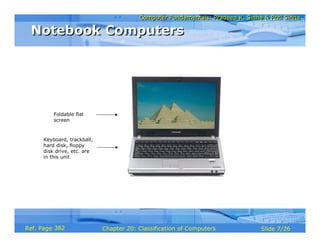
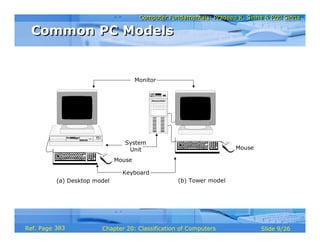
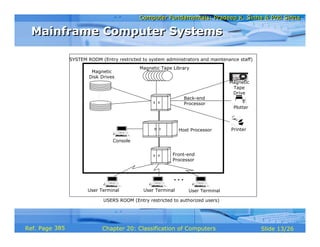
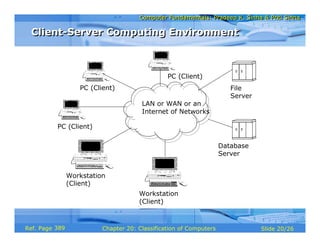
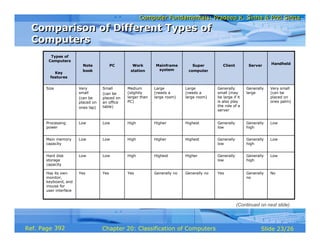
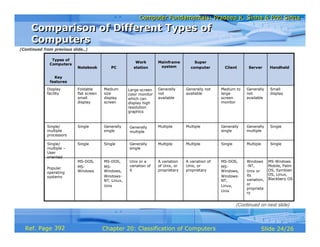
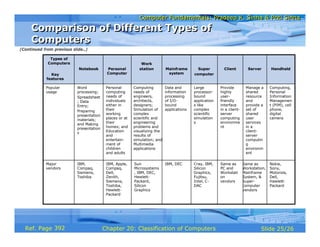
The document discusses different types of computers based on their mode of use. It describes notebook computers, personal computers, workstations, mainframe systems, supercomputers, clients and servers, and handheld computers. For each type, it provides details on their typical uses, characteristics, operating systems, vendors, and how they differ from each other.