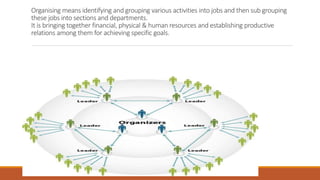
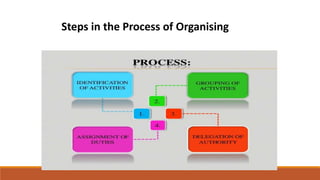
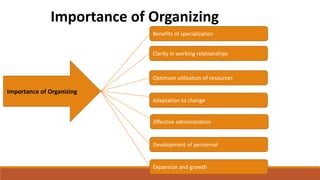
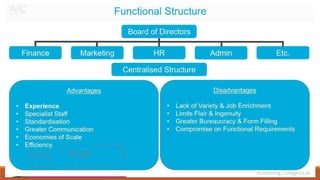
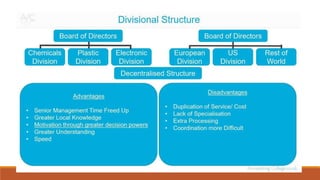
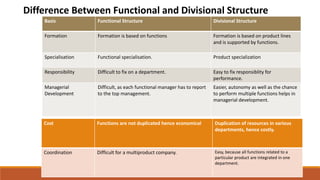
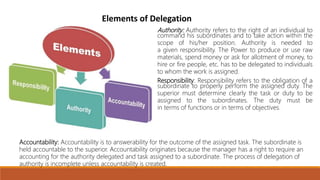
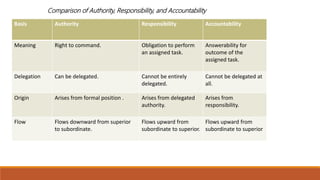
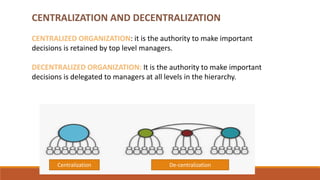
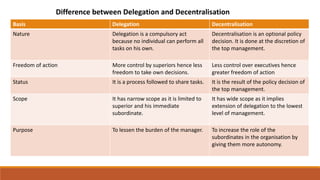
Organizing involves identifying and grouping activities into jobs, departments, and sections. It brings together resources to achieve goals. The key steps are: (1) identifying and dividing work, (2) grouping similar activities into departments, (3) assigning duties to employees, and (4) establishing reporting relationships. Organizing provides benefits like specialization, clear relationships, optimal resource use, adaptability, and effective administration. Functional and divisional structures are two common organizing structures. A functional structure groups jobs by similarity, while a divisional structure splits the organization into semi-autonomous product-based divisions.