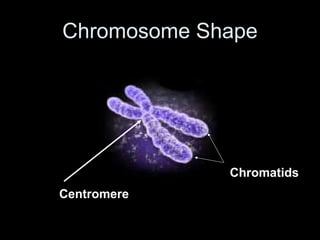
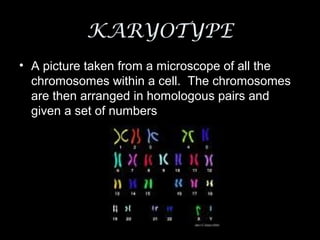
Chromosomes are rod-shaped structures made of DNA and proteins that contain genetic information. DNA is wrapped around protein structures called histones. Chromosomes exist in pairs called homologous chromosomes that contain the same genetic information. Chromosomes are only visible during cell division and exist as chromatin between divisions. Prokaryotes have circular chromosomes without nuclei, while eukaryotes have linear chromosomes within the cell nucleus. A karyotype maps the chromosomes, and cells are either diploid with two sets of chromosomes or haploid with one set.