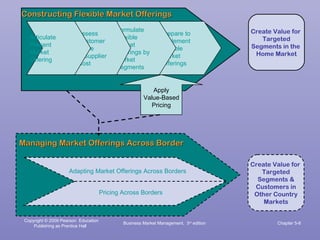
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 5 of the third edition of the textbook "Business Market Management" regarding managing market offerings. It discusses constructing flexible market offerings to meet the needs of different customer segments, assessing customer value to determine pricing, and adapting offerings across international borders. The summary provides an overview of the key topics covered in the chapter in 3 sentences or less.