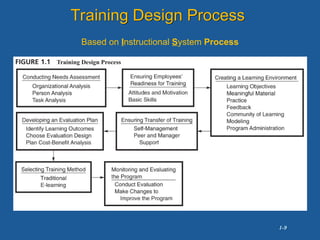
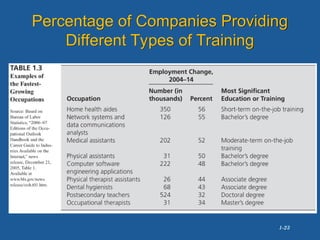
The document discusses the importance of employee training and development, highlighting Boston Pizza's implementation of training programs that enhance soft skills and improve business competitiveness. It details the training design process, the influence of globalization, and the significance of continuous learning and intangible assets in organizational success. The document emphasizes aligning training with strategic business goals to foster employee performance and customer service.