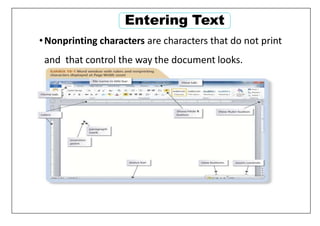
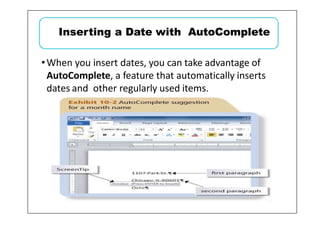
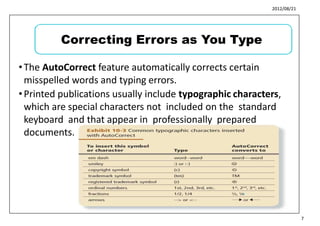
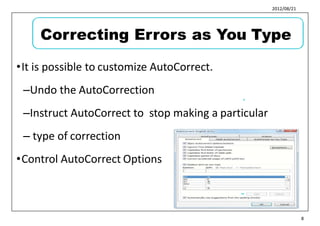
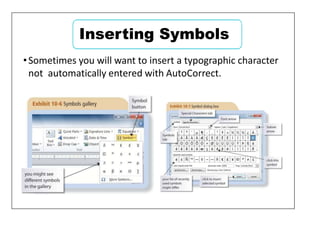
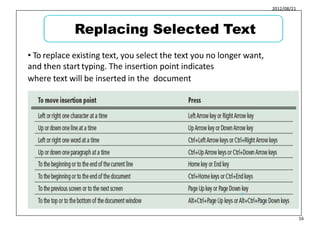
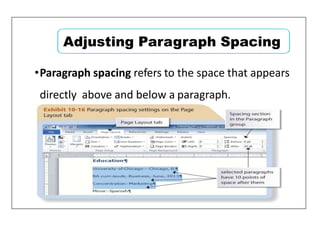
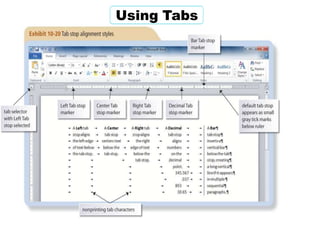
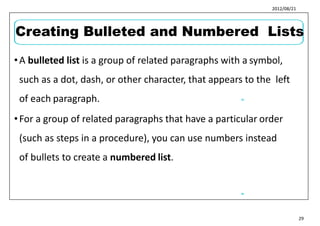
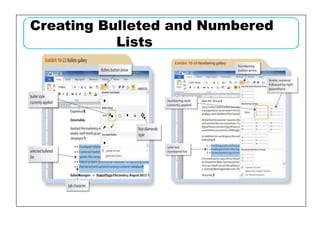
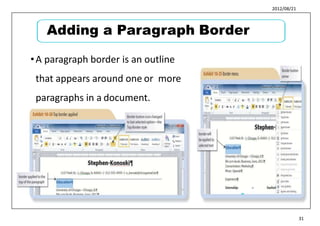
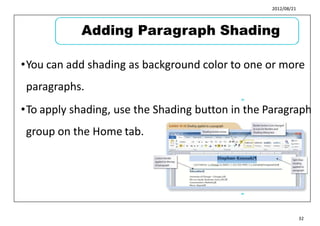
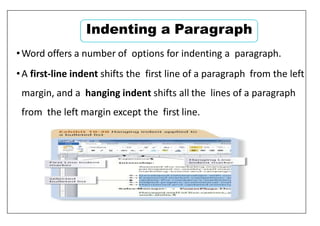
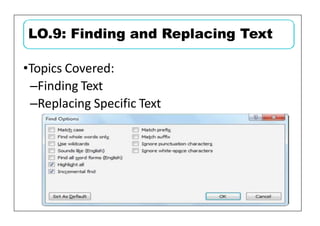
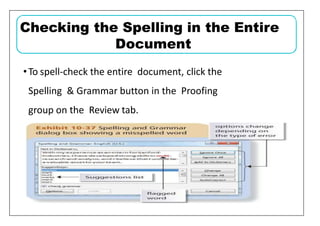
This document provides learning objectives and instructions for using various features in Microsoft Word 2010, including entering and editing text, formatting paragraphs and documents, finding and replacing text, and checking spelling and grammar. It covers topics such as inserting symbols, undoing and redoing actions, selecting and replacing text, adjusting font styles and paragraph spacing, creating bulleted and numbered lists, copying formats between paragraphs, and previewing and printing documents.