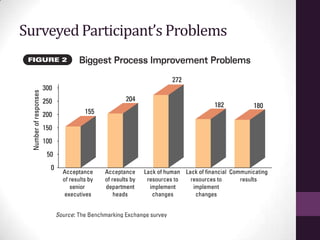
This document discusses two case studies: (1) best practices in process improvement which recommends identifying problems, choosing a cross-functional team, process mapping to identify gaps, setting goals and communicating progress; and (2) the role of statistical thinking in management which involves understanding variation, using data to guide actions, and learning workshops to evaluate processes. Statistical thinking benefits managers by viewing work as interconnected processes, understanding that variation exists, and reducing variation leads to success.