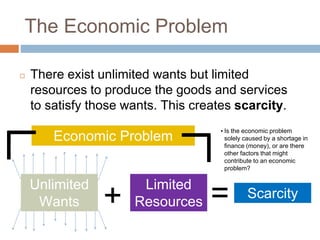
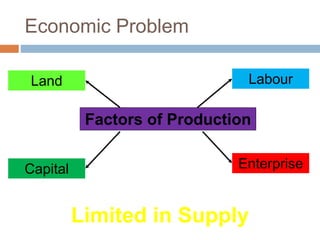
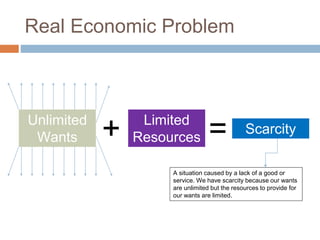
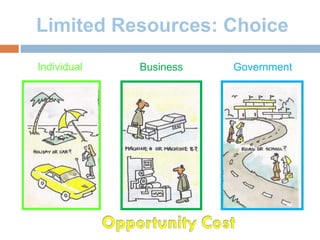
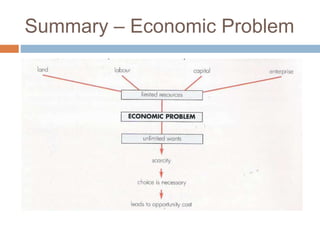
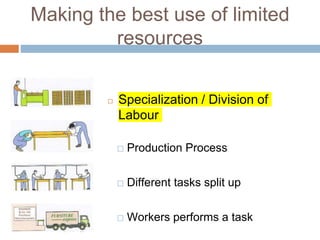
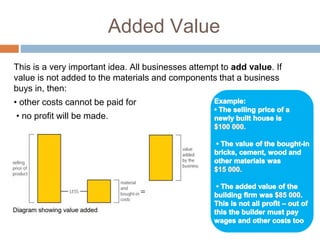
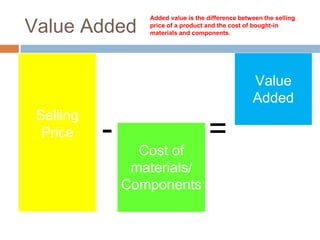
The document provides an overview of key concepts in business studies including the economic problem, factors of production, scarcity, opportunity cost, specialization, and added value. It defines needs and wants, and explains that unlimited human wants but limited resources lead to scarcity and the economic problem. Factors of production include land, labor, capital and enterprise, which are in limited supply. Specialization and division of labor allow for more efficient production by concentrating on specific tasks. Businesses combine factors of production to create goods and services, adding value through production and sale above the cost of materials.