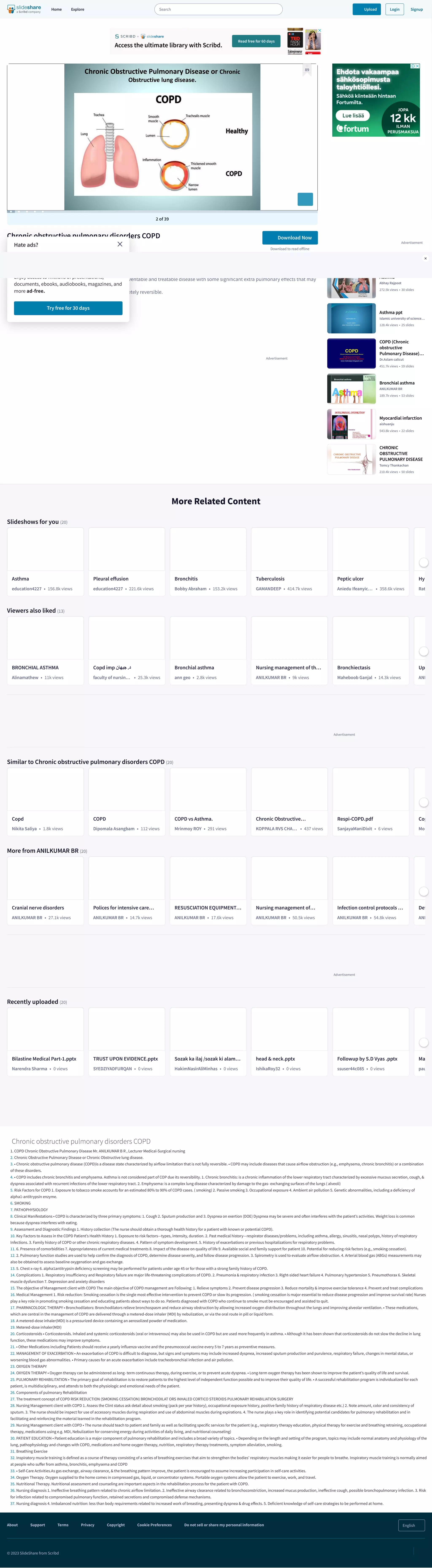
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a preventable and treatable disease characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully reversible. It includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The main risk factor is exposure to tobacco smoke, which accounts for 80-90% of COPD cases. Patients experience symptoms of cough, sputum production, and dyspnea on exertion. Treatment focuses on smoking cessation, bronchodilators, corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation, and oxygen therapy to relieve symptoms and reduce exacerbations. Nursing care includes education on disease management, breathing exercises, medication administration, and promoting lifestyle changes to improve quality of life.