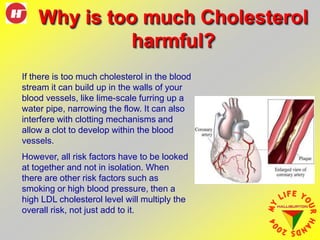
Cholesterol is a vital lipid found in various body tissues, crucial for cell membranes, hormone production, and digestion. Excess cholesterol can lead to cardiovascular issues, especially when combined with other risk factors like smoking or high blood pressure. Regular cholesterol checks are recommended for individuals with heart disease, a family history of high cholesterol, diabetes, or high blood pressure, and lifestyle changes can help manage cholesterol levels.