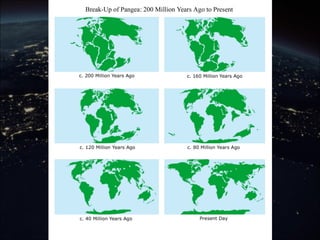
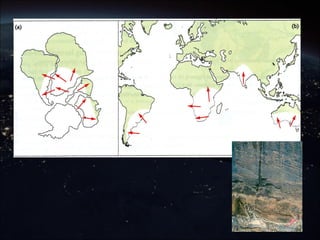
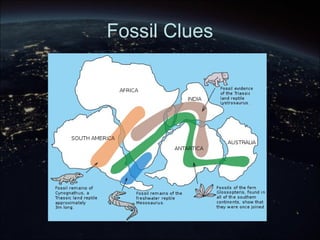
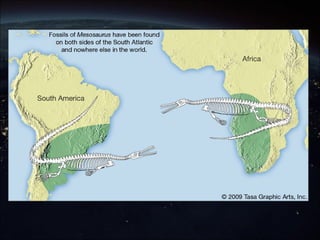
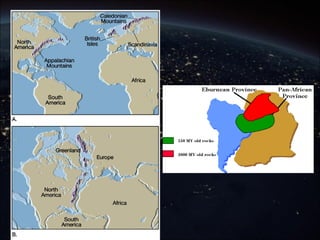
The continental drift hypothesis, proposed by Alfred Wegener, suggests that all continents were once part of a supercontinent called Pangaea and have since moved to their current positions. Evidence supporting this hypothesis includes the fitting shapes of continents, fossil correlations, and similarities in mountain ranges across different continents. Despite initial skepticism, Wegener's ideas gained acceptance decades later, particularly after the discovery of plate tectonics.