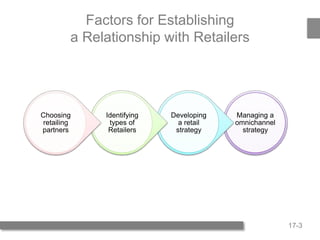
1) The document discusses factors manufacturers should consider when developing relationships with retailers and strategies for omnichannel marketing. It outlines the four factors - channel structure, customer expectations, channel member characteristics, and distribution intensity.
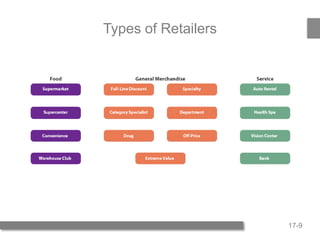
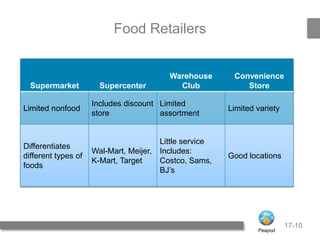
2) It then describes the types of retailers - food, general merchandise, and services. It also discusses developing a retail strategy using the four P's of product, price, promotion, and place.
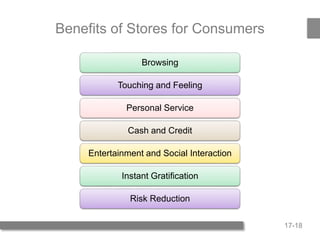
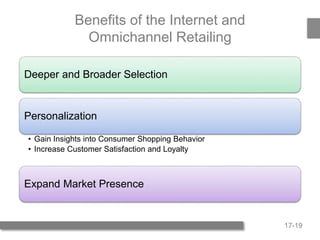
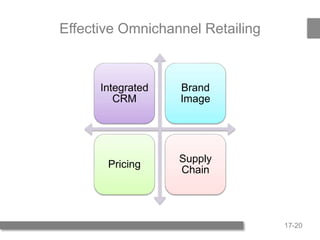
3) Benefits of stores include browsing, touching products, personal service, and instant gratification. Benefits of omnichannel include deeper selection, personalization, and expanding market presence. Effective omnichannel requires integrated strategies across CRM, brand, pricing, and supply chain.