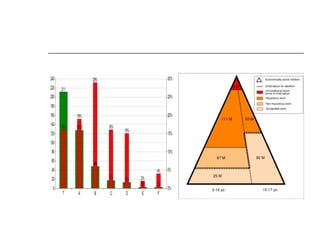
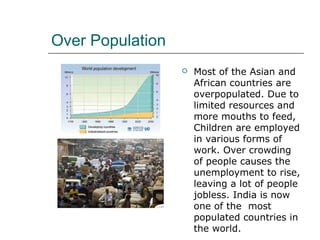
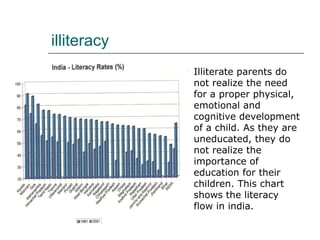
Poverty, lack of access to education, overpopulation, and urbanization are key drivers of child labor in India. Millions of children work instead of attending school due to their families' economic hardships. Child labor robs children of their education and development, perpetuates the cycle of poverty, and exposes them to physical and mental dangers. While some international organizations work to end child labor worldwide, stronger government support and public involvement are still needed to adequately address this issue in India.