This document provides an overview of computer concepts including:
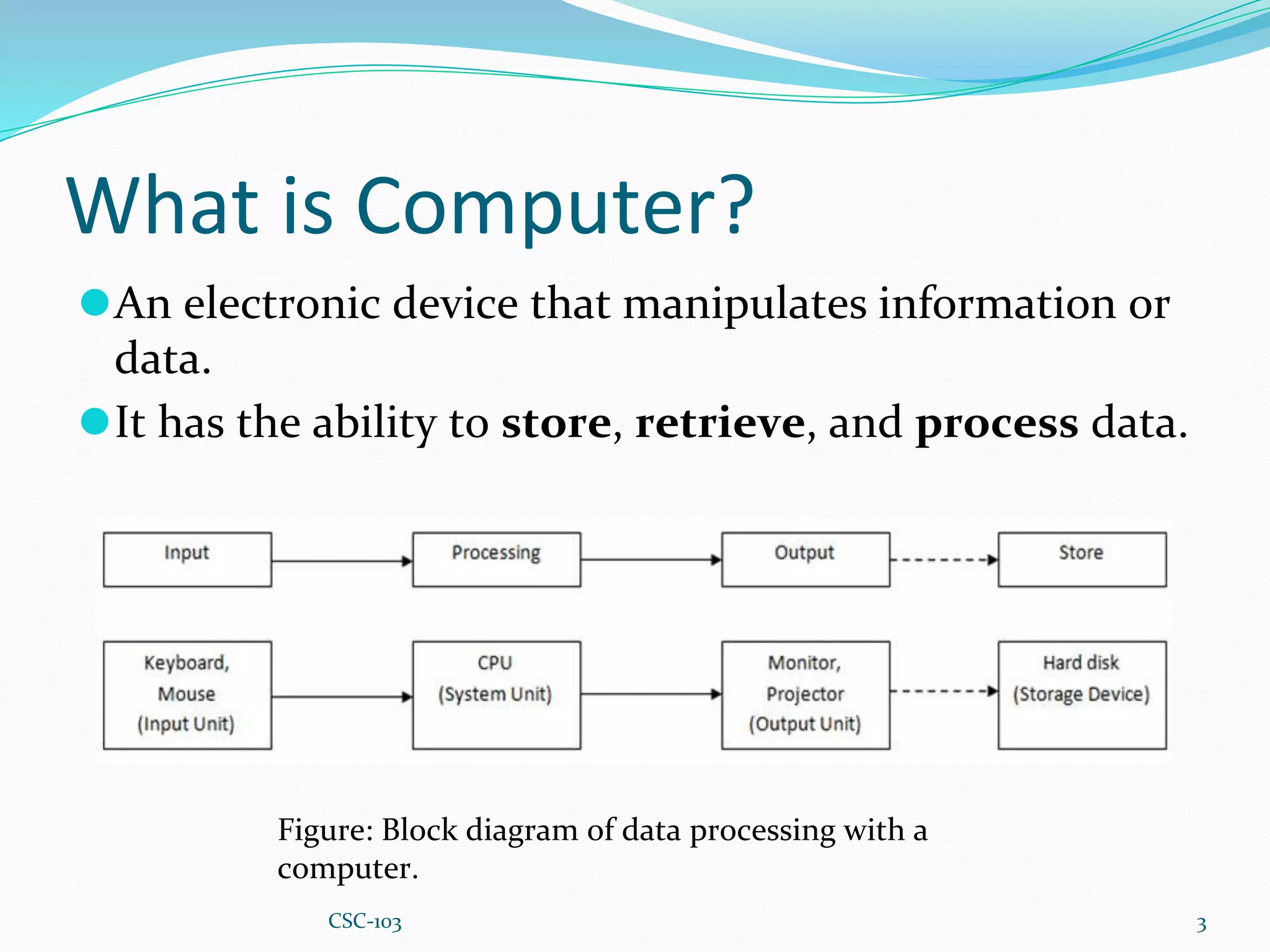
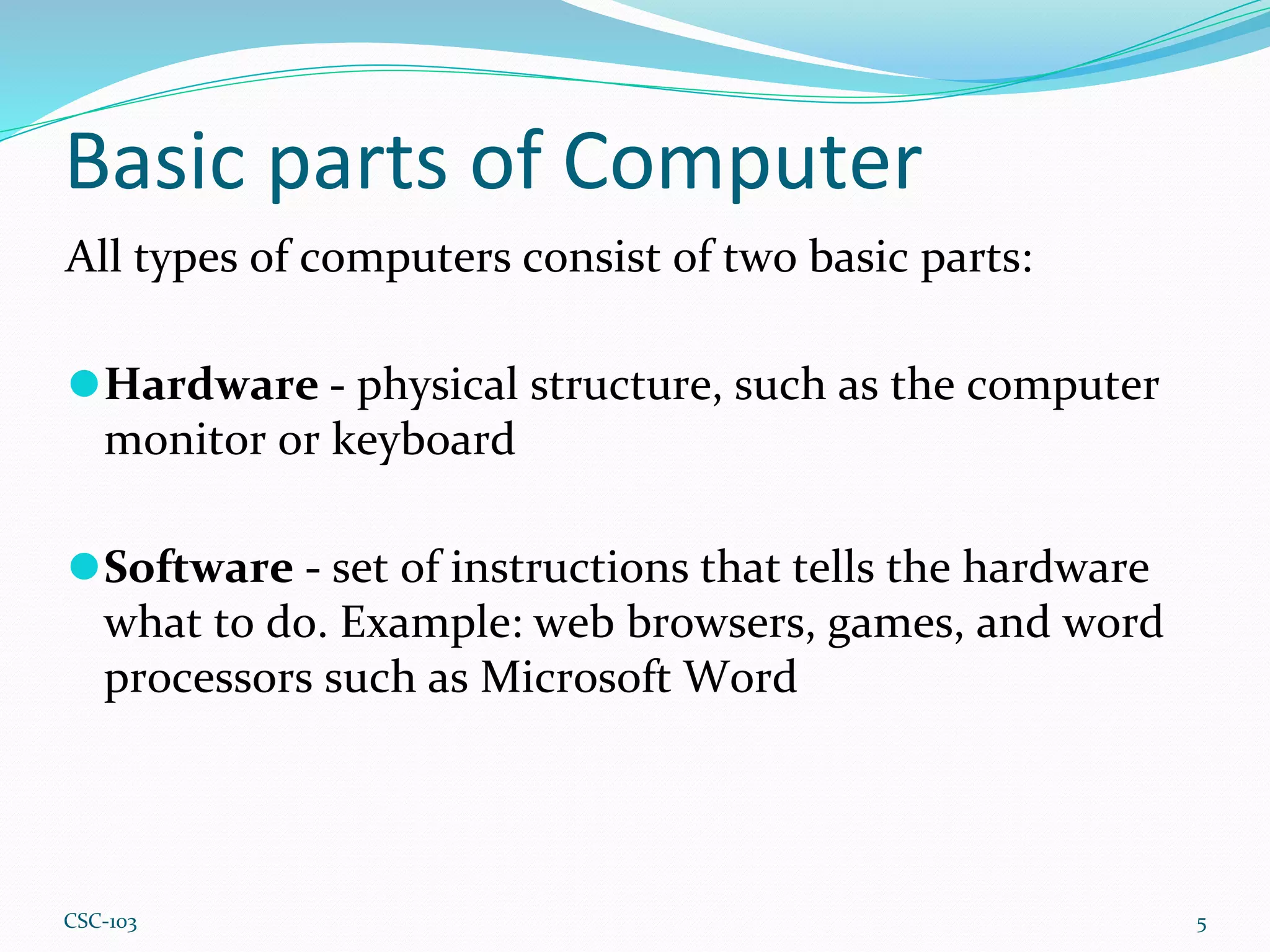
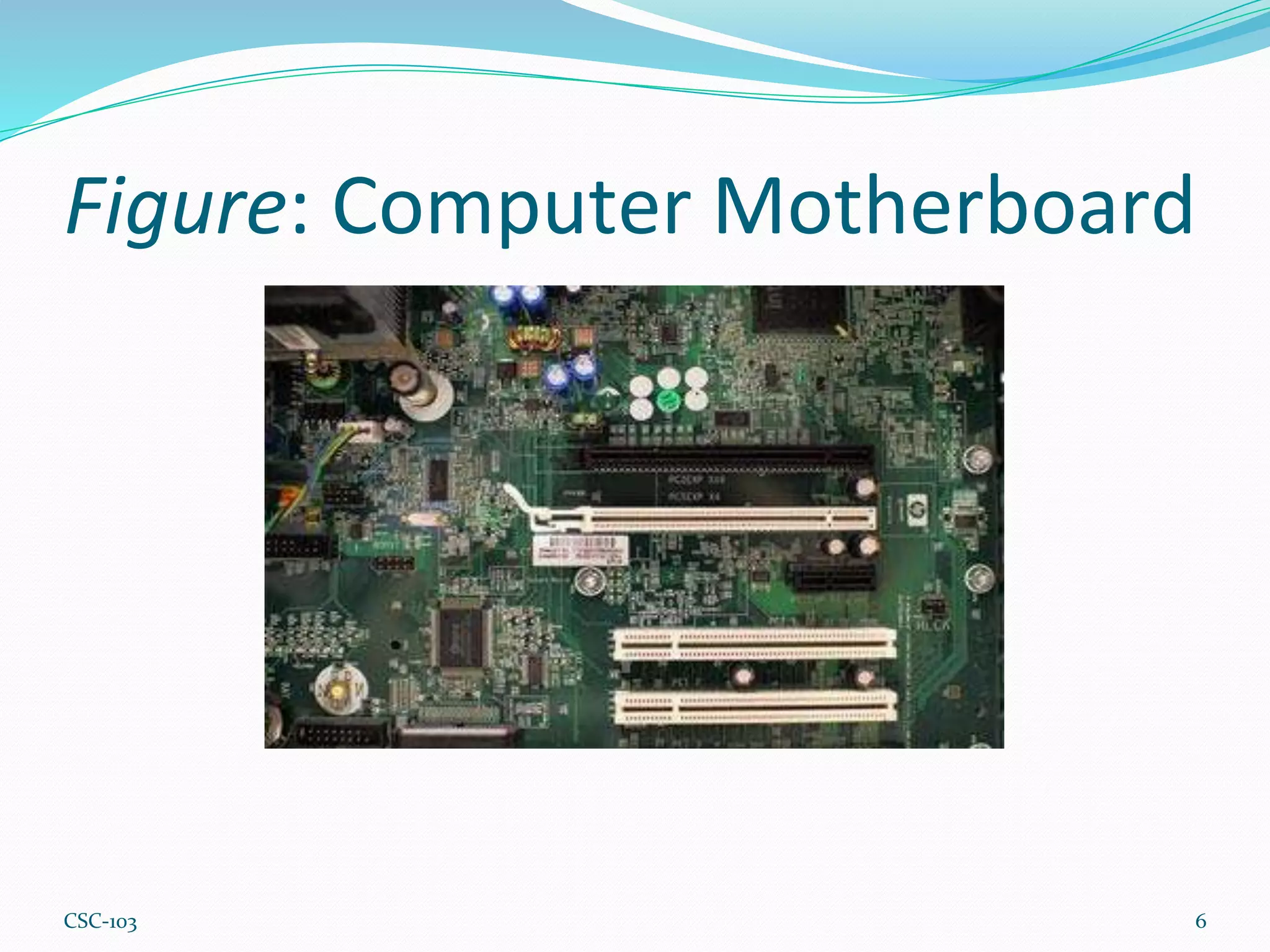
- Computers are electronic devices that can store, process, and manipulate data using hardware and software. Hardware is the physical components, software are the instructions that direct the hardware.
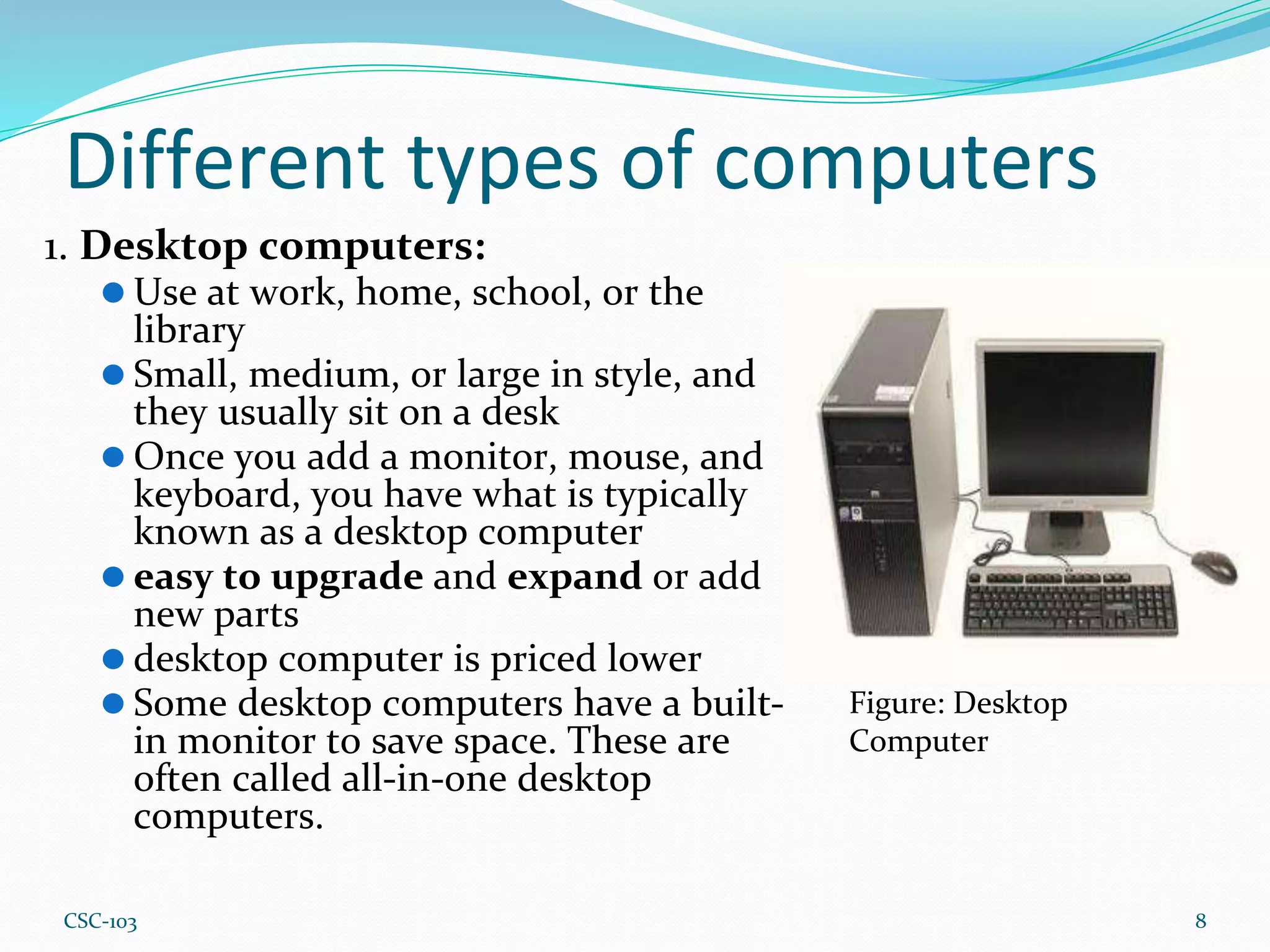
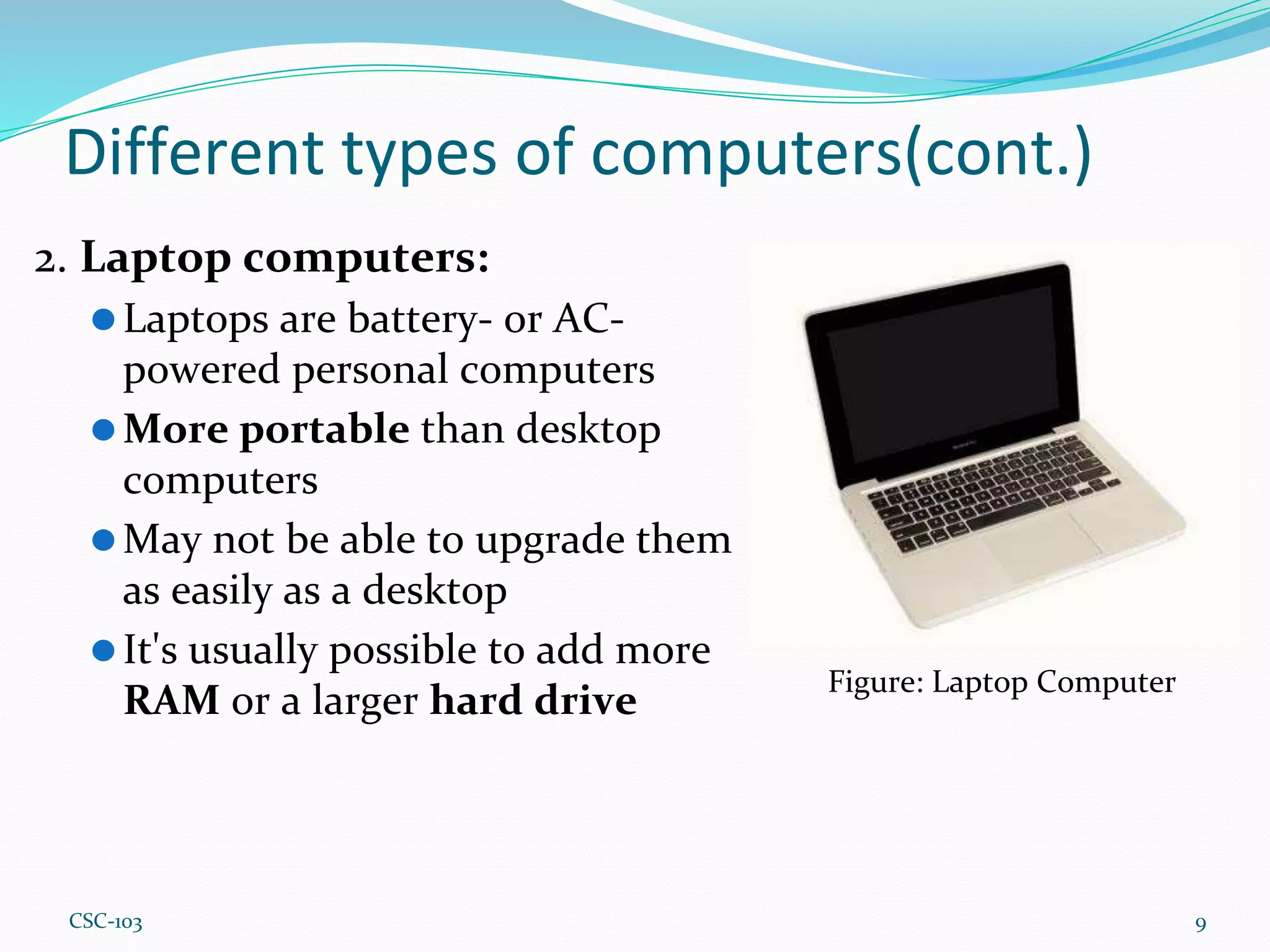
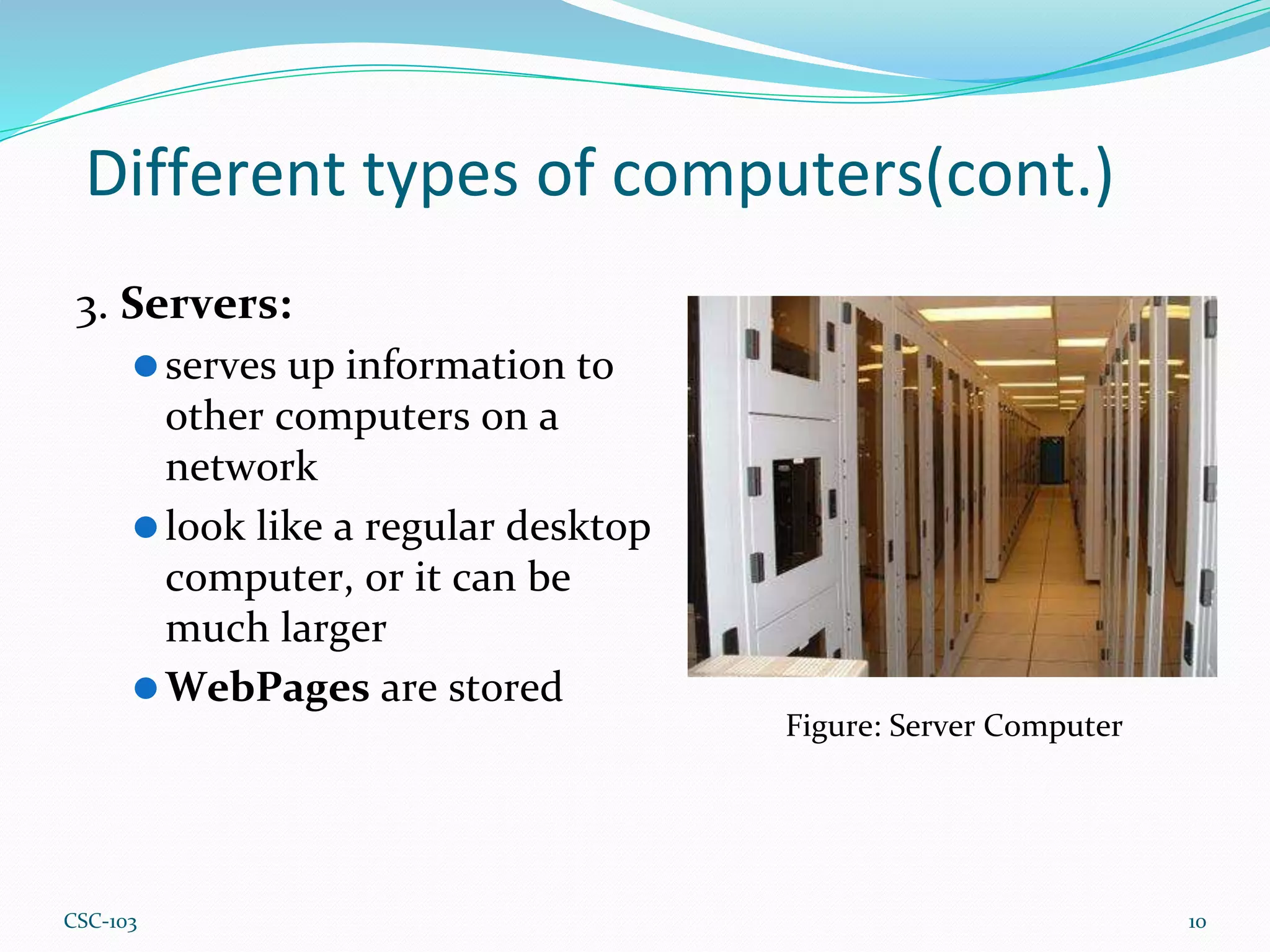
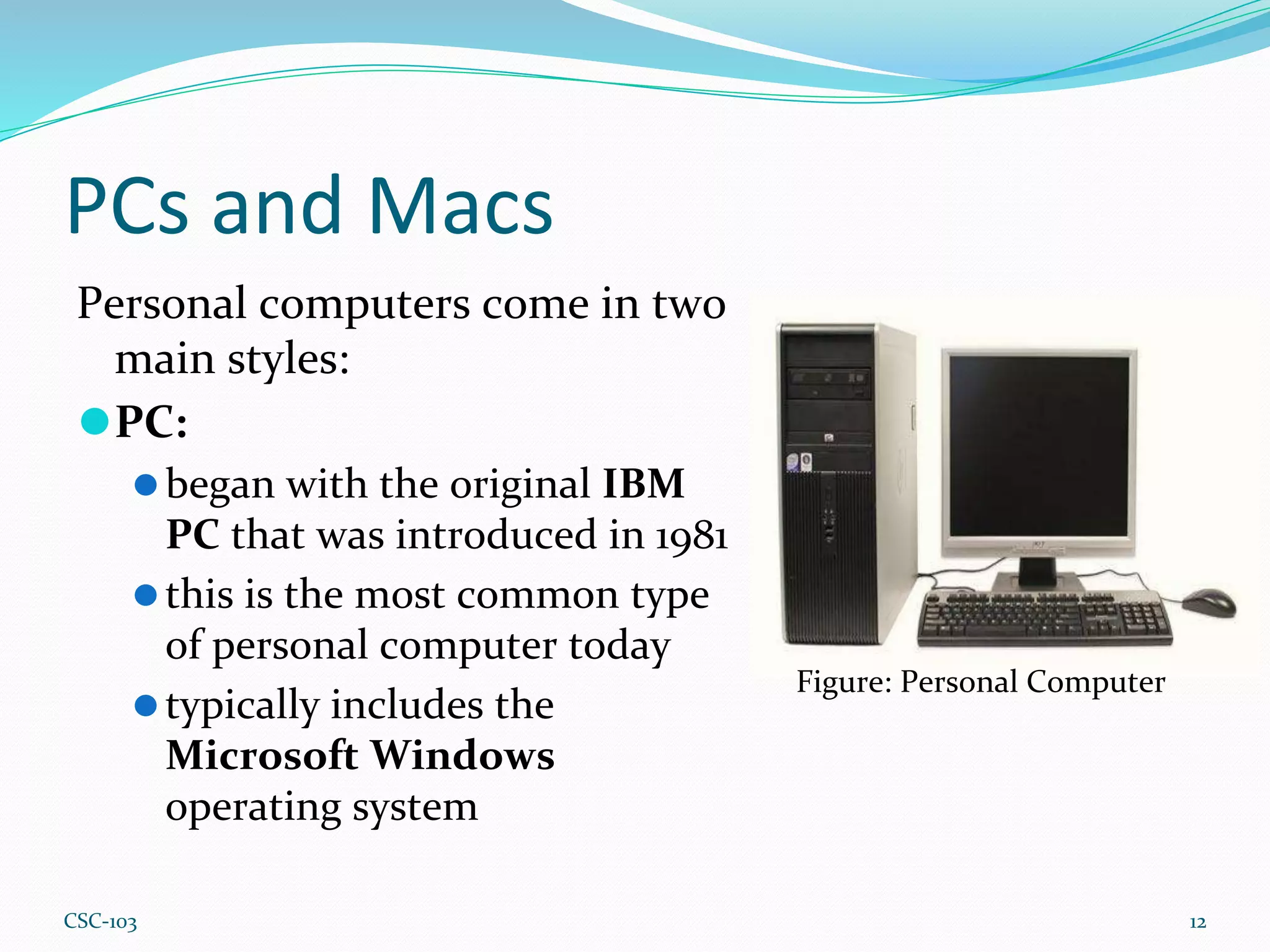
- There are different types of computers including desktops, laptops, servers, tablets, PCs, and Macs. Desktops are designed for regular use at home or work while laptops are portable. Servers manage network resources.
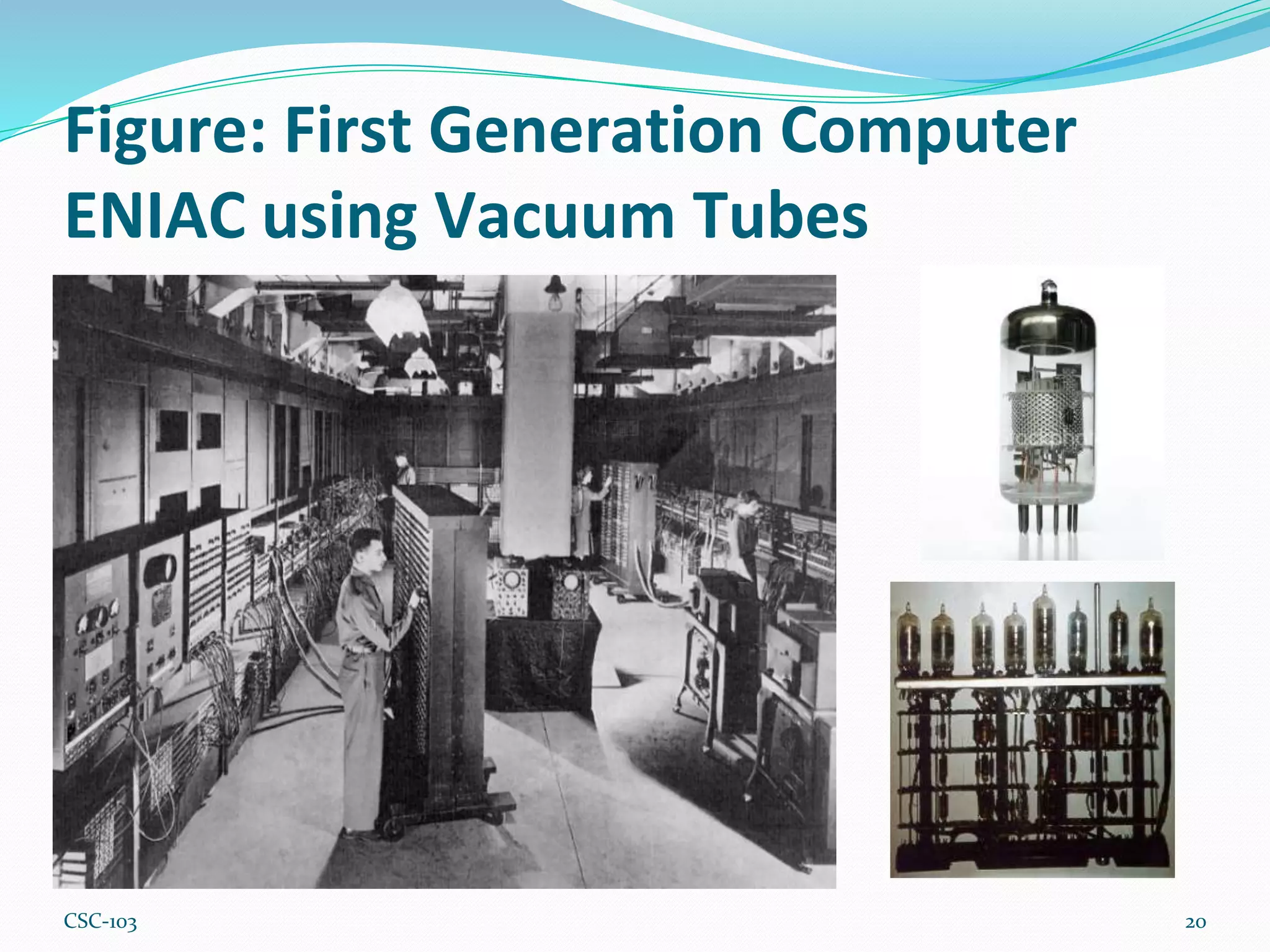
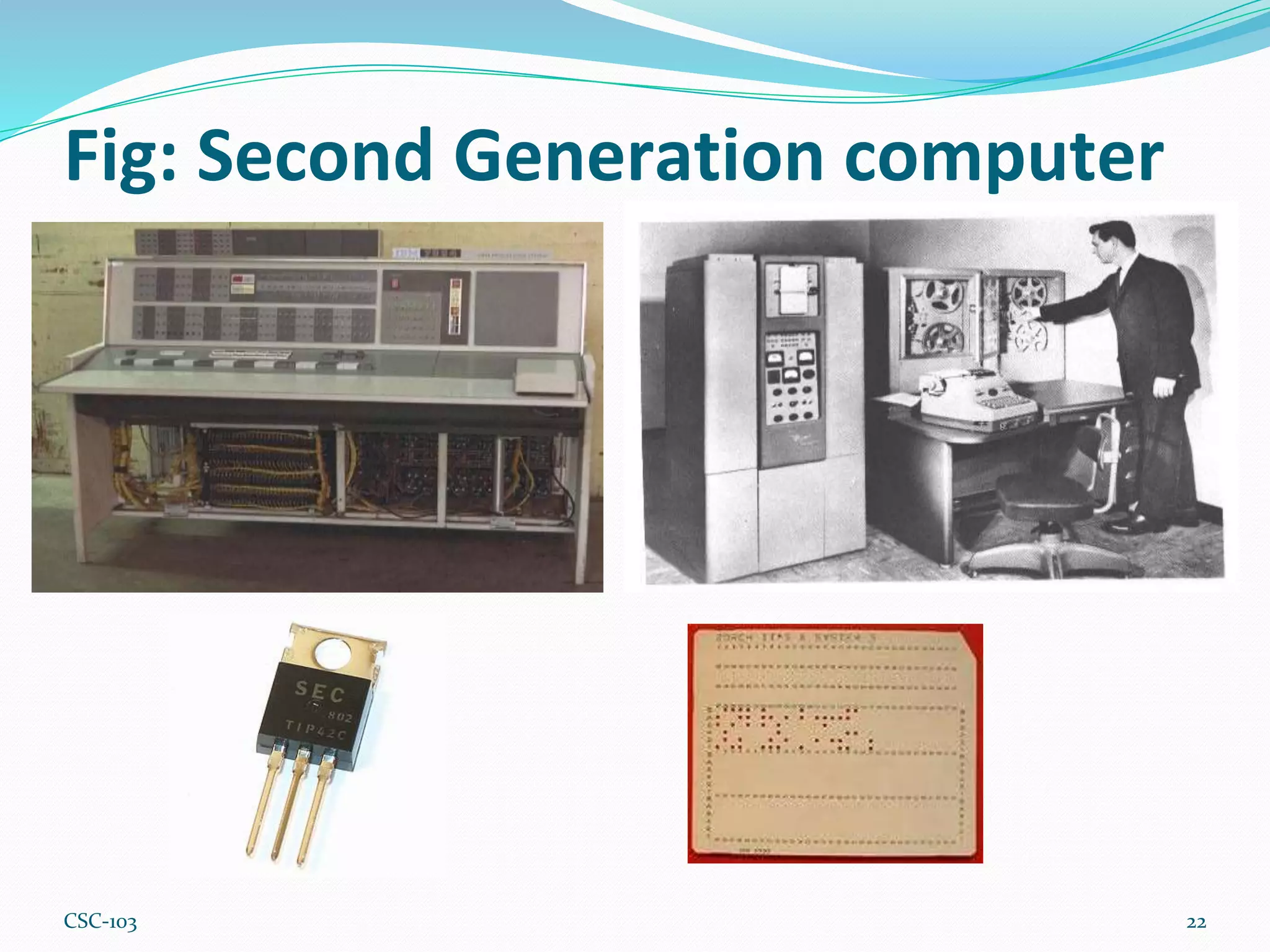
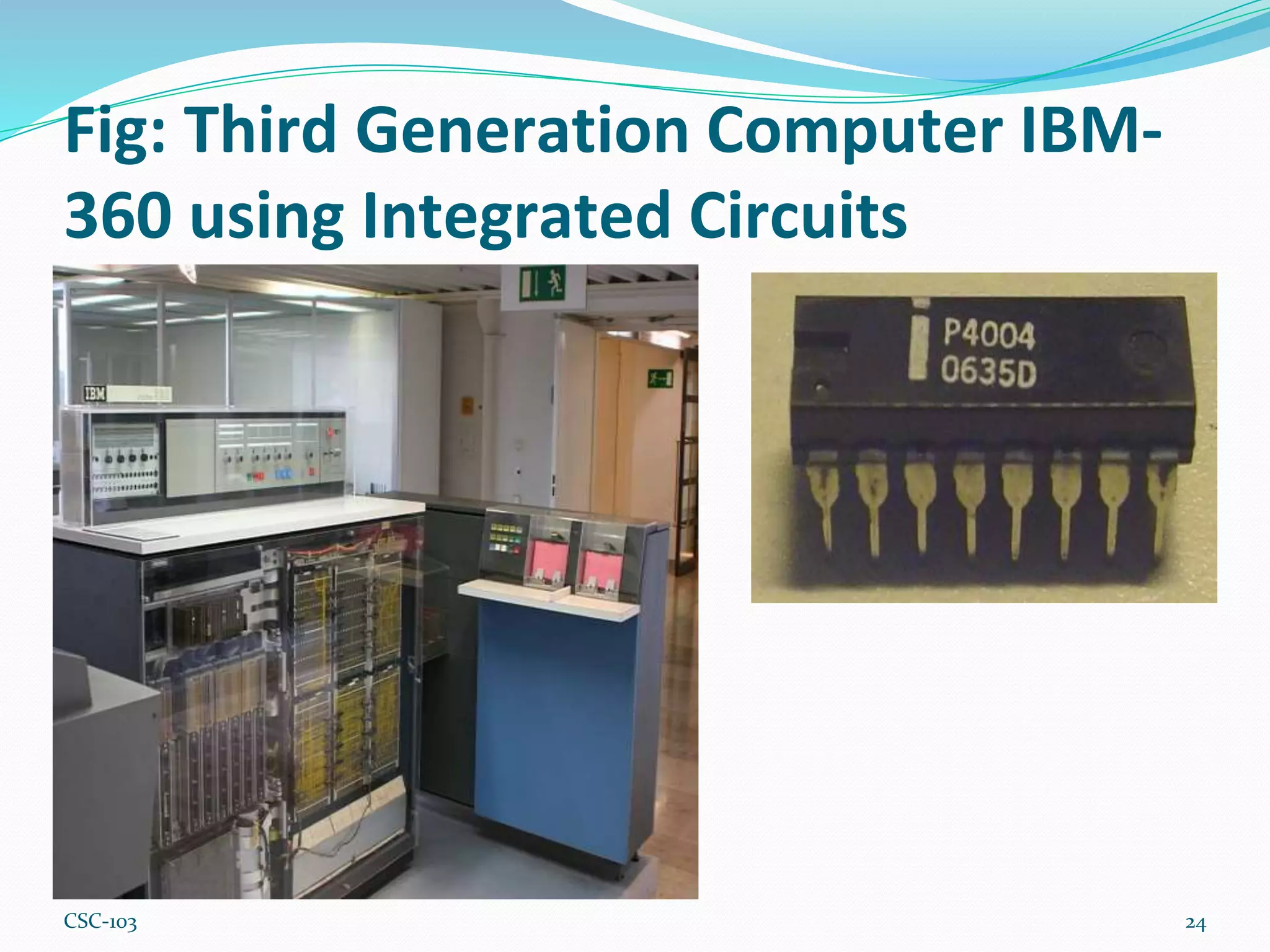
- Computer generations progressed from vacuum tubes to transistors to integrated circuits and now microprocessors. Earlier computers were larger, slower, and less powerful while modern computers are smaller, faster, and more powerful due to advances in processing technology.