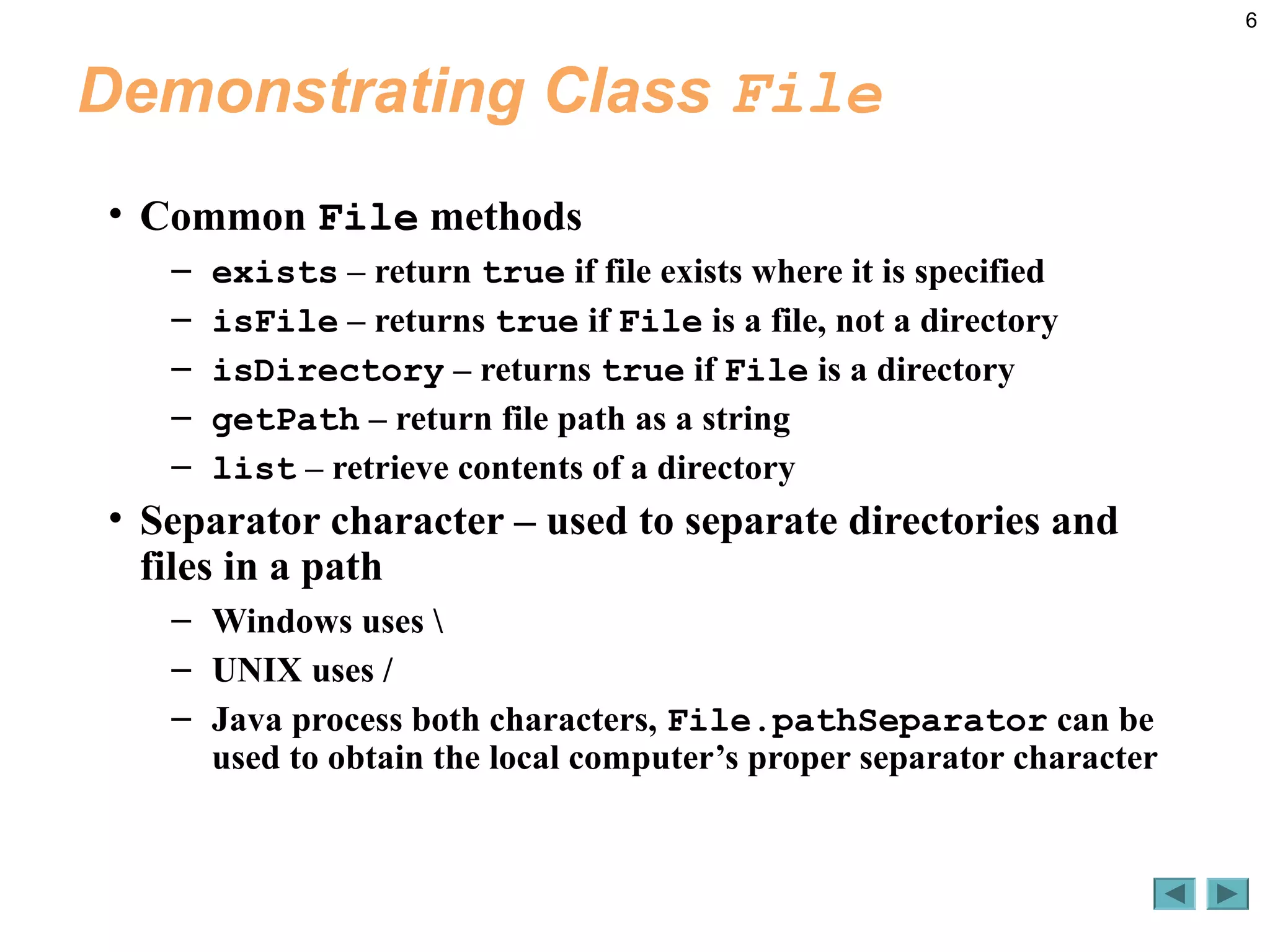
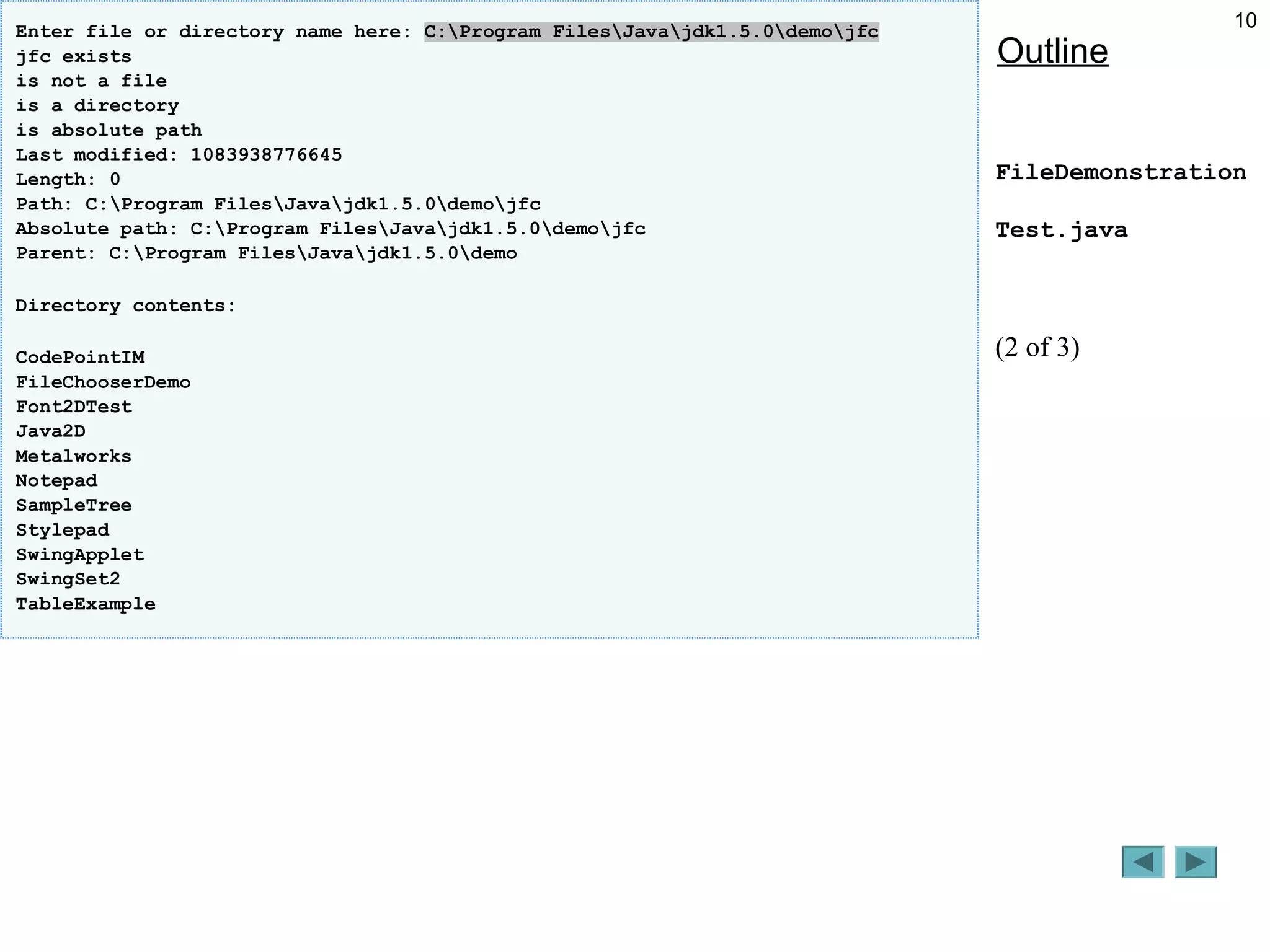
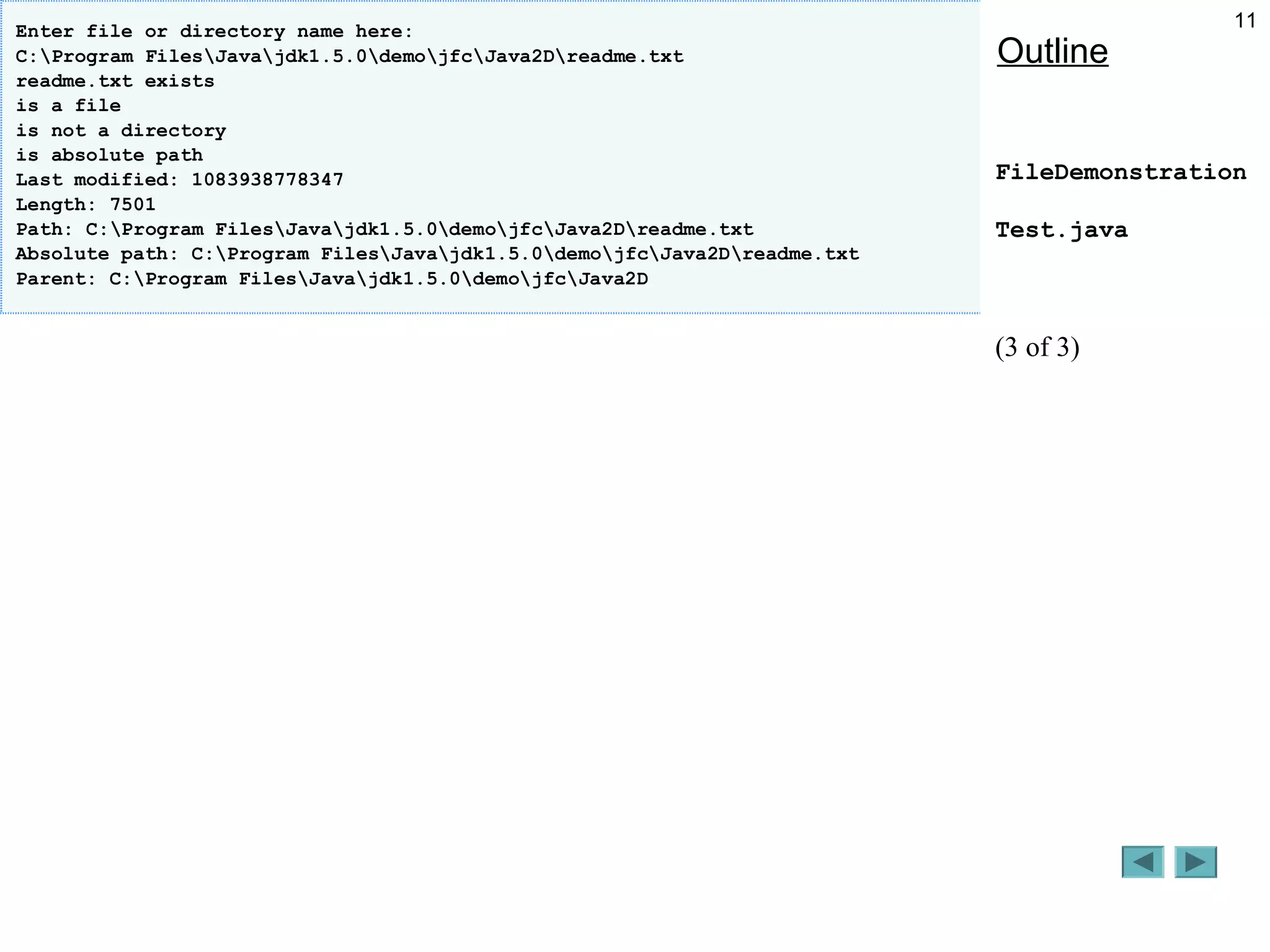
The document discusses the File class in Java, which represents files and directories on disk without providing file processing capabilities. It describes the File class constructors and common methods like exists(), isFile(), isDirectory(), getPath(), and list(). Examples are provided to demonstrate analyzing a file or directory path specified by the user, including checking if it exists, retrieving information about it, and listing the contents if it is a directory. The document also notes some common errors like using \ instead of \\ in file paths in string literals.



![4
Fig.5.1 | File methods.
(Part 2 of 2)
Method Description
String getAbsolutePath() Returns a string with the absolute path of the file or directory.
String getName() Returns a string with the name of the file or directory.
String getPath() Returns a string with the path of the file or directory.
String getParent() Returns a string with the parent directory of the file or directory (i.e.,
the directory in which the file or directory can be found).
long length() Returns the length of the file, in bytes. If the File object represents a
directory, 0 is returned.
long lastModified() Returns a platform-dependent representation of the time at which the
file or directory was last modified. The value returned is useful only for
comparison with other values returned by this method.
String[] list() Returns an array of strings representing the contents of a directory.
Returns null if the File object does not represent a directory.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-150212175409-conversion-gate01/75/Chapter-5-Class-File-4-2048.jpg)

![8
Outline
FileDemonstration
.java
(2 of 2)
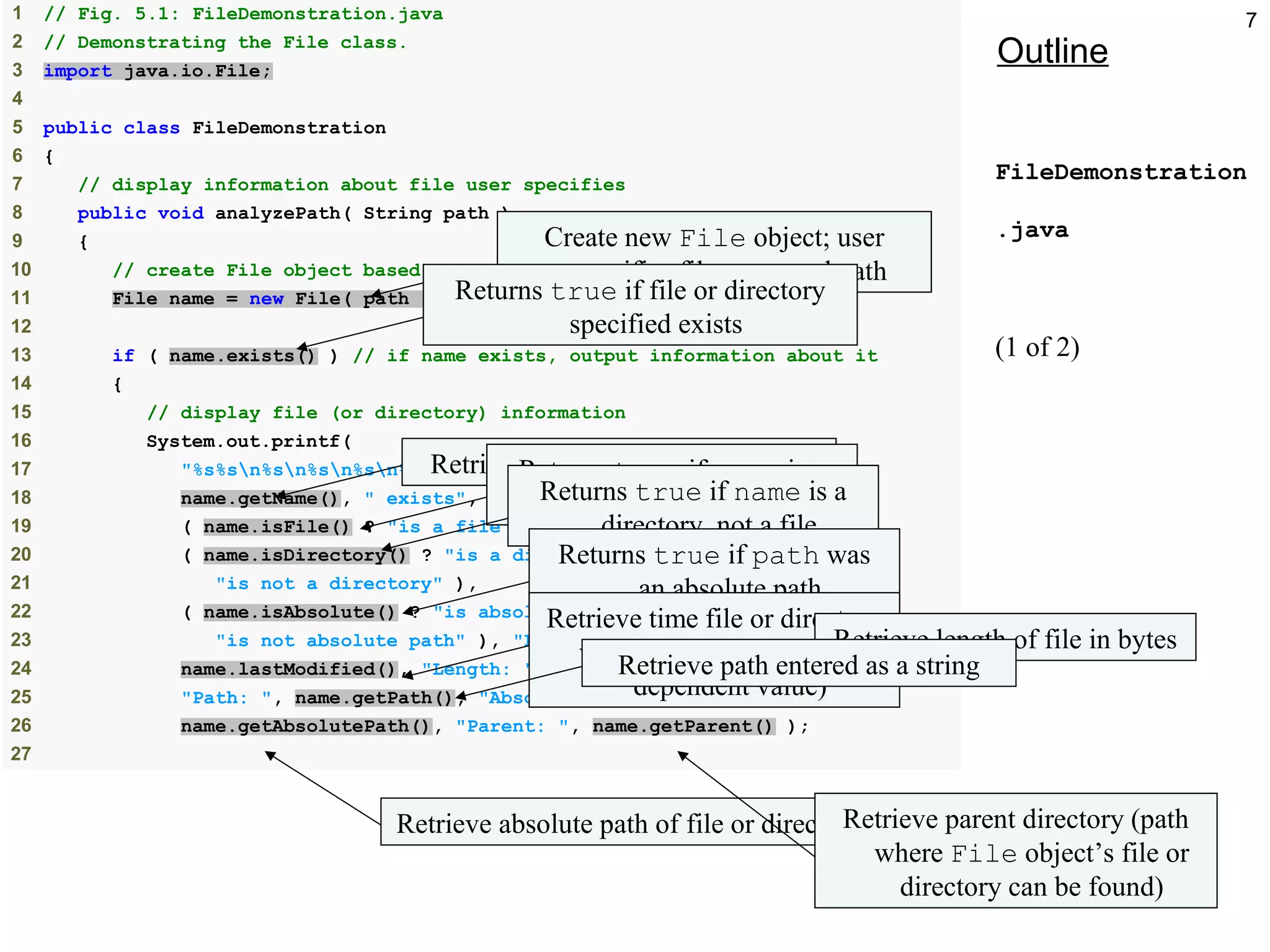
28 if ( name.isDirectory() ) // output directory listing
29 {
30 String directory[] = name.list();
31 System.out.println( "nnDirectory contents:n" );
32
33 for ( String directoryName : directory )
34 System.out.printf( "%sn", directoryName );
35 } // end else
36 } // end outer if
37 else // not file or directory, output error message
38 {
39 System.out.printf( "%s %s", path, "does not exist." );
40 } // end else
41 } // end method analyzePath
42 } // end class FileDemonstration
Returns true if File is a directory, not a file
Retrieve and display
contents of directory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-150212175409-conversion-gate01/75/Chapter-5-Class-File-8-2048.jpg)
![9
Outline
FileDemonstration
Test.java
(1 of 3)
1 // Fig. 5.2: FileDemonstrationTest.java
2 // Testing the FileDemonstration class.
3 import java.util.Scanner;
4
5 public class FileDemonstrationTest
6 {
7 public static void main( String args[] )
8 {
9 Scanner input = new Scanner( System.in );
10 FileDemonstration application = new FileDemonstration();
11
12 System.out.print( "Enter file or directory name here: " );
13 application.analyzePath( input.nextLine() );
14 } // end main
15 } // end class FileDemonstrationTest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-150212175409-conversion-gate01/75/Chapter-5-Class-File-9-2048.jpg)

![© 2005 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved.
import java.io.*;
class File {
public static void main (String args[]) throws Exception{
java.io.File file=new java.io.File (“file.txt”);
if (file.exists()){
System.out.print(“File exists”);
System.exit(0);//1M
}
//create file
java.io.PrintWriter output=new java.io.PrintWriter(file);
output.print(“hello world”);
}
output.close()
}
}
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-150212175409-conversion-gate01/75/Chapter-5-Class-File-13-2048.jpg)