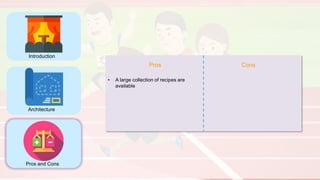
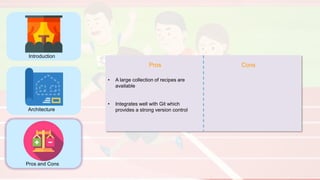
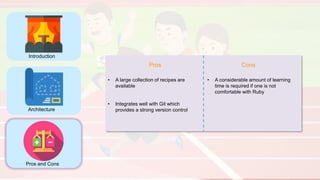
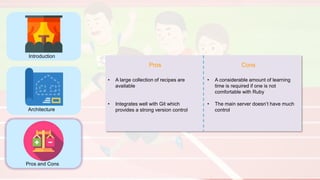
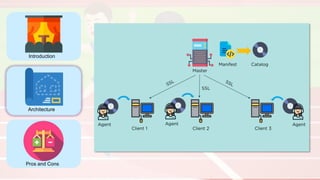
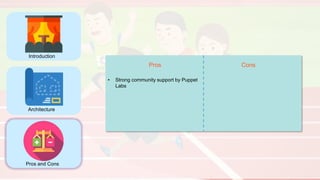
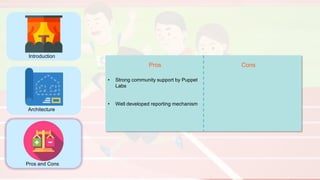
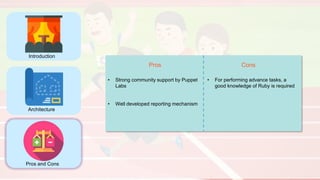
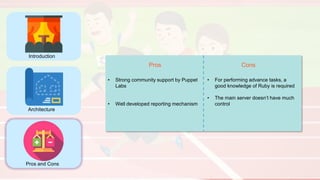
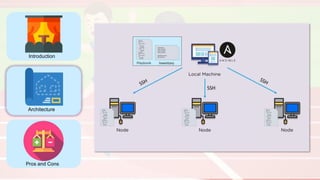
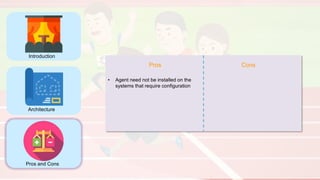
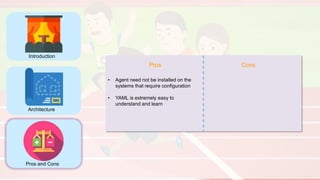
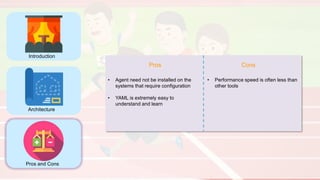
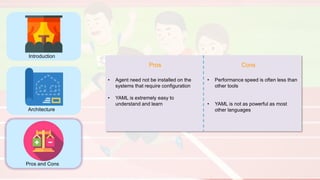
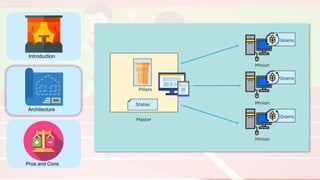
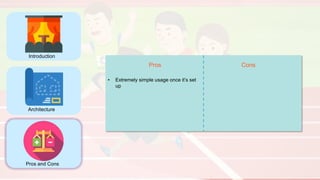
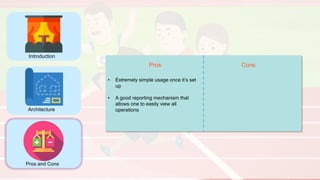
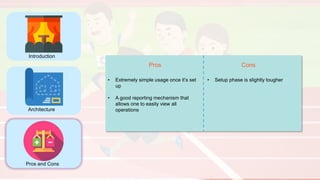
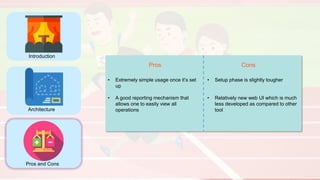
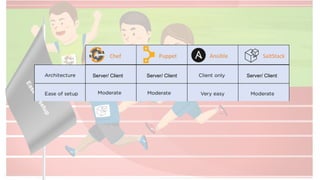
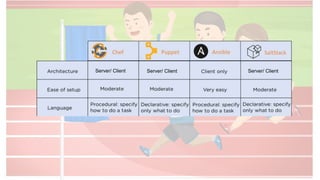
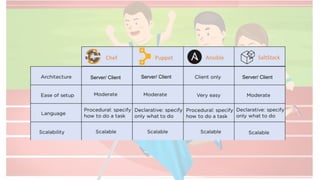
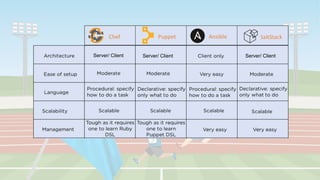
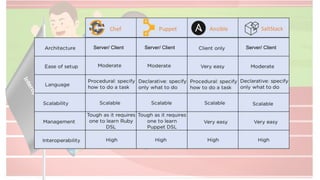
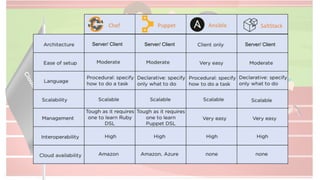
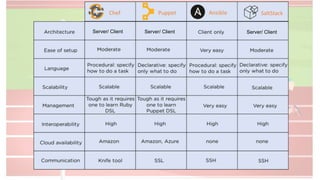
The document compares four configuration management tools: Chef, Puppet, Ansible, and SaltStack, detailing their features, pros, and cons. Each tool has unique strengths, such as Chef's rich recipe collection, Puppet's strong community support, Ansible's simplicity, and SaltStack's ease of use post-setup. The choice of the best tool depends on specific organizational needs and environments.