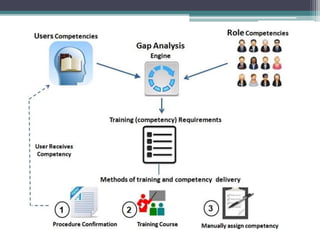
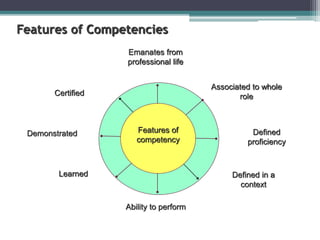
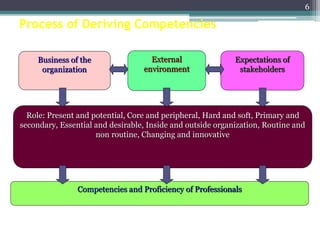
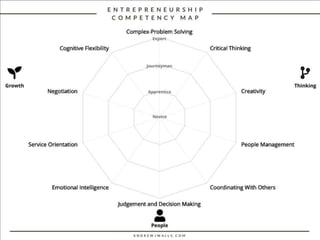
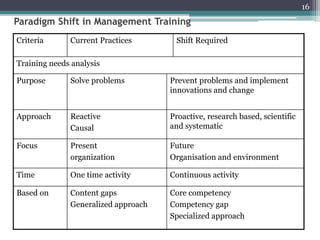
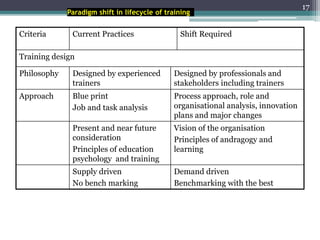
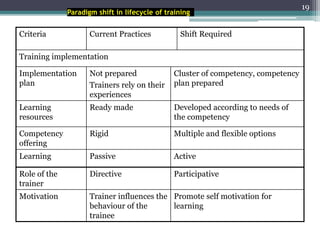
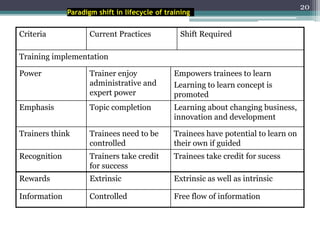
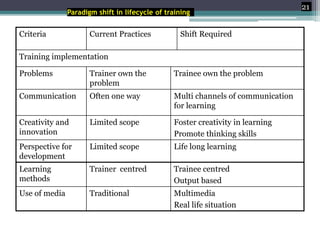
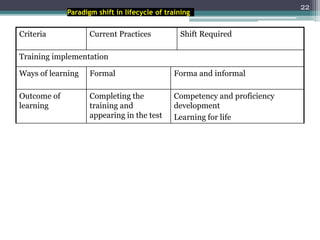
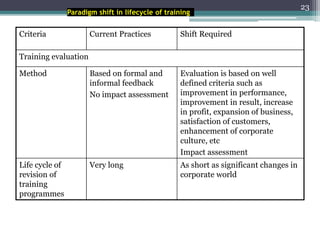
This document discusses competency-based management training, defining competencies as specific skills or attributes essential for effective performance in professional roles. It highlights the importance of matching training to individual learning needs, emphasizing flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and efficiency in competency-based training programs. Additionally, it outlines the paradigm shifts needed in training design, implementation, and evaluation to adapt to changing organizational demands and enhance learning outcomes.

![What is a Competency
• Simply defined, a competency is a specific skill, trait or attribute that meets the
following criteria:
• Is behavioral
• Is part of a larger skill set or discipline
• Can be learned or developed –
• Identifies “what can be done” vs. “what is known”
• The competency is a link between the role and the role holder.
• It enables the role holder to perform competently, proficiently, productively,
creatively, innovatively to assure quality of products and services at minimum price,
without waste, on right time, with minimum efforts and without stress.
• Competency is ability to do or perform or take responsibility. [Phil Race]
• There are two principal types of competencies-
• General Competencies: Address skills relevant to broad groups of individuals,
regardless of job role. For example, communication and leadership skills.
• Technical Competencies: Address skills relevant to specific job roles or families of
job roles.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-7-240703044508-7cc66d1a/85/CHAPTER-7-pptx-Competency-Based-Management-Training-2-320.jpg)