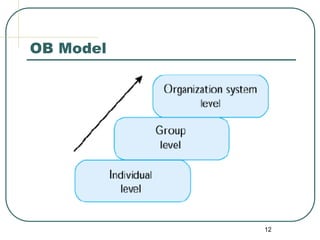
This document provides an overview of organizational behavior. It defines OB as the study of how individual and group behavior impacts organizational performance. It discusses management functions like planning, organizing, and leading. Key topics in OB include individual factors, group dynamics, and organizational systems and culture. The document also outlines challenges for OB like managing diversity and globalization, and how OB insights can help with issues like customer service, innovation, and work-life balance.