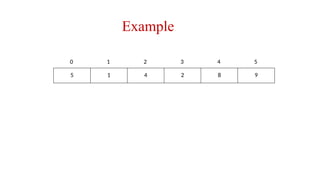
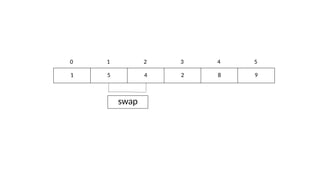
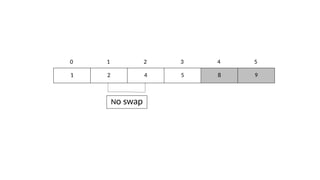
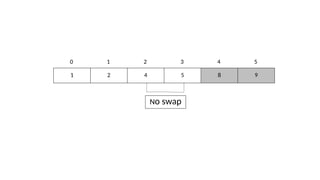
The document explains sorting and bubble sort, a simple comparison-based algorithm that arranges data in ascending or descending order by repeatedly comparing and swapping adjacent elements. It provides a detailed implementation process along with a code snippet in C++. Additionally, the document discusses the time complexity of bubble sort, which is O(n^2).

























![Code snippet
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int size,i,j,temp;
cout<<"Enter The size of array:n"; cin>>size;
int arr[size]; cout<<"Enter The Elements:n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++){ cin>>arr[i]; }
cout<<"Before Sorting:"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<size;i++){ cout<<arr[i]<<"t"; }
Data Structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4bubblesort-241113091939-6d3a32e0/85/Chapter-4-Bubble-Sort-jfdkjffdfdf-pptx-30-320.jpg)
![Code snippet
for(i=0;i<size;i++){
for(j=0;j<size-1;j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
temp=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp; }
cout<<"n After Sorting:"<<endl;
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<"t";
}
Data Structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4bubblesort-241113091939-6d3a32e0/85/Chapter-4-Bubble-Sort-jfdkjffdfdf-pptx-31-320.jpg)
