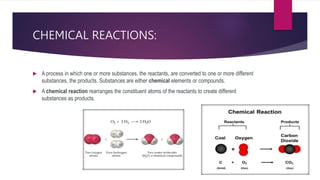
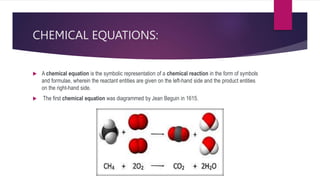
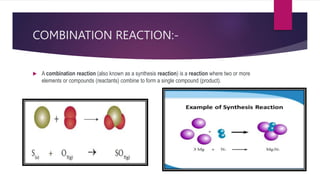
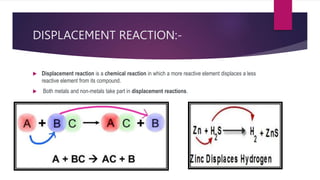
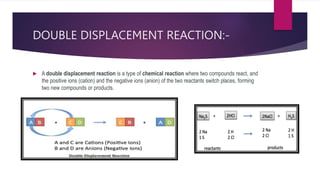
The document discusses various topics related to chemical reactions and equations. It defines physical and chemical changes, and explains that a chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances. It also defines key concepts like chemical equations, skeletal equations, balanced equations, and different types of chemical reactions such as combination, decomposition, displacement and double displacement. Additionally, it explains oxidation-reduction reactions, oxidizing and reducing agents, and phenomena like corrosion and rancidity that involve redox reactions.