITOS PARALELOS R23= 4.6ῼ + 5.2 ῼ= 9.8 ῼ RT= ( 𝟒.𝟒)(𝟗.𝟖) 𝟒.𝟒+𝟗.𝟖 = 𝟑. 𝟎𝟑 ῼ I1= 𝟏𝟏𝟎𝑽 𝟒.𝟒ῼ = 𝟐𝟓 𝑨 I1= 𝟏𝟏𝟎𝑽 𝟗.𝟖ῼ = 𝟏𝟏. 𝟐𝟐 𝑨 IT= 25 A +11.22 A = 36.22 A Se conecta enparalelo una líneade 110 v tres resistencias¿Cuál es resistenciatotal? Si el circuito se empleo10 hrs ¿Cuál esla potenciatotal? ¿Cuál esEN ??? RT= 𝟏 𝟏 𝟗 + 𝟏 𝟏𝟒 + 𝟏 𝟐𝟗 RT= 4.59ῼ I1 = 110𝑉 9ῼ = 12.22𝐴 I2 = 110𝑉 14ῼ = 7.85𝐴 I3 = 110𝑉 29ῼ = 3.79𝐴 IT = 110𝑉 4.59ῼ = 23.96𝐴 P1= (110V) (12.22A) = 1344.5W PT= 110 V( 23.69A )= 2605.9W P2= (110V) (7.85A) = 863.5W P3= (110V) (3.79A) = 416.9W En1 = (1344.5W) (10HORAS)= 13445Wh EnT= 13445Wh +8635Wh +4169Wh= 26249Wh En2 = (863.5W) (10HORAS)= 8635Wh En3 = (416.9W) (10HORAS)= 4169Wh
- 6. 6 Si se conecta en paralelo un alinea de 220 v 4 resistencias sacar RT , PT , ENT si el circuito se emplea 3 hrs. RT= 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏𝟓 + 𝟏 𝟐𝟎 + 𝟏 𝟏𝟎 + 𝟏 𝟓𝟎 = 2.20 ῼ IT = 220𝑉 2.20ῼ = 100𝐴 PT= 220 V( 100A )= 22000W EnT = 22000W( 3HRS)=66000Wh Sacar el voltaje de cada resistencia, RT, IT, Y PT RT= 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏.𝟔 + 𝟏 𝟐 + 𝟏 𝟑 = 0.6875 ῼ I1 = 16𝑉 1.6ῼ = 10𝐴 I2 = 16𝑉 2ῼ = 8𝐴 I3 = 16𝑉 3ῼ = 5.3𝐴 IT = 16𝑉 0.6875ῼ = 23.27𝐴 P1= (16V) (10A) = 160W PT= 16 V( 23.27A )= 372.32W P2= (16V) (8A) = 128W P3= (16V) (5.3A) = 84.8W
- 7. 7 RT= 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏𝟎 + 𝟏 𝟑𝟎 = 7.5 ῼ IT = 12𝑉 7.5ῼ = 1.6𝐴 I1 = 12𝑉 10ῼ = 1.2𝐴 I2 = 12𝑉 30ῼ = 0.4𝐴 P1= (12V) (1.2A) = 14.4W PT= 12 V( 1.6A )= 19.2W P2= (12V) (0.4A) = 4.8W En1 = (14.4W) (3HORAS)= 43.2Wh EnT= 19.2W(3HRS)= 57.6Wh En2 = (4.8W) (3HORAS)=14.4Wh RT= 𝟏 𝟏 𝟑𝟎 + 𝟏 𝟏𝟎𝟎 + 𝟏 𝟏𝟑𝟎 = 19.59 ῼ IT = 220𝑉 19.59ῼ = 11.23𝐴 PT= 220 V( 11.23A )= 2470.6W EnT= 2470.6W(8HRS)= 19764.8Wh
- 8. 8 RT= 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏𝟎 + 𝟏 𝟏𝟎𝟎 + 𝟏 𝟑𝟎 = 6.97 ῼ IT = 8𝑉 6.97ῼ = 1.147𝐴 I1 = 8𝑉 10ῼ = 0.8𝐴 I2 = 8𝑉 100ῼ = 0.08𝐴 I3 = 8𝑉 30ῼ = 0.26𝐴 P1= (8V) (0.8A) = 6.4W P2= (8V) (0.08A) = 0.64W PT= 8 V( 1.147A )= 9.17W P3= (8V) (0.26A) = 2.08W RT= 𝟏 𝟏 𝟓𝟎 + 𝟏 𝟒𝟎 = 22.2 ῼ IT = 220𝑉 22.2ῼ = 9.90𝐴 I1 = 220𝑉 50ῼ = 4.4𝐴 I2 = 220𝑉 40ῼ = 5.5𝐴 P1= (220V) (4.4A) = 968W P2= (220V) (5.5A) = 1210W PT= 220 V( 9.90A )= 2178W En1 = (968W) (5HORAS)= 4840Wh EnT= 2178W(5HRS)= 10890Wh En2 = (1210W) (5HORAS)=6050Wh
- 9. 9 I1 = 75𝑊 110𝑉 = 0.68 𝐴 I2 = 60𝑊 110𝑉 = 0.54𝐴 I3 = 45𝑊 110𝑉 = 0.409𝐴 IT= 0.68 A + 0.54 A + 0.409 A = 1.629 A R1= 𝟏𝟏𝟎𝑽 𝟎.𝟔𝟖𝑨 = 𝟏𝟔𝟏. 𝟕𝟔 ῼ R2= 𝟏𝟏𝟎𝑽 𝟎.𝟓𝟒𝑨 = 𝟐𝟎𝟑. 𝟕 ῼ R3= 𝟏𝟏𝟎𝑽 𝟎.𝟒𝟎𝟗𝑨 = 𝟐𝟔𝟖. 𝟗𝟒 ῼ RT= 𝟏𝟏𝟎𝑽 𝟏.𝟔𝟐𝟗𝑨 = 𝟔𝟕. 𝟓𝟐 ῼ I1 = 100𝑊 110𝑉 = 0.90 𝐴 I2 = 75𝑊 110𝑉 = 0.681𝐴 IT= 0.90 A + 0.681 A = 1.58 A R1= 𝟏𝟏𝟎𝑽 𝟎.𝟗𝟎𝑨 = 𝟏𝟐𝟐. 𝟐 ῼ R2= 𝟏𝟏𝟎𝑽 𝟎.𝟔𝟖𝟏𝑨 = 𝟏𝟔𝟏. 𝟓𝟐 ῼ RT= 𝟏𝟏𝟎𝑽 𝟏.𝟓𝟖𝑨 = 𝟔𝟗. 𝟔𝟐 ῼ
- 10. 10 CIRCUITOS SERIE-PARALELO R23= 1 1 15 + 1 10 = 6 ῼ RT= 20ῼ+6ῼ= 26ῼ I1 =IT= 4.23 A I2 = 25.98 𝑉 15ῼ = 1.73𝐴 I3 = 25.98 10ῼ = 2.59𝐴 E1=4.23 A (20ῼ ) = 84.6V E23=4.23 A ( 6ῼ ) = 25.38V ET= 84.6 V + 25.38 V = 109.9 V R234= 1 1 30 + 1 10 + 1 20 5.45 ῼ RT= 5.45ῼ+15ῼ=20.45ῼ I1 =IT= 5.86 A I2 = 31.93 𝑉 10ῼ = 3.193𝐴 I3 = 31.93𝑉 30ῼ = 1.064𝐴 I4 = 31.93𝑉 20ῼ = 1.59𝐴 IT = 120𝑉 20.45ῼ = 5.86𝐴 E1=5.86 A (15ῼ ) = 87.9V E234= 5.86A ( 5.45ῼ ) = 31.93V ET= 119.83 V
- 11. 11 R12= (6)(4) 6+4 = 2.4ῼ RT= 20ῼ +2.4ῼ = 22.4 ῼ I1 = 11.784𝑉 6ῼ = 1.964 𝐴 I2 = 11.784𝑉 4ῼ = 2.946 𝐴 I3 = 98.2𝑉 20ῼ = 4.91 𝐴 IT = 110𝑉 22.4ῼ = 4.91 𝐴 E12=4.91 A (2.4ῼ ) = 11.784V E3=4.91A (20ῼ ) = 98.2V R123= 1 1 2.4 + 1 3 + 1 10 0.85 ῼ RT= 0.85ῼ + 15 ῼ = 15.85ῼ I1 = 11.79𝑉 2.4ῼ = 4.91 𝐴 I2 = 11.79𝑉 3ῼ = 3.93 𝐴 I3 = 11.79𝑉 10ῼ = 1.17 𝐴 I4 = 208.2𝑉 15ῼ = 13.88 𝐴 IT = 220𝑉 22.4ῼ = 13.88 𝐴 E123=13.88A (0.85ῼ ) = 11.79V E4= 15 ῼ ( 13.88 A ) = 208.2 V
- 12. 12 R234= 1 1 6 + 1 9 + 1 12 2.76 ῼ RT= 2.76ῼ + 3 ῼ = 5.76 ῼ I1 = 229.14𝑉 3ῼ = 76.38 𝐴 I2 = 210.8𝑉 6ῼ = 35.1 𝐴 I3 = 210.8𝑉 9ῼ = 23.42 𝐴 I4 = 210.8𝑉 12ῼ = 17.56 𝐴 IT = 440𝑉 5.76ῼ = 76.38 𝐴 E234=76.38A (2.76ῼ ) = 210.80V E1= 3 ῼ ( 76.38 A ) = 229.14 V R34= (10)(5) 10+15 2 ῼ RT= 30ῼ + 20ῼ + 2ῼ = 52ῼ I1=I2=IT= 8.46 A I3 = 16.92𝑉 10ῼ = 1.692 𝐴 I4 = 16.92𝑉 5ῼ = 3.384 𝐴 E34=8.46A (2ῼ ) = 16.92V IT = 440𝑉 52ῼ = 8.46 𝐴 E1= 30 ῼ ( 8.46 A ) = 253.8 V E2= 20 ῼ ( 8.46 A ) = 169.2 V
- 13. 13 R34= (20)(5) 20+5 = 4 ῼ RT= 4ῼ+ 10ῼ +15ῼ= 29ῼ I1=I2=IT= 0.4137 A I2 = 1.6548𝑉 20ῼ = 0.0827 𝐴 I3 = 1.6548𝑉 5ῼ = 0.33096 𝐴 IT = 12𝑉 29ῼ = 0.4137 𝐴 E1= 10 ῼ ( 0.4137 A ) = 4.13 V E2= 15 ῼ ( 0.4137 A ) = 6.20 V E34=0.4137A (4ῼ ) = 1.6548V R345= 1 1 30 + 1 40 + 1 50 = 12.76 ῼ RT= 10ῼ+ 20ῼ +12.76ῼ= 42.76ῼ I1=I2=IT= 15.43 A I3 = 196.8𝑉 30ῼ = 6.56 𝐴 I4 = 196.84𝑉 40ῼ = 4.42 𝐴 I5 = 196.84𝑉 50ῼ = 3.93 𝐴 E1= 10 ῼ ( 15.4 A) = 154.3 V IT = 220𝑉 277.63ῼ = 0.79𝐴 E2= 20 ῼ ( 15.43 A ) = 308.6 V E345=15.43A (12.76ῼ ) = 196.8V
- 14. 14 R34= 1 1 15 + 1 35 = 10.5 ῼ RT= 10ῼ+ 20ῼ +10.5ῼ+ 5ῼ = 42.5ῼ I1=I2=I5=IT= 2.41 A I3 = 25.3𝑉 15ῼ = 1.68 𝐴 I4 = 25.3𝑉 35ῼ = 0.722 𝐴 E1= 10 ῼ ( 15.43 A ) = 154.3 V IT = 110𝑉 45.5ῼ = 2.41𝐴 E2= 20 ῼ ( 15.43 A ) = 308.6 V E345=15.43A (12.76ῼ ) = 196.8V R456= 1 1 70 + 1 60 + 1 10 = 7.63 ῼ RT= 100ῼ+ 90ῼ +80ῼ + 7.63ῼ= 277.63 ῼ IT = 220𝑉 277.63ῼ = 0.7924 𝐴 I1=I2=I3=IT= 0.7924 A I4 = 6.04𝑉 70ῼ = 0.0862 𝐴 I5 = 6.04𝑉 60ῼ = 0.100 𝐴 I6 = 6.04𝑉 10ῼ = 0.604 𝐴 E1= 100ῼ ( 0.7924 A ) = 79.24 V E2= 90 ῼ ( 0.7924 A ) = 71.31 V E3=0.7924A (80ῼ ) = 63.39V E456=0.7924A (7.63ῼ ) = 6.04V
- 15. 15 CIRCUITO PARALELO-SERIE R23= 30ῼ +15ῼ = 45ῼ RT= (10)(45) 10+45 = 8.18ῼ IT = 110𝑉 8.18ῼ = 13.44 𝐴 I1 = 110𝑉 10ῼ = 11 𝐴 I23 = 110𝑉 45ῼ = 2.4 𝐴 E1= 10ῼ ( 11 A ) = 110 V E2= 30 ῼ ( 2.4 A ) = 72 V E3= 2.4A (15ῼ ) = 36V P1= (13.44A)2 (10ῼ) =1806.33W P23= (13.44A)2 (45ῼ)=8128.512W PT= 1806.33W+8128.512W=9434.84W R12=3ῼ +5ῼ=8ῼ RT= (8)(10) 8+10 = 4.44 ῼ IT = 220𝑉 4.44ῼ = 49.54 𝐴 I12= 220𝑉 8ῼ = 27.5 A I3= 220𝑉 10ῼ = 22 A E1= 3ῼ ( 27.5 A ) = 82.5 V E2= 5ῼ( 27.5 A ) = 137.5 V E3= 22A (10ῼ ) = 220V P12= (49.54A)2 (8ῼ) =19633.6W PT=44175.71W P3= (49.54A)2 (10ῼ) =24542.11W
- 16. 16 R12=10ῼ +11ῼ=21ῼ R34=50ῼ +80ῼ=130ῼ RT= (21)(130) 21+130 = 18.07ῼ IT = 220𝑉 18.07ῼ = 12.17 𝐴 I12= 220𝑉 21ῼ = 10.47 A I34= 220𝑉 130ῼ = 1.69 A P12= (10.47A)2 (21ῼ) = 2302.03W E1= 10ῼ ( 10.47 A ) = 104.7 V P34= (10.47A)2 (130ῼ) =14250.71W E2= 11ῼ ( 10.47 A ) = 115.17 V E3= 50ῼ ( 1.69 A ) = 84.54 V E4= 80ῼ ( 1.69 A ) = 135.2 V PT= 2302.03W+14250.71W= 16552.747 W R12= 3.2ῼ +5.2ῼ=8.4ῼ R34=4.2ῼ +9.2ῼ=13.4ῼ RT= (8.4)(13.4) 8.4+13.4 = 5.16ῼ IT = 24𝑉 5.16ῼ = 4.65 𝐴 I12= 24𝑉 8.4ῼ = 2.85 A I34= 24𝑉 13.4ῼ = 1.79 A P12= (2.85A)2 (8.4ῼ) = 68.22W E1= 3.2ῼ ( 2.85 A ) = 9.12 V P34= (1.79A)2 (13.4ῼ) =42.93W E2= 5.2ῼ ( 2.85 A ) = 14.82 V E3= 4.2ῼ ( 1.79 A ) = 7.51 V E4= 9.2ῼ ( 1.79 A ) = 16.468 V PT= 68.22W+42.93W= 111.15 W
- 17. 17 R234=4ῼ +5ῼ+ 8ῼ=17ῼ RT= (5)(17) 5+17 = 3.86ῼ IT = 12𝑉 3.86ῼ = 3.10 𝐴 I1= 12𝑉 5ῼ = 2.4 A I234= 12𝑉 73ῼ = 0.70 A E1= 5ῼ ( 2.4 A ) = 12 V E2= 4ῼ ( 0.70 A ) = 2.8 V E3= 5ῼ ( 0.70 A ) = 3.5 V E4= 8ῼ ( 0.70 A ) = 5.6 V P1= (2.4A)2 (5ῼ) =28.8W P234= (0.70A)2 (17ῼ) =8.33W R123= 10ῼ +12ῼ+14ῼ=36ῼ RT= (36)(20) 36+20 = 12.8ῼ IT = 220𝑉 12.8ῼ = 17.18 𝐴 I123 = 220𝑉 36ῼ = 6.1 𝐴 I4 = 220𝑉 20ῼ = 11 𝐴 A E1= 10ῼ ( 6.1 A ) = 61 V E2= 12ῼ (6.1A ) = 73.2 V E3= 14ῼ ( 6.1 A ) = 85.4 V E4= 20ῼ ( 11 A ) = 220V P123= (6.1A)2 (36ῼ) =1339.56W P4= (11A)2 (20ῼ) =2420W PT= 1339.56W+2420W=3759.56W
- 18. 18 R12= 3ῼ +5ῼ=8ῼ R34= 6ῼ +4ῼ=10ῼ R56= 10ῼ +8ῼ=18ῼ R78= 2ῼ +8ῼ=10ῼ RT= 1 1 8 + 1 10 + 1 18 + 1 10 = 2.62 ῼ IT = 110𝑉 2.62ῼ = 41.98 𝐴 I12 = 110𝑉 8ῼ = 13.7 𝐴 I34 = 110𝑉 10ῼ = 11 𝐴 I56 = 110𝑉 18ῼ = 6.1 𝐴 I78 = 110𝑉 10ῼ = 11 𝐴 P12= (13.7A)2 (8ῼ)=1501.5W P34= (11A)2 (10ῼ) =1210W P56= (6.1A)2 (18ῼ)=669.78W P78= (11A)2 (10ῼ) =1210W PT= 4591.28W R123= 10ῼ +20ῼ+ 30ῼ=60ῼ RT= (60)(60) 60+60 = 30ῼ IT = 24𝑉 30ῼ = 0.8 𝐴 I123 = 24𝑉 60ῼ = 0.4 𝐴 I4 = 24𝑉 60ῼ = 0.4 𝐴 A E1= 10ῼ ( 0.4 A ) = 4V E2= 20ῼ (0.4A ) = 8 V E3= 30ῼ ( 0.4 A ) = 12 V E4= 60ῼ ( 0.4 A ) = 24V P123= (0.4A)2 (60ῼ) =9.6W P4= (0.4A)2 (60ῼ) =2420W PT= 9.6W+9.6W=19.2W
- 19. 19 R12=60ῼ +80ῼ=140ῼ RT= (140)(80) 140+80 = 50.90 ῼ IT = 100𝑉 50.90ῼ = 1.96 𝐴 I12= 100𝑉 140ῼ = 0.71 A I3= 100𝑉 80ῼ = 1.25 A P12= (0.71A)2 (140ῼ) =70.57W P3= (1.25A)2 (80ῼ) =125W PT=70.57W+125W=195.57W R12= 10ῼ +100ῼ=110ῼ R345= 20ῼ +40ῼ+60ῼ=120ῼ RT= (120)(110) 120+110 = 57.39 ῼ IT = 660𝑉 57.39ῼ = 11.50 𝐴 I345 = 660𝑉 120ῼ = 5.5 𝐴 I12 = 660𝑉 110ῼ = 6 𝐴 A E1= 10ῼ ( 6 A ) = 60V E2= 100ῼ (6A ) = 600 V E3= 20ῼ ( 5.5 A ) = 110 V E4= 40ῼ ( 5.5 A ) = 220V E= 60ῼ ( 5.5 A ) = 330V P12= (6A)2 (110ῼ) =3960W P345= (5.5A)2 (120ῼ)=3630W PT= 7590W