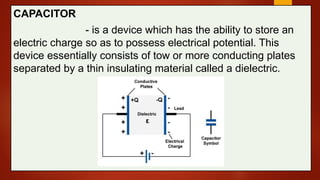
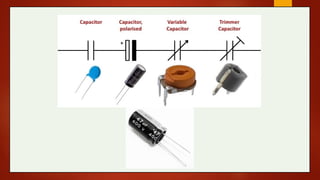
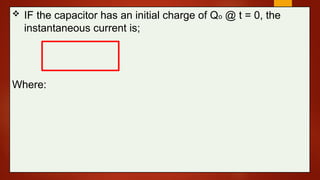
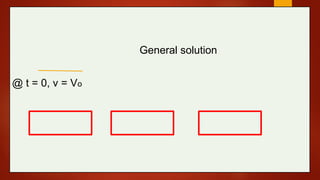
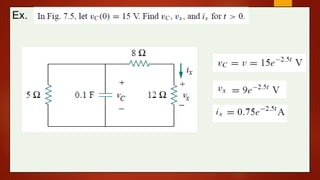
The document explains the function and characteristics of capacitors in RC circuits, including concepts such as capacitance, time constants, and formulas for instantaneous current and voltage in both charging and discharging scenarios. It provides examples and calculations for various capacitor and resistor configurations, illustrating the behavior of the circuit over time. Key topics include energy storage, power dissipation, and transient responses in DC circuits.