Here are the answers to the pop quiz:
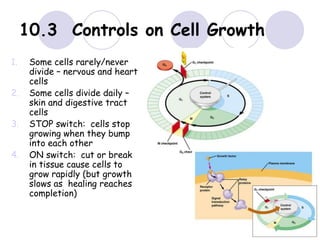
1. The main goal of cell division is to replicate the cell's DNA and divide it evenly between two daughter cells.
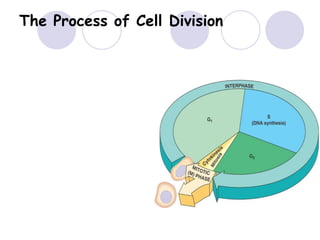
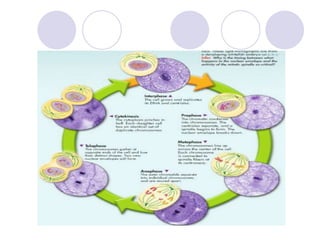
2. The 3 phases of interphase are G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase.
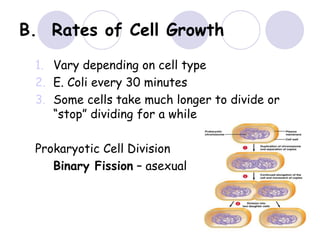
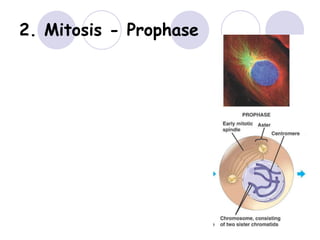
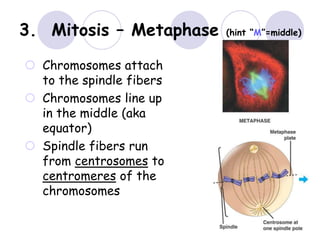
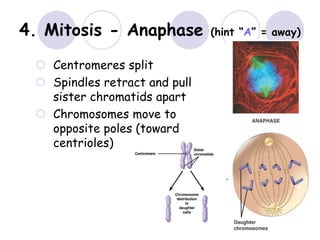
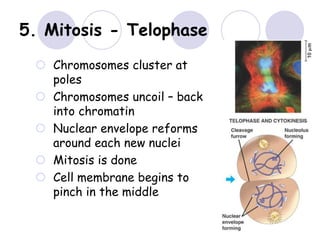
3. The 4 phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
4. If a cell has 12 chromosomes and undergoes cell division, there will be two daughter cells at the end.
5. Each of the two daughter cells will have 12 chromosomes, the same number as the original parent cell.